
Nested polymerase chain reaction (nested PCR) is a modification of polymerase chain reaction intended to reduce non-specific binding in products due to the amplification of unexpected primer binding sites. [1]

Nested polymerase chain reaction (nested PCR) is a modification of polymerase chain reaction intended to reduce non-specific binding in products due to the amplification of unexpected primer binding sites. [1]
Polymerase chain reaction itself is the process used to amplify DNA samples, via a temperature-mediated DNA polymerase. The products can be used for sequencing or analysis, and this process is a key part of many genetics research laboratories, along with uses in DNA fingerprinting for forensics and other human genetic cases. Conventional PCR requires primers complementary to the termini of the target DNA. The amount of product from the PCR increases with the number of temperature cycles that the reaction is subjected to. A commonly occurring problem is primers binding to incorrect regions of the DNA, giving unexpected products. This problem becomes more likely with an increased number of cycles of PCR.
Nested polymerase chain reaction involves two sets of primers, used in two successive runs of polymerase chain reaction, the second set intended to amplify a secondary target within the first run product. This allows amplification for a low number of runs in the first round, limiting non-specific products. The second nested primer set should only amplify the intended product from the first round of amplification and not non-specific product. This allows running more total cycles while minimizing non-specific products. This is useful for rare templates or PCR with high background.
The target DNA undergoes the first run of polymerase chain reaction with the first set of primers, shown in green. The selection of alternative and similar primer binding sites gives a selection of products, only one containing the intended sequence.
The product from the first reaction undergoes a second run with the second set of primers, shown in red. It is very unlikely that any of the unwanted PCR products contain binding sites for both the new primers, ensuring the product from the second PCR has little contamination from unwanted products.

The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA sufficiently to enable detailed study. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation. Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993.

A primer is a short single-stranded nucleic acid used by all living organisms in the initiation of DNA synthesis. A synthetic primer may also be referred to as an oligo, short for oligonucleotide. DNA polymerase enzymes are only capable of adding nucleotides to the 3’-end of an existing nucleic acid, requiring a primer be bound to the template before DNA polymerase can begin a complementary strand. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides after binding to the RNA primer and synthesizes the whole strand. Later, the RNA strands must be removed accurately and replace them with DNA nucleotides forming a gap region known as a nick that is filled in using an enzyme called ligase. The removal process of the RNA primer requires several enzymes, such as Fen1, Lig1, and others that work in coordination with DNA polymerase, to ensure the removal of the RNA nucleotides and the addition of DNA nucleotides. Living organisms use solely RNA primers, while laboratory techniques in biochemistry and molecular biology that require in vitro DNA synthesis usually use DNA primers, since they are more temperature stable. Primers can be designed in laboratory for specific reactions such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR). When designing PCR primers, there are specific measures that must be taken into consideration, like the melting temperature of the primers and the annealing temperature of the reaction itself. Moreover, the DNA binding sequence of the primer in vitro has to be specifically chosen, which is done using a method called basic local alignment search tool (BLAST) that scans the DNA and finds specific and unique regions for the primer to bind.
Protein engineering is the process of developing useful or valuable proteins through the design and production of unnatural polypeptides, often by altering amino acid sequences found in nature. It is a young discipline, with much research taking place into the understanding of protein folding and recognition for protein design principles. It has been used to improve the function of many enzymes for industrial catalysis. It is also a product and services market, with an estimated value of $168 billion by 2017.

Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It is primarily used to measure the amount of a specific RNA. This is achieved by monitoring the amplification reaction using fluorescence, a technique called real-time PCR or quantitative PCR (qPCR). Combined RT-PCR and qPCR are routinely used for analysis of gene expression and quantification of viral RNA in research and clinical settings.
Helicase-dependent amplification (HDA) is a method for in vitro DNA amplification that takes place at a constant temperature.
The touchdown polymerase chain reaction or touchdown style polymerase chain reaction is a method of polymerase chain reaction by which primers avoid amplifying nonspecific sequences. The annealing temperature during a polymerase chain reaction determines the specificity of primer annealing. The melting point of the primer sets the upper limit on annealing temperature. At temperatures just above this point, only very specific base pairing between the primer and the template will occur. At lower temperatures, the primers bind less specifically. Nonspecific primer binding obscures polymerase chain reaction results, as the nonspecific sequences to which primers anneal in early steps of amplification will "swamp out" any specific sequences because of the exponential nature of polymerase amplification.
Taq polymerase is a thermostable DNA polymerase I named after the thermophilic eubacterial microorganism Thermus aquaticus, from which it was originally isolated by Chien et al. in 1976. Its name is often abbreviated to Taq or Taq pol. It is frequently used in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a method for greatly amplifying the quantity of short segments of DNA.
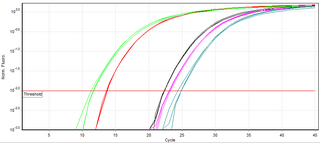
A real-time polymerase chain reaction is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR, not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively and semi-quantitatively.
TaqMan probes are hydrolysis probes that are designed to increase the specificity of quantitative PCR. The method was first reported in 1991 by researcher Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation, and the technology was subsequently developed by Hoffmann-La Roche for diagnostic assays and by Applied Biosystems for research applications.
SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles. SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase of interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a commonly used molecular biology tool for amplifying DNA, and various techniques for PCR optimization which have been developed by molecular biologists to improve PCR performance and minimize failure.

Oligomer Restriction is a procedure to detect an altered DNA sequence in a genome. A labeled oligonucleotide probe is hybridized to a target DNA, and then treated with a restriction enzyme. If the probe exactly matches the target, the restriction enzyme will cleave the probe, changing its size. If, however, the target DNA does not exactly match the probe, the restriction enzyme will have no effect on the length of the probe. The OR technique, now rarely performed, was closely associated with the development of the popular polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method.

The history of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has variously been described as a classic "Eureka!" moment, or as an example of cooperative teamwork between disparate researchers. Following is a list of events before, during, and after its development:
The versatility of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has led to modifications of the basic protocol being used in a large number of variant techniques designed for various purposes. This article summarizes many of the most common variations currently or formerly used in molecular biology laboratories; familiarity with the fundamental premise by which PCR works and corresponding terms and concepts is necessary for understanding these variant techniques.
The ligase chain reaction (LCR) is a method of DNA amplification. The ligase chain reaction (LCR) is an amplification process that differs from PCR in that it involves a thermostable ligase to join two probes or other molecules together which can then be amplified by standard polymerase chain reaction (PCR) cycling. Each cycle results in a doubling of the target nucleic acid molecule. A key advantage of LCR is greater specificity as compared to PCR. Thus, LCR requires two completely different enzymes to operate properly: ligase, to join probe molecules together, and a thermostable polymerase to amplify those molecules involved in successful ligation. The probes involved in the ligation are designed such that the 5′ end of one probe is directly adjacent to the 3′ end of the other probe, thereby providing the requisite 3′-OH and 5′-PO4 group substrates for the ligase.
A primer dimer (PD) is a potential by-product in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a common biotechnological method. As its name implies, a PD consists of two primer molecules that have attached (hybridized) to each other because of strings of complementary bases in the primers. As a result, the DNA polymerase amplifies the PD, leading to competition for PCR reagents, thus potentially inhibiting amplification of the DNA sequence targeted for PCR amplification. In quantitative PCR, PDs may interfere with accurate quantification.
Multiplex polymerase chain reaction refers to the use of polymerase chain reaction to amplify several different DNA sequences simultaneously. This process amplifies DNA in samples using multiple primers and a temperature-mediated DNA polymerase in a thermal cycler. The primer design for all primers pairs has to be optimized so that all primer pairs can work at the same annealing temperature during PCR.
Hot start PCR is a modified form of conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) that reduces the presence of undesired products and primer dimers due to non-specific DNA amplification at room temperatures. Many variations and modifications of the PCR procedure have been developed in order to achieve higher yields; hot start PCR is one of them. Hot start PCR follows the same principles as the conventional PCR - in that it uses DNA polymerase to synthesise DNA from a single stranded template. However, it utilizes additional heating and separation methods, such as inactivating or inhibiting the binding of Taq polymerase and late addition of Taq polymerase, to increase product yield as well as provide a higher specificity and sensitivity. Non-specific binding and priming or formation of primer dimers are minimized by completing the reaction mix after denaturation. Some ways to complete reaction mixes at high temperatures involve modifications that block DNA polymerase activity in low temperatures, use of modified deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), and the physical addition of one of the essential reagents after denaturation.
Recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) is a single tube, isothermal alternative to the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). By adding a reverse transcriptase enzyme to an RPA reaction it can detect RNA as well as DNA, without the need for a separate step to produce cDNA,. Because it is isothermal, RPA can use much simpler equipment than PCR, which requires a thermal cycler. Operating best at temperatures of 37–42 °C and still working, albeit more slowly, at room temperature means RPA reactions can in theory be run quickly simply by holding a tube. This makes RPA an excellent candidate for developing low-cost, rapid, point-of-care molecular tests. An international quality assessment of molecular detection of Rift Valley fever virus performed as well as the best RT-PCR tests, detecting less concentrated samples missed by some PCR tests and an RT-LAMP test. RPA was developed and launched by TwistDx Ltd., a biotechnology company based in Cambridge, UK.

RNase H-dependent PCR (rhPCR) is a modification of the standard PCR technique. In rhPCR, the primers are designed with a removable amplification block on the 3’ end. Amplification of the blocked primer is dependent on the cleavage activity of a hyperthermophilic archaeal Type II RNase H enzyme during hybridization to the complementary target sequence. This RNase H enzyme possesses several useful characteristics that enhance the PCR. First, it has very little enzymatic activity at low temperature, enabling a “hot start PCR” without modifications to the DNA polymerase. Second, the cleavage efficiency of the enzyme is reduced in the presence of mismatches near the RNA residue. This allows for reduced primer dimer formation, detection of alternative splicing variants, ability to perform multiplex PCR with higher numbers of PCR primers, and the ability to detect single-nucleotide polymorphisms.