The Lower Mainland is a geographic and cultural region of the mainland coast of British Columbia that generally comprises the regional districts of Metro Vancouver and the Fraser Valley. Home to approximately 3.05 million people as of the 2021 Canadian census, the Lower Mainland contains sixteen of the province's 30 most populous municipalities and approximately 60% of the province's total population.

Richmond is a city in the coastal Lower Mainland region of British Columbia, Canada. Mainly a suburban city, it occupies almost the entirety of Lulu Island, between the two estuarine distributaries of the Fraser River. Encompassing the adjacent Sea Island and several other smaller islands and uninhabited islets to its north and south, the suburb neighbours Vancouver and Burnaby on the Burrard Peninsula to the north, New Westminster and Annacis Island to the east, Delta to the south, and the Strait of Georgia to the west.

View Royal is a town in Greater Victoria and a member municipality of the Capital Regional District of British Columbia, Canada. View Royal has a population of 11,575 residents. With over 700 hectares of parkland, View Royal includes Thetis, McKenzie, Pike, and Prior Lakes and portions of Esquimalt Harbour and Portage Inlet.

Golden is a town in southeastern British Columbia, Canada, 262 kilometres (163 mi) west of Calgary, Alberta, and 713 kilometres (443 mi) east of Vancouver.

The Sunshine Coast Regional District is a regional district in British Columbia, Canada. It is located on the southern mainland coast, across Georgia Strait from Vancouver Island. It borders on the qathet Regional District to the north, the Squamish-Lillooet Regional District to the east, and, across Howe Sound, the Metro Vancouver District to the south. The regional district offices are located in the District Municipality of Sechelt.

North Cowichan is a district municipality established in 1873 on Vancouver Island, in British Columbia, Canada. The municipality is part of the Cowichan Valley Regional District. North Cowichan is noted for a landscape including forests, beaches, rivers, and lakes. The municipality encompasses the communities of Chemainus; Westholme; Crofton; Maple Bay; and "the South End". The latter is an informal name for a built-up area which is essentially a suburb of the City of Duncan, a separate municipality.

Central Saanich is a district municipality in Greater Victoria, British Columbia, Canada, and a member municipality of the Capital Regional District. It is located on the Saanich Peninsula, in the far south-east of Vancouver Island. It is the traditional territory of the W̱SÁNEĆ people. The district began as a farming community, and many hobby farms, along working farms and vineyards, still exist. In recent decades, the area has seen increasing residential, commercial, and industrial development, especially around the neighbourhoods of Brentwood Bay and Saanichton, which are occasionally referred to as separate communities.
The District of Metchosin is a municipality and community in Greater Victoria on the southern tip of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. It is a coastal community adjacent to the Strait of Juan de Fuca. Metchosin is part of the Western Communities and one of the 13 regional municipalities.

South Asian Canadians are Canadians who were either born in or can trace their ancestry to South Asia or the Indian subcontinent, which includes the nations of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka and the Maldives. The term also includes immigrants from South Asian communities in East and South Africa, Guyana, Trinidad and Tobago, Fiji, Mauritius and the rest of the world.

The Cariboo Regional District spans the Cities and Districts of Quesnel, Williams Lake, 100 Mile House, and Wells in the Central Interior of British Columbia.

New Westminster—Burnaby is a federal electoral district in British Columbia, Canada, that was represented in the House of Commons of Canada from 1988 to 1997 and since 2015.

Port Hardy is a district municipality in British Columbia, Canada located on the north-east tip of Vancouver Island. Port Hardy has a population of 3,902 as of the 2021 census.
The demographics of Toronto, Ontario, Canada make Toronto one of the most multicultural and multiracial cities in the world. In 2021, 57.0 percent of the residents of the metropolitan area belonged to a visible minority group, compared with 51.4 percent in 2016, and 13.6 percent in 1981. Toronto also has established ethnic neighbourhoods such as the multiple Chinatowns, Corso Italia, Little Italy, Little India, Greektown, Koreatown, Little Tokyo, Little Jamaica, Little Portugal, Little Malta, Roncesvalles (Polish), and Bloor West Village (Ukrainian), all of which celebrate the city's multiculturalism. Data from the suburban municipalities are also included for some metrics as most of these municipalities are part of the Toronto CMA.
The demographics of Metro Vancouver indicate a multicultural and multiracial region. Metro Vancouver is a metropolitan area, with its major urban centre being Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. The Vancouver census metropolitan area, as defined by Statistics Canada, encompasses roughly the same territory as the Metro Vancouver Regional District, a regional district in British Columbia. The regional district includes 23 local authorities. Figures provided here are for the Vancouver census metropolitan area and not for the City of Vancouver.

British Columbia is a Canadian province with a population of about 5.6 million people. The province represents about 13.2% of the population of the Canadian population. Most of the population is between the ages of 15 and 49. About 60 percent of British Columbians have European descent with significant Asian and Aboriginal minorities. Just under 30% of British Columbians are immigrants. Over half of the population is irreligious, with Christianity and Sikhism being the most followed religions.

Asian Canadians are Canadians who were either born in or can trace their ancestry to the continent of Asia. Canadians with Asian ancestry comprise both the largest and fastest growing group in Canada, after European Canadians, forming approximately 20.2 percent of the Canadian population as of 2021. Most Asian Canadians are concentrated in the urban areas of Southern Ontario, Southwestern British Columbia, Central Alberta, and other large Canadian cities.
South Asian Canadians in Metro Vancouver are the third-largest pan-ethnic group in the region, comprising 369,295 persons or 14.2 percent of the total population as of 2021. Sizable communities exist within the city of Vancouver along with the adjoining city of Surrey, which houses one of the world's largest South Asian enclaves.
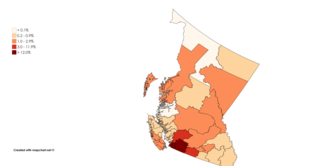
The South Asian community in British Columbia was first established in 1897. The first immigrants originated from Punjab, British India, a northern region and state in modern-day India and Pakistan. Punjabis originally settled in rural British Columbia at the turn of the twentieth century, working in the forestry and agricultural industries.

Sikhism in Greater Vancouver is one of the main religions across the region, especially among the Indo-Canadian population. The Sikh community in Vancouver is the oldest, largest and most influential across Canada, having begun in the late 19th century.
Edmonds is a neighbourhood in the southeast of Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada. It is one of the city's four officially designated town centres.