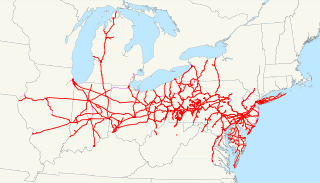
The Pennsylvania Railroad was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and was headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was so named because it was established in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania.

The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Detroit, and Syracuse. New York Central was headquartered in New York City's New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal.

The Delaware, Lackawanna & Western Railroad was a U.S. Class 1 railroad that connected Buffalo, New York, and Hoboken, New Jersey, a distance of about 400 miles (640 km). Incorporated in 1853, the DL&W was profitable during the first two decades of the twentieth century, but its margins were gradually hurt by declining traffic in coal and competition from trucks. In 1960, the DL&W merged with rival Erie Railroad to form the Erie Lackawanna Railroad.
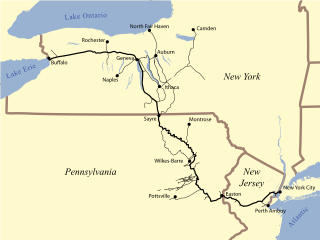
The Lehigh Valley Railroad was one of a number of railroads built in the northeastern United States primarily to haul anthracite coal. The railroad was authorized on April 21, 1846, for freight and transportation of passengers, goods, wares, merchandise and minerals in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the railroad was incorporated/established on September 20, 1847, as the Delaware, Lehigh, Schuylkill and Susquehanna Railroad Company. On January 7, 1853, the railroad's name was changed to Lehigh Valley Railroad. It was sometimes known as the Route of the Black Diamond, named after the anthracite it transported. At the time, anthracite was transported by boat down the Lehigh River; the railroad was meant to be faster transportation. The railroad ended operations in 1976 and merged into Conrail along with several northeastern railroads that same year.

NJ Transit Rail Operations is the rail division of NJ Transit. It operates commuter rail service in New Jersey, with most service centered on transportation to and from New York City, Hoboken, and Newark. NJ Transit also operates rail service in Orange and Rockland counties in New York under contract to Metro-North Railroad. The commuter rail lines had an average weekday ridership of 306,892 from June 1, 2015 to June 30, 2016. This does not include NJ Transit's light rail operations.
Huntingdon & Broad Top Mountain Railroad (H&BTM) is a former short line railroad company operating passenger and freight service on standard gauge track in south central Pennsylvania.

The Grand Trunk Western Railroad Company is an American subsidiary of the Canadian National Railway operating in Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. Since a corporate restructuring in 1971, the railroad has been under CN's subsidiary holding company, the Grand Trunk Corporation. Grand Trunk Western's routes are part of CN's Michigan Division. Its primary mainline between Chicago and Port Huron, Michigan serves as a connection between railroad interchanges in Chicago and rail lines in eastern Canada and the Northeastern United States. The railroad's extensive trackage in Detroit and across southern Michigan has made it an essential link for the automotive industry as a hauler of parts and automobiles from manufacturing plants.

Conrail, formally the Consolidated Rail Corporation, was the primary Class I railroad in the Northeastern United States between 1976 and 1999. The trade name Conrail is a portmanteau based on the company's legal name, and while it no longer operates trains, it continues to do business as an asset management and network services provider in three Shared Assets Areas that were excluded from the division of its operations during its acquisition by CSX Corporation and the Norfolk Southern Railway.
The Belvidere Delaware Railroad was a railroad running along the eastern shore of the Delaware River from Trenton, New Jersey north via Phillipsburg, New Jersey to the small village of Manunka Chunk, New Jersey. It became an important feeder line for the Lehigh Valley Railroad's join to the Central Railroad of New Jersey, which was constructed into Phillipsburg, NJ at about the same time. This connected Philadelphia and Trenton, NJ at one end of the shortline railroad to the rapidly growing lower Wyoming Valley region, and via the Morris Canal or the CNJ, a slow or fast connection to New York City ferries crossing New York Harbor from Jersey City, NJ. In 1871 the CNJ leased various railroads in Pennsylvania, most from the Lehigh Coal & Navigation Company allowing the CNJ to penetrate to the upper Wyoming Valley, over some stretches, competing directly with the Lehigh Valley Railroad and with the Lehigh Canal and the trunk road connection of the Belvidere Delaware Railroad to New York became less profitable since Philadelphia connected more easily to Northeastern Pennsylvania thereafter without needing a double-crossing of the Delaware River; a general revenue decline ensued, leading to the Pennsylvania Railroad acquiring the rights, where it served as part of the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) system, carrying mainly anthracite coal and iron ore from northeastern Pennsylvania to population centers along the coast.
The North Pennsylvania Railroad was a railroad company which served Philadelphia, Montgomery County, Bucks County and Northampton County, Pennsylvania. It was formed in 1852 and began operation in 1855. The Philadelphia and Reading Railway, predecessor to the Reading Company, leased the North Pennsylvania in 1879. Its tracks were transferred to Conrail and the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) in 1976.

The Reading Blue Mountain and Northern Railroad, sometimes shortened to Reading and Northern Railroad, is a regional railroad operating in eastern Pennsylvania, with headquarters located in Port Clinton. The RBMN provides freight service on 300 miles (480 km) of track, with its mainline consisting of the Reading Division between Reading and Packerton and the Lehigh Division between Lehighton and Dupont. In addition to freight service, passenger excursions also run along the RBMN system. The Lehigh Gorge Scenic Railway (LGSR) is a tourist railroad that operates passenger excursions along the RBMN between Jim Thorpe and Lehigh Gorge State Park. The RBMN also operates passenger excursions from Reading and Port Clinton to Jim Thorpe.
The Dunkirk, Allegheny Valley and Pittsburgh Railroad is a historic railroad company that operated in Pennsylvania and New York.
The Indian Creek Railroad is a short-line railroad in Madison County, Indiana, United States. The 4.55-mile (7.32 km) line is owned by Kokomo Grain Company, an agricultural products and services company, and connects their property at 40°11′30″N85°44′40″W with the Norfolk Southern Railway's Marion Branch in northern Anderson, carrying outbound grain and inbound fertilizer.

The Western New York and Pennsylvania Railroad is a short-line railroad that operates freight trains in Western New York and Northwest Pennsylvania, United States. The company is controlled by the Livonia, Avon and Lakeville Railroad, with which it does not connect. It started operations in 2001 on the Southern Tier Extension, a former Erie Railroad line between Hornell and Corry, owned by the public Chautauqua, Cattaraugus, Allegany and Steuben Southern Tier Extension Railroad Authority (STERA). Through acquisitions and leases, the line was extended from Corry to Meadville in 2002 and to Oil City in 2006, and in 2007 the WNY&P leased and sub-leased portions of the north-south Buffalo Line, a former Pennsylvania Railroad line mostly built by a predecessor of the defunct Western New York and Pennsylvania Railway. The two lines cross at Olean.

The Rochester and Genesee Valley Railroad Museum (RGVRRM) is an operating railroad museum located in Industry, New York. The museum started in 1971 with the purchase of a former Erie Railroad Depot from the Erie Lackawanna Railroad. Since then the museum has grown to include a one-mile demonstration railroad, connecting it with the New York Museum of Transportation in Rush, making it one of the only operating railroad museums in New York State. The museum was formerly an operation of the Rochester Chapter National Railway Historical Society until 2011. The organization rosters more than 40 pieces of historic railroad equipment, including diesel and steam locomotives, electric trolley and multiple-unit cars, freight cars, cabooses, passenger cars, and work equipment. The museum campus includes a number of preserved railroad structures, including the 1909 Industry Depot built by the Erie Railroad, a waiting shelter from the Rochester, Lockport & Buffalo Railroad, and a crossing watchman's shanty from the New York Central. Train rides are operated and the museum is open to the public on select weekends from June through October, and is staffed entirely by volunteers.

The East Penn Railroad is a short-line railroad that operates a number of mostly-unconnected lines in the U.S. states of Pennsylvania and Delaware. Except for two industrial park switching operations, all are former Pennsylvania Railroad or Reading Company lines, abandoned or sold by Conrail or its predecessors.

The Black River and Western Railroad is a freight and heritage railroad operating in Hunterdon County, New Jersey, between Flemington, Lambertville and Ringoes. The railroad operates vintage steam and diesel powered locomotives.
The Eastern Berks Gateway Railroad is a short-line railroad in Pennsylvania that runs from Boyertown south to Pottstown, where it interchanges with the Norfolk Southern Railway. The railroad was operated by U.S. Rail Partners until 2013, when the Colebrookdale Railroad Preservation Trust took over.

The Lehigh Line is a railroad line in central New Jersey and northeastern Pennsylvania. It is owned and operated by the Norfolk Southern Railway. The line runs west from the vicinity of the Port of New York and New Jersey (via Conrail's Lehigh Line to the Susquehanna River valley at the south end of the Wyoming Valley Coal Region. Administratively it is part of Norfolk Southern's Harrisburg Division and is also part of the Crescent Corridor. As of 2016 the line is freight-only, although there are perennial proposals to restore passenger service over all or part of the line.

















