The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are used to make isoprenoids, a diverse class of over 30,000 biomolecules such as cholesterol, vitamin K, coenzyme Q10, and all steroid hormones.

Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate is an isoprenoid precursor. It is a product of both the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and exists in virtually all life forms. The enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase catalyzes isomerization between DMAPP and IPP.

Mevalonic acid (MVA) is a key organic compound in biochemistry; the name is a contraction of dihydroxymethylvalerolactone. The carboxylate anion of mevalonic acid, which is the predominant form in biological environments, is known as mevalonate and is of major pharmaceutical importance. Drugs like statins stop the production of mevalonate by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase.

Isopentenyl pyrophosphate is an isoprenoid precursor. IPP is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway and in the non-mevalonate MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. Isoprenoid precursors such as IPP, and its isomer DMAPP, are used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids.

β-Hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), also known as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A, is an intermediate in the mevalonate and ketogenesis pathways. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase. The research of Minor J. Coon and Bimal Kumar Bachhawat in the 1950s at University of Illinois led to its discovery.
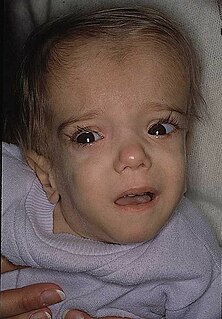
Mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that disrupts the biosynthesis of cholesterol and isoprenoids. It is a very rare genetic disease.
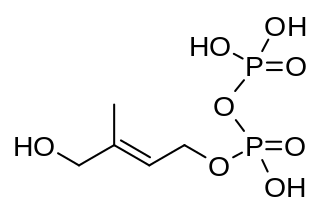
(E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate of the MEP pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. The enzyme HMB-PP synthase catalyzes the conversion of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) into HMB-PP. HMB-PP is then converted further to isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) by HMB-PP reductase.
The non-mevalonate pathway—also appearing as the mevalonate-independent pathway and the 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate/1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (MEP/DOXP) pathway—is an alternative metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of the isoprenoid precursors isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP). The currently preferred name for this pathway is the MEP pathway, since MEP is the first committed metabolite on the route to IPP.

Acetoacetyl CoA is the precursor of HMG-CoA in the mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol biosynthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies synthesis (ketogenesis) pathway of the liver. In the ketone bodies digestion pathway, it is no longer associated with having HMG-CoA as a product or as a reactant.

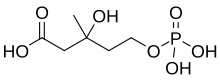
Mevalonate kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MVK gene. Mevalonate kinases are found in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals. This enzyme catalyzes the following reaction:

5-Diphosphomevalonic acid is an intermediate in the mevalonate pathway.

DXP reductoisomerase is an enzyme that interconverts 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) and 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP).
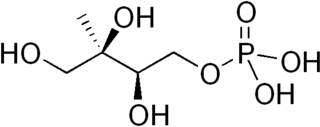
2-C-Methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) is an intermediate on the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It is the first committed metabolite on that pathway on the route to IPP and DMAPP.

1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate is an intermediate in the non-mevalonate pathway.

Diphosphomevalonate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.33), most commonly referred to in scientific literature as mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In molecular biology, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase or HMG-CoA synthase EC 2.3.3.10 is an enzyme which catalyzes the reaction in which acetyl-CoA condenses with acetoacetyl-CoA to form 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA). This reaction comprises the second step in the mevalonate-dependent isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway. HMG-CoA is an intermediate in both cholesterol synthesis and ketogenesis. This reaction is overactivated in patients with diabetes mellitus type 1 if left untreated, due to prolonged insulin deficiency and the exhaustion of substrates for gluconeogenesis and the TCA cycle, notably oxaloacetate. This results in shunting of excess acetyl-CoA into the ketone synthesis pathway via HMG-CoA, leading to the development of diabetic ketoacidosis.
4-Diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methylerythritol is an intermediate in the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It is produced by the enzyme 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase (IspD) and is a substrate for CDP-ME kinase (IspE).
4-Hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase (EC 1.17.1.2, isopentenyl-diphosphate:NADP+ oxidoreductase, LytB, (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate reductase, HMBPP reductase, IspH, LytB/IspH) is an enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway. It acts upon (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (or "HMB-PP").

Secologanin is a secoiridoid monoterpene synthesized from geranyl pyrophosphate in the mevalonate pathway. Secologanin then proceeds with dopamine or tryptamine to form ipecac and terpene indole alkaloids, respectively.

Perillyl alcohol and its precursor limonene are naturally occurring monocyclic terpenes derived from the mevalonate pathway in plants. Perillyl alcohol can be found in the essential oils of various plants, such as lavender, lemongrass, sage, and peppermint. It has a number of manufacturing, household, and medical applications. For example, perillyl alcohol may be used as an ingredient in cleaning products and cosmetics.