The Lake Shore and Michigan Southern Railway, established in 1833, and sometimes referred to as the Lake Shore, was a major part of the New York Central Railroad's Water Level Route from Buffalo, New York, to Chicago, Illinois, primarily along the south shore of Lake Erie and across northern Indiana. The line's trackage remains a major rail transportation corridor used by Amtrak passenger trains and several freight lines; in 1998, its ownership was split at Cleveland, Ohio, between CSX Transportation to the east and Norfolk Southern Railway in the west.

The Pittsburg and Shawmut Railroad, also known as the Shawmut Line, was a short line railroad company operating passenger and freight service on standard gauge track in central and southwestern Pennsylvania. Since 2004, it has been operated as part of the Buffalo and Pittsburgh Railroad, which is owned by Genesee & Wyoming Inc.

The Pittsburg, Shawmut & Northern Railroad also known as the Shawmut Line, was a Class I railroad company operating passenger and freight service on standard gauge track in central Pennsylvania and western New York. The line was financially troubled for its entire life span and declared bankruptcy after just six years of operation. It would spend the remaining 42 year of its existence in receivership or trusteeship: one of the longest bankruptcy proceedings in American railroading history.
The Genesee Valley Canal Railroad was a part of the Pennsylvania Railroad system in western New York. It was built on the former Genesee Valley Canal alignment.
The Allegheny and Eastern Railroad was a shortline railroad operating in Pennsylvania, owned by Genesee & Wyoming Inc. It is now operated by the Buffalo and Pittsburgh Railroad.
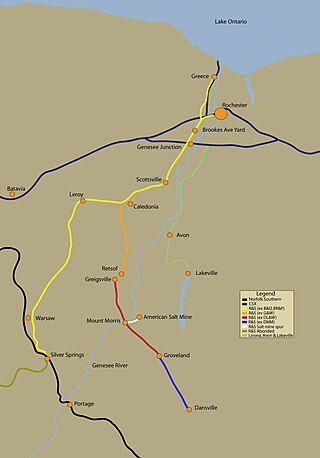
The Rochester and Southern Railroad, a subsidiary of Genesee & Wyoming Inc., is a class III shortline that runs from the city of Rochester in Monroe County to Silver Springs, NY. The RSR started in 1986, when the B&O sold off its Buffalo and Rochester branches. The trackage was purchased by Genesee & Wyoming Inc., and split into two railroads, the Buffalo and Pittsburgh Railroad and the Rochester and Southern Railroad. The Rochester branch was scrapped from Silver Springs south to Machias, New York.

The P&W Subdivision is a railroad line owned and operated by CSX Transportation, the Allegheny Valley Railroad (AVR), and the Buffalo and Pittsburgh Railroad (BPRR) in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The line runs from Rankin north through Pittsburgh to West Pittsburg along a former Baltimore and Ohio Railroad line, once the Pittsburgh and Western Railroad.

The Allegheny Valley Railroad is a class III railroad that operates in Western Pennsylvania, and is owned by Carload Express, Inc.
The Northern Subdivision is a railroad line owned and operated by the Buffalo and Pittsburgh Railroad (BPRR), which is owned by Genesee and Wyoming Industries, in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The line is one of the oldest in Pennsylvania, and at one time, stretched all the way from Callery, to Mount Jewett, Pennsylvania. Today, more than half the line is gone.

The Western New York and Pennsylvania Railroad is a short-line railroad that operates freight trains in Western New York and Northwest Pennsylvania The company is controlled by the Livonia, Avon and Lakeville Railroad, with which it does not connect. It started operations in 2001 on the Southern Tier Extension, a former Erie Railroad line between Hornell, New York and Corry, Pennsylvania, owned by the public Chautauqua, Cattaraugus, Allegany and Steuben Southern Tier Extension Railroad Authority (STERA).
The Allegheny Railroad was an American railroad company operating in northwestern Pennsylvania.
The Rochester and State Line Railroad was a 19th-century railroad company in New York state.
The Buffalo, Rochester, and Pittsburgh Railway was one of the more than ten thousand railroad companies founded in North America. It lasted much longer than most, serving communities from the shore of Lake Ontario to the center of western Pennsylvania.

The Youngstown Belt Railroad is a part of the Ohio Central Railroad System, which was bought by Genesee & Wyoming Inc. in 2008, serving the area northwest of Youngstown, Ohio. It began operations in 1997, mainly on ex-Erie Railroad trackage owned by the affiliated Warren and Trumbull Railroad (W&T), which acquired the "Lordstown Cluster" from Conrail in 1996. It also leases a short ex-Baltimore and Ohio Railroad segment from CSX Transportation, formerly operated by the W&T.

The Warren and Trumbull Railroad is a part of the Ohio Central Railroad System, which was bought by Genesee & Wyoming Inc. in 2008, operating three lines in and near Warren. It began operations in 1994 on a line formerly operated by CSX Transportation, and expanded in 1996 on two ex-Conrail lines.

The Columbus & Ohio River Railroad is a railroad in the U.S. state of Ohio owned by Genesee & Wyoming Inc.










