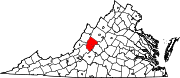
Rockbridge County is a county in the Shenandoah Valley on the western edge of the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 22,650. Its county seat is the city of Lexington. Rockbridge County completely surrounds the independent cities of Buena Vista and Lexington. The Bureau of Economic Analysis combines the independent cities of Buena Vista and Lexington with Rockbridge County for statistical purposes.

The George Washington and Jefferson National Forests is an administrative entity combining two U.S. National Forests into one of the largest areas of public land in the Eastern United States. The forests cover 1.8 million acres (2,800 sq mi) of land in the Appalachian Mountains of Virginia, West Virginia, and Kentucky. Approximately 1 million acres (1,600 sq mi) of the forest are remote and undeveloped and 139,461 acres (218 sq mi) have been designated as wilderness areas, which prohibits future development.

The Cacapon River, located in the Appalachian Mountains of West Virginia's Eastern Panhandle region, is an 81.0-mile-long (130.4 km) shallow river known for its fishing, boating, wildlife, hunting, and wilderness scenery. As part of the Potomac River watershed, it is an American Heritage River.

The Trough is a 6-mile long wooded gorge carved by the South Branch Potomac River (SBPR) and situated in the Allegheny Mountains of Hampshire and Hardy Counties, West Virginia, USA. The area was the site of a 1756 skirmish of the French and Indian War, known as the "Battle of the Trough".

State Route 39 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. The state highway runs 59.17 miles (95.22 km) from the West Virginia state line near Mountain Grove, where the highway continues as West Virginia Route 39, east to U.S. Route 11 in East Lexington. SR 39 connects Lexington with several communities formed around hot springs in Bath County. In Rockbridge County, the state highway passes through the town of Goshen and Goshen Pass, a gorge formed by the Maury River.

U.S. Route 60 (US 60) in the Commonwealth of Virginia runs 303 miles (488 km) west to east through the central part of the state, generally close to and paralleling the Interstate 64 corridor, except for the crossing of the Blue Ridge Mountains, and in the South Hampton Roads area.

Virginia State Route 130 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. The state highway runs 34.69 miles (55.83 km) from U.S. Route 11 at Natural Bridge east to SR 669 and SR 670 east of US 29 near Madison Heights. SR 130 runs concurrently with US 501 from Glasgow through the James River gorge through the Blue Ridge Mountains, connecting eastern Rockbridge County with western and southern Amherst County near Lynchburg.
Rocky Mountain is a peak of the Blue Ridge Mountains in Virginia. It is located about 2 miles (3.5 km) east of Irish Gap, on the border of Rockbridge County and Amherst County; it is the highest point of both counties. Rocky Mountain is flanked to the northeast by Elk Pond Mountain, to the southwest by Grapevine Ridge, and to the south by Tar Jacket Ridge.
Elk Pond Mountain is a peak of the Blue Ridge Mountains, on the border of Nelson and Rockbridge counties in Virginia. Elk Pond Mountain is flanked to the east by Maintop Mountain, and to the southwest by Rocky Mountain.

Doughton Park is the largest recreation area the National Park Service manages on the Blue Ridge Parkway. It is located between mile markers 238.5 - 244.7 on the border between Wilkes and Alleghany Counties in North Carolina. Doughton Park consists of highland meadows with numerous scenic overlooks, miles of hiking and bridle trails, areas for camping and cookouts, and it is one of the few areas on the Parkway that has a restaurant along with an adjacent visitors center maintained by the National Park Service. Elevations in Doughton Park generally range from 3,500 to 4,000 feet. The park is named after North Carolina politician Robert L. Doughton, who lived in nearby Laurel Springs, North Carolina and who as a US Congressman played a key role in the creation of the Blue Ridge Parkway in the 1930s.

Barbours Creek Wilderness is a U.S. wilderness area in the Eastern Divide Ranger District of George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia, United States. The wilderness area was established in 1988 and consists of 5,382 acres (2,178 ha) of forests in the Appalachian Mountains ranging in elevation from 1,700 to 3,800 feet.

The James River Face Wilderness is an 8,907-acre area located near Natural Bridge, Virginia that is protected by the Eastern Wilderness Act of Congress to maintain its present, natural condition. As part of the National Wilderness Preservation System, it helps to preserve a variety of natural life forms and contributes to a diversity of plant and animal gene pools. Over half of the ecosystems in the United States exist within designated wilderness.

The Thunder Ridge Wilderness is a 2,344 acres (949 ha) area located near Natural Bridge, Virginia, which is protected by the Eastern Wilderness Act of Congress to maintain its present, natural condition. As part of the National Wilderness Preservation System, it helps to preserve a variety of natural life forms and contributes to a diversity of plant and animal gene pools. Over half of the ecosystems in the United States exist within designated wilderness.

White Oak Ridge-Terrapin Mountain is a wildland in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia that has been recognized by the Wilderness Society as a special place worthy of protection from logging and road construction. With over 1200 acres of possible old growth forest, this is a rugged area with a rich diversity of geology and plant life.

North Creek (conservation area) is a wildland in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia that has been recognized by the Wilderness Society as a special place worthy of protection from logging and road construction. Tall evergreen and hardwood trees in the area around Apple Orchard Falls tower above ferns and wildflowers. The area includes a valley which extends from Sunset Fields in the east to its western border near the North Creek Camping Area.
James River Face Wilderness Addition is a wildland in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia that has been recognized by the Wilderness Society as a special place worthy of protection from logging and road construction. Adjacent to the James River Face Wilderness, it extends the wildland opportunities of the wilderness on the east to the Jefferson National Forest boundary. The area, managed for bear, has hardwood forests with ages between 60 and almost 100 years.
Wilson Mountain is a wildland in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia that has been recognized by the Wilderness Society as a special place worthy of protection from logging and road construction.
Cove Mountain is a wildland in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia that has been recognized by the Wilderness Society as a special place worthy of protection from logging and road construction.
The Glenwood Cluster is a region in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests recognized by The Wilderness Society for its rich biodiversity, scenery, wildflower displays, cold-water trout streams and horse trails. It offers a unique habitat for rare plants, salamanders and other rare species. The Blue Ridge Parkway and the Appalachian Trail traverse the area, giving ready access with views to the east of the Piedmont region and to the west of the Valley of Virginia.

The Angels Rest Cluster is a region in the Jefferson National Forest recognized by The Wilderness Society for its diversity of habitats with steep mountains, an isolated valley, a waterfall and wetlands. It is named after a high point on Pearis Mountain with views of the New River and surrounding area. It contains two large wild areas connected by the Appalachian Trail.