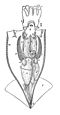
The rest of the body of the snail is shown in green. The food is shown in blue. Muscles that control the radula are shown in brown. The surface of the radula ribbon, with numerous teeth, is shown as a zig-zag line
The odontophore is part of the feeding mechanism in molluscs. It is the cartilage which underlies and supports the radula, a ribbon of teeth. [1] The radula is found in every class of molluscs except for the bivalves. [2]
The feeding apparatus can be extended from the mouth of the animal, and the radular ribbon can slide over the odontophore. By moving the radula and odontophore over a surface, the teeth cut and scoop up food particles and convey them into the mouth, whence they enter the oesophagus.
The diagrams here show the feeding apparatus of a generalized gastropod. The details shown do not necessarily apply to predatory species such as the cone snails, which have a highly specialized feeding mechanism.