
Phosphatidylcholines (PC) are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup. They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources, such as egg yolk or soybeans, from which they are mechanically or chemically extracted using hexane. They are also a member of the lecithin group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues. Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (lecithin) is a major component of the pulmonary surfactant, and is often used in the lecithin–sphingomyelin ratio to calculate fetal lung maturity. While phosphatidylcholines are found in all plant and animal cells, they are absent in the membranes of most bacteria, including Escherichia coli. Purified phosphatidylcholine is produced commercially.
Phosphatidic acids are anionic phospholipids important to cell signaling and direct activation of lipid-gated ion channels. Hydrolysis of phosphatidic acid gives rise to one molecule each of glycerol and phosphoric acid and two molecules of fatty acids. They constitute about 0.25% of phospholipids in the bilayer.
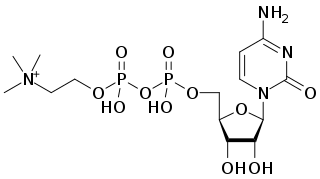
Citicoline (INN), also known as cytidine diphosphate-choline (CDP-Choline) or cytidine 5'-diphosphocholine is an intermediate in the generation of phosphatidylcholine from choline, a common biochemical process in cell membranes. Citicoline is naturally occurring in the cells of human and animal tissue, in particular the organs.

Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase is a transferase enzyme which converts phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to phosphatidylcholine (PC) in the liver. In humans it is encoded by the PEMT gene within the Smith–Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK4 gene.

The enzyme phosphatidate phosphatase (PAP, EC 3.1.3.4) is a key regulatory enzyme in lipid metabolism, catalyzing the conversion of phosphatidate to diacylglycerol:

In enzymology, a CDP-diacylglycerol—inositol 3-phosphatidyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a CDP-diacylglycerol—serine O-phosphatidyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
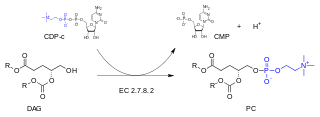
In enzymology, a diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a sphingomyelin synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK1 gene.

Diacylglycerol kinase zeta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DGKZ gene.

Diacylglycerol kinase alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DGKA gene.

Choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCYT1A gene.

Diacylglycerol kinase delta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DGKD gene.

CDP-diacylglycerol—inositol 3-phosphatidyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDIPT gene.

Diacylglycerol kinase theta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DGKQ gene.
In molecular biology, the choline/ethanolamine kinase family includes choline kinase(EC 2.7.1.32) and ethanolamine kinase.
In enzymology, a ceramide phosphoethanolamine synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The CDP-choline pathway, first identified by Eugene P. Kennedy in 1956, is the predominant mechanism by which mammalian cells synthesize phosphatidylcholine (PC) for incorporation into membranes or lipid-derived signalling molecules. The CDP-choline pathway represents one half of what is known as the Kennedy pathway. The other half is the CDP-ethanolamine pathway which is responsible for the biosynthesis of the phospholipid phosphatidylethanolamine (PE).
















