
Chamaecyparis obtusa is a species of cypress native to central Japan in East Asia, and widely cultivated in the temperate northern hemisphere for its high-quality timber and ornamental qualities, with many cultivars commercially available.
The lignans are a large group of low molecular weight polyphenols found in plants, particularly seeds, whole grains, and vegetables. The name derives from the Latin word for "wood". Lignans are precursors to phytoestrogens. They may play a role as antifeedants in the defense of seeds and plants against herbivores.

Arame, sea oak is a species of kelp, of the brown algae, best known for its use in Japanese cuisine.

Schizonepeta is a genus of herbs. It should not be confused with the true catnips of the genus Nepeta known for their euphoria-inducing effect on domestic cats.

Lindera obtusiloba, the blunt-lobed spice bush, is a species of flowering plant in the laurel family Lauraceae, native to China, Korea and Japan. It is a spreading deciduous shrub or small tree growing to 6 m (20 ft) tall and wide, with glossy aromatic leaves and deep yellow flowers which appear in spring before the leaves. Juvenile leaves are lobed and are deep purple. The leaves often turn yellow in autumn.

Magnolol is an organic compound that is classified as lignan. It is a bioactive compound found in the bark of the Houpu magnolia or in M. grandiflora. The compound exists at the level of a few percent in the bark of species of magnolia, the extracts of which have been used in traditional Chinese and Japanese medicine. In addition to magnolol, related lignans occur in the extracts including honokiol, which is an isomer of magnolol.

CD99 antigen, also known as MIC2 or single-chain type-1 glycoprotein, is a heavily O-glycosylated transmembrane protein that is encoded by the CD99 gene in humans. The protein has a mass of 32 kD. Unusually for a gene present on the X chromosome, the CD99 gene does not undergo X inactivation, and it was the first such pseudoautosomal gene to be discovered in humans.

Leukotriene B4 receptor 2, also known as BLT2, BLT2 receptor, and BLTR2, is an Integral membrane protein that is encoded by the LTB4R2 gene in humans and the Ltbr2 gene in mice.

CXXC-type zinc finger protein 5 is a protein that is encoded by the CXXC5 gene in humans.

Mirodenafil belongs to the drug class PDE5 inhibitors, which includes avanafil, sildenafil, tadalafil, udenafil, and vardenafil, and is the first-line treatment for erectile dysfunction. Developed by SK Chemicals Life Science, mirodenafil is marketed in Korea under the trade name Mvix, offered both as tablets and as orally dissolving film.
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Gintonin</span> Protein found in [[ginseng]]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c0/Gintonin_structure.jpg/320px-Gintonin_structure.jpg)
Gintonin is a glycolipoprotein fraction isolated from ginseng. The non-saponin ingredient was designated as gintonin, where gin was derived from ginseng, ton from the tonic effects of ginseng, and in from protein. The main component of gintonin is a complex of lysophosphatidic acids (LPA) and ginseng proteins such as ginseng major latex-like protein151 (GLP151) and ginseng ribonuclease-like storage protein.
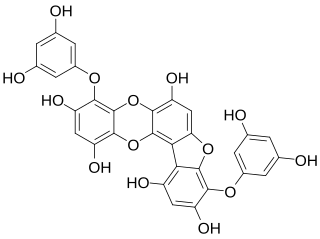
Phlorofucofuroeckol A is a phlorotannin isolated from brown algae species such as Eisenia bicyclis, Ecklonia cava, Ecklonia kurome or Ecklonia stolonifera.

Kaang Bong-Kiun was born in Jeju-do, South Korea, on November 21, 1961. He is a professor of neuroscience in the Department of Biological Sciences of Seoul National University. He is a Fellow of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
Seong Hoe Park is a Korean immunologist and pathologist and a distinguished professor of pathology at the Seoul National University College of Medicine. He served as the chair of the Department of Pathology (2000–2004), the chair of the Graduate Program of Immunology (2002–2006), the president of Center for Animal Resource Development (2004–2006) at Seoul National University. He was the president of the Korean Association of Immunologists (2000–2001). Throughout his career as a T cell immunologist, Park established the theory of T cell-T cell interaction in human thymus, in which T cells expressing MHC class II drive previously unrecognized types of T cells and provide another significant developmental mechanism of T cells.
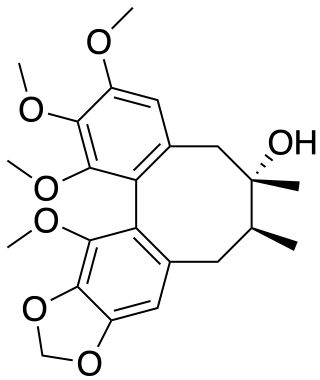
Gomisin A is a bio-active compound isolated from Schisandra chinensis.

Schisandrins (schizandrins) are a group of bioactive chemical compounds found in Schisandra rubriflora, Schisandra sphenanthera, and Schisandra chinensis. Schizandrin is a tannin.
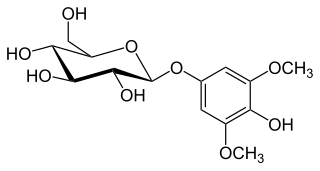
Koaburaside is an anti-histamine compound isolated from Lindera obtusiloba.

Radotinib (INN; trade name Supect), and sometimes referred to by its investigational name IY5511, is a drug for the treatment of different types of cancer, most notably Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) with resistance or intolerance of other Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitors, such as patients resistant or intolerant to imatinib.

Obovatol is a biphenolic anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic, and nootropic isolated from the bark of Magnolia obovata. It is a biphenyl lignan.

Nyasol, also known as cis-hinokiresinol or as (Z)-hinokiresinol, is a lignan that is found in Anemarrhena asphodeloides. It has estrogenic activity, acting as a selective agonist of the ERβ, and hence is a phytoestrogen. In addition, (-)-nyasol has been found to inhibit the production of eicosanoids and nitric oxide in vitro and shows anti-inflammatory effects.










![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Gintonin</span> Protein found in [[ginseng]]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c0/Gintonin_structure.jpg/320px-Gintonin_structure.jpg)







