
Kumquats, or cumquats in Australian English, are a group of small fruit-bearing trees in the flowering plant family Rutaceae. Their taxonomy is disputed. They were previously classified as forming the now-historical genus Fortunella or placed within Citrus, sensu lato. Different classifications have alternatively assigned them to anywhere from a single species, C. japonica, to numerous species representing each cultivar. Recent genomic analysis would define three pure species, Citrus hindsii, C. margarita and C. crassifolia, with C. x japonica being a hybrid of the last two.

Citrus is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus Citrus is native to South Asia, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Melanesia, and Australia. Various citrus species have been used and domesticated by indigenous cultures in these areas since ancient times. From there its cultivation spread into Micronesia and Polynesia by the Austronesian expansion ; and to the Middle East and the Mediterranean via the incense trade route, and onwards to Europe and the Americas.

Pectin is a heteropolysaccharide, a structural acid contained in the primary lamella, in the middle lamella, and in the cell walls of terrestrial plants. The principal, chemical component of pectin is galacturonic acid which was isolated and described by Henri Braconnot in 1825. Commercially produced pectin is a white-to-light-brown powder, produced from citrus fruits for use as an edible gelling agent, especially in jams and jellies, dessert fillings, medications, and sweets; and as a food stabiliser in fruit juices and milk drinks, and as a source of dietary fiber.

Citrus hystrix, called the kaffir lime or makrut lime, is a citrus fruit native to tropical Southeast Asia.

Citrus myrtifolia, the myrtle-leaved orange tree, is a species of Citrus with foliage similar to that of the common myrtle. It is a compact tree with small leaves and no thorns which grows to a height of three metres (10 ft) and can be found in Malta, Libya, the south of France, and Italy.

The tangerine is a type of citrus fruit that is orange in color. Its scientific name varies. It has been treated as a separate species under the name Citrus tangerina or Citrus × tangerina, or treated as a variety of either Citrus reticulata, the mandarin orange, or Citrus × aurantium, the bitter orange. Citrus tangerina is also treated as a synonym of Citrus deliciosa. It is a group of orange-colored citrus fruit consisting of hybrids of mandarin orange varieties, with some pomelo contribution.

Psyllidae, the jumping plant lice or psyllids, are a family of small plant-feeding insects that tend to be very host-specific, i.e. each plant-louse species only feeds on one plant species (monophagous) or feeds on a few closely related plants (oligophagous). Together with aphids, phylloxerans, scale insects and whiteflies, they form the group called Sternorrhyncha, which is considered to be the most "primitive" group within the true bugs (Hemiptera). They have traditionally been considered a single family, Psyllidae, but recent classifications divide the group into a total of seven families; the present restricted definition still includes more than 70 genera in the Psyllidae. Psyllid fossils have been found from the Early Permian before the flowering plants evolved. The explosive diversification of the flowering plants in the Cretaceous was paralleled by a massive diversification of associated insects, and many of the morphological and metabolic characters that the flowering plants exhibit may have evolved as defenses against herbivorous insects.

The trifoliate orange, Citrus trifoliata or Poncirus trifoliata, is a member of the family Rutaceae. Whether the trifoliate oranges should be considered to belong to their own genus, Poncirus, or be included in the genus Citrus is debated. The species is unusual among citrus for having deciduous, compound leaves and pubescent (downy) fruit.

Citrus bergamia, the bergamot orange, is a fragrant citrus fruit the size of an orange, with a yellow or green color similar to a lime, depending on ripeness.

Synephrine, or, more specifically, p-synephrine, is an alkaloid, occurring naturally in some plants and animals, and also in approved drugs products as its m-substituted analog known as neo-synephrine. p-Synephrine and m-synephrine are known for their longer acting adrenergic effects compared to epinephrine and norepinephrine. This substance is present at very low concentrations in common foodstuffs such as orange juice and other orange products, both of the "sweet" and "bitter" variety. The preparations used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), also known as Zhi Shi (枳实), are the immature and dried whole oranges from Citrus aurantium. Extracts of the same material or purified synephrine are also marketed in the US, sometimes in combination with caffeine, as a weight-loss-promoting dietary supplement for oral consumption. While the traditional preparations have been in use for millennia as a component of TCM-formulas, synephrine itself is not an approved over the counter drug. As a pharmaceutical, m-synephrine (phenylephrine) is still used as a sympathomimetic, mostly by injection for the treatment of emergencies such as shock, and rarely orally for the treatment of bronchial problems associated with asthma and hay-fever.

Citrus canker is a disease affecting Citrus species caused by the bacterium Xanthomonas. Infection causes lesions on the leaves, stems, and fruit of citrus trees, including lime, oranges, and grapefruit. While not harmful to humans, canker significantly affects the vitality of citrus trees, causing leaves and fruit to drop prematurely; a fruit infected with canker is safe to eat, but too unsightly to be sold. Citrus canker is mainly a leaf-spotting and rind-blemishing disease, but when conditions are highly favorable, it can cause defoliation, shoot dieback, and fruit drop.

The Kinnow is a high yield mandarin hybrid cultivated extensively in the wider Punjab region of India and Pakistan.

Chlorophyllase is an essential enzyme in chlorophyll metabolism. It is a membrane proteins commonly known as chlase (EC 3.1.1.14, CLH) with systematic name chlorophyll chlorophyllidohydrolase. It catalyzes the reaction

Rhoifolin is a chemical compound. It is first isolated from plant Rhus succedanea. The term "Rhoi" derived from generic name of plant Rhus. It is a flavone, a type of flavonoid isolated from Boehmeria nivea, China grass or ramie (leaf), from Citrus limon, Canton lemon (leaf), from Citrus x aurantium, the bigarade or bitter orange (plant), from Citrus x paradisi, the grapefruit (leaf), from Ononis campestris, the cammock (shoot) and from Sabal serratula, the serenoa or sabal fruit (plant).
Citrus halimii, or mountain citron, is a citrus with sour fruit. Historically placed within the polyphyletic grouping of papedas, it has since been determined to be a wild species most closely related to the kumquats, and is not related to the true citron. It was first discovered and catalogued in 1973.

Clara Henriette Hasse was an American botanist whose research focused on plant pathology. She is known for identifying the cause of citrus canker, which was threatening crops in the Deep South.
The micrantha is a wild citrus from the papeda group, native to southern Philippines, particularly islands of Cebu and Bohol. Two varieties are recognized: small-flowered papeda, locally known as biasong, and small-fruited papeda or samuyao.

Planococcus citri, commonly known as the citrus mealybug, is a species of mealybugs native to Asia. It has been introduced to the rest of the world, including Europe, the Americas, and Oceania, as an agricultural pest. It is associated with citrus, but it attacks a wide range of crop plants, ornamental plants, and wild flora.
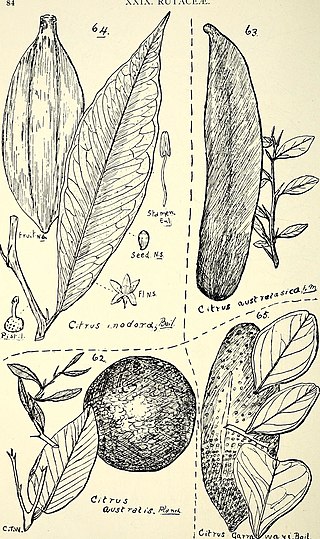
Citrus garrawayi, the Mount White lime, is a tree native to the Cape York region of northern Queensland in Australia. It is an understory tree in tropical rainforests.

















