History
In the 1820s, New York State removed all property qualifications for the right to vote for whites but retained them for blacks. In 1846 voters in New York State rejected a proposed amendment to the state constitution that would guarantee blacks the same voting rights as whites. In 1870, however, five years after the Civil War, the 15th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution was ratified, giving blacks throughout the United States the same voting rights as whites.

New York City introduced a uniform ballot listing all candidates in 1880. To get on it, an office seeker would have to be nominated by a political party or submit nominating petitions, laying the groundwork for a system that persists to this day. In 1894 bipartisan control of elections was introduced, establishing a system in effect to this day. All election positions, from Board of Elections commissioners to election inspectors, must be divided equally between the two major parties.
A voting machine developed by Jacob H. Myers, was used in Lockport, New York in 1892. By the early 1920s, voting machines would be used for all general elections in New York City. A 1915 referendum giving women the vote was defeated by city and state voters, but in 1920 the 19th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution was signed into law, guaranteeing women throughout the United States the right to vote.
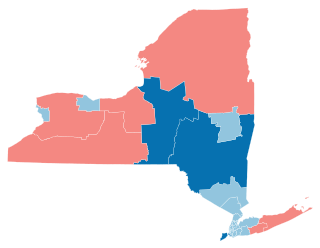
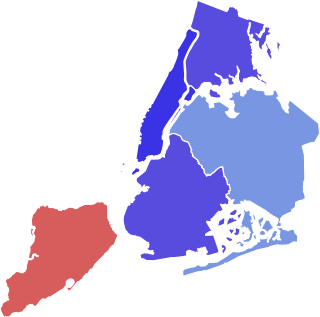
In 1967, a suit brought under the Voting Rights Act passed by the U.S. Congress two years earlier led to the creation of the majority black 12th Congressional District in Brooklyn. Previously, black voters had been divided among several predominantly white districts. Under the Act, Manhattan, Brooklyn, and the Bronx are subject to preclearance by the Department of Justice before implementing any changes affecting voting. In 1968, voters in the district elected Shirley Chisholm as the first black woman ever in the U.S. House of Representatives. Since then, congressional, state legislative, and City Council districts have been drawn so as to ensure minority representation.
Non-citizens who have children in public schools were given the right to vote in elections for members of community school boards in 1969 (those boards no longer exist). Starting in 1975 election information was provided in Spanish as well as English, and in 1992 the City introduced ballots in Chinese.
As of May 2013, a new bill has begun working its way through the NYC political system to allow noncitizens living in the five boroughs the right to vote in local elections. It has enough projected votes in the NYC City Council to overrule an expected Mayoral veto. It is unclear whether this new law (if passed) will actually be valid. [8]
In December 2021, the city council voted to allow non-citizens within New York City to vote in elections. [9]
Electoral reform
In 1937, New York City began to elect its city council through Single transferable voting. Unusually the variety of STV it adopted used the "uniform quota" where anyone who received 75,000 votes was elected and perhaps others who came close if that was needed to fill the seats.
As well, the city used its boroughs as its electoral districts and they had a range of district magnitude (number of members). In fact the NYC STV had a novel provision that the number of councilors representing a borough was tied to voter turnout in that borough. This meant that the number of councilors varied from election to election, but it intuitively ensured that each borough had the representation that it deserved, which had not been the case previously due to the city's districting lagging behind shifts in population. [10] Under NYC's STV, total seats on council varied: 1937 New York City Council election 25 seats, 1939 New York City Council election 21 seats, 1941 26 seats, 1943 17 seats, and 1945 23 seats. [11]
Term limits and campaign finance
New York has a municipal campaign finance system. The New York City Campaign Finance Board (NYCCFB) gives public matching funds to qualifying candidates, who in exchange submit to strict contribution and spending limits and a full audit of their finances. Citywide candidates in the program are required to take part in debates. Corporate contributions are banned and political action committees must register with the city.
A two-term limit was imposed on most elected officials, including the Mayor and City Council, but excluding the Districts Attorney, after a 1993 referendum. [12] In 1996, voters turned down a City Council proposal to extend term limits. The movement to introduce term limits was led by Ronald Lauder, a cosmetics heir, who spent $4 million on the two referendums.
In 2008 the City Council voted 29–22 to overturn two referendums and to extend the term limits to three terms. [13] [14] These limits were reinstated as part of an NYC Charter update voted in by the electorate.