
Rhodium is a chemical element with the symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is a very rare, silvery-white, hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal. It is a noble metal and a member of the platinum group. It has only one naturally occurring isotope: 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is usually found as a free metal or as an alloy with similar metals and rarely as a chemical compound in minerals such as bowieite and rhodplumsite. It is one of the rarest and most valuable precious metals.

Wilkinson's catalyst is the common name for chloridotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I), a coordination complex of rhodium with the formula [RhCl(PPh3)3], where 'Ph' denotes a phenyl group). It is a red-brown colored solid that is soluble in hydrocarbon solvents such as benzene, and more so in tetrahydrofuran or chlorinated solvents such as dichloromethane. The compound is widely used as a catalyst for hydrogenation of alkenes. It is named after chemist and Nobel laureate Sir Geoffrey Wilkinson, who first popularized its use.

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of n, the material is either a dense brown solid or a soluble reddish salt. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis, notably for the industrial production of acetic acid and hydroformylation.
Cycloocta-1,5-diene is a cyclic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C8H12, specifically [−(CH2)2−CH=CH−]2.

Rhodium(III) oxide (or Rhodium sesquioxide) is the inorganic compound with the formula Rh2O3. It is a gray solid that is insoluble in ordinary solvents.

Cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer is the organorhodium compound with the formula Rh2Cl2(C8H12)2, commonly abbreviated [RhCl(COD)]2 or Rh2Cl2(COD)2. This yellow-orange, air-stable compound is a widely used precursor to homogeneous catalysts.
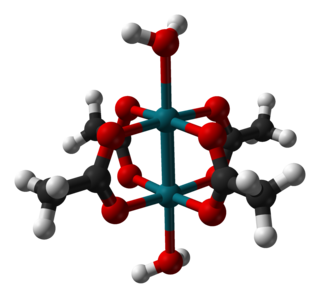
Rhodium(II) acetate is the coordination compound with the formula Rh2(AcO)4, where AcO− is the acetate ion (CH
3CO−
2). This dark green powder is slightly soluble in polar solvents, including water. It is used as a catalyst for cyclopropanation of alkenes. It is a widely studied example of a transition metal carboxylate complex.

Organorhodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a rhodium-carbon chemical bond, and the study of rhodium and rhodium compounds as catalysts in organic reactions.

Ruthenium(III) acetylacetonate is a coordination complex with the formula Ru(O2C5H7)3. O2C5H7− is the ligand called acetylacetonate. This compound exists as a dark violet solid that is soluble in most organic solvents. It is used as a precursor to other compounds of ruthenium.
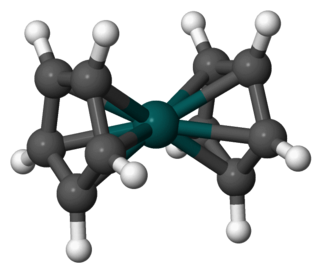
Rhodocene is a chemical compound with the formula [Rh(C5H5)2]. Each molecule contains an atom of rhodium bound between two planar aromatic systems of five carbon atoms known as cyclopentadienyl rings in a sandwich arrangement. It is an organometallic compound as it has (haptic) covalent rhodium–carbon bonds. The [Rh(C5H5)2] radical is found above 150 °C (302 °F) or when trapped by cooling to liquid nitrogen temperatures (−196 °C [−321 °F]). At room temperature, pairs of these radicals join via their cyclopentadienyl rings to form a dimer, a yellow solid.
Metal acetylacetonates are coordination complexes derived from the acetylacetonate anion (CH
3COCHCOCH−
3) and metal ions, usually transition metals. The bidentate ligand acetylacetonate is often abbreviated acac. Typically both oxygen atoms bind to the metal to form a six-membered chelate ring. The simplest complexes have the formula M(acac)3 and M(acac)2. Mixed-ligand complexes, e.g. VO(acac)2, are also numerous. Variations of acetylacetonate have also been developed with myriad substituents in place of methyl (RCOCHCOR′−). Many such complexes are soluble in organic solvents, in contrast to the related metal halides. Because of these properties, acac complexes are sometimes used as catalyst precursors and reagents. Applications include their use as NMR "shift reagents" and as catalysts for organic synthesis, and precursors to industrial hydroformylation catalysts. C
5H
7O−
2 in some cases also binds to metals through the central carbon atom; this bonding mode is more common for the third-row transition metals such as platinum(II) and iridium(III).
The Buchner ring expansion is a two-step organic C-C bond forming reaction used to access 7-membered rings. The first step involves formation of a carbene from ethyl diazoacetate, which cyclopropanates an aromatic ring. The ring expansion occurs in the second step, with an electrocyclic reaction opening the cyclopropane ring to form the 7-membered ring.

Carbonyl hydrido tris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I) [Carbonyl(hydrido)tris(triphenylphosphane)rhodium(I)] is an organorhodium compound with the formula [RhH(CO)(PPh3)3] (Ph = C6H5). It is a yellow, benzene-soluble solid, which is used industrially for hydroformylation.
Barium acetylacetonate is a compound with formula Ba(C5H7O2)2. It is the Ba2+ complex of the anion acetylacetonate. The compound is typically encountered as an ill-defined hydrate, which would accord with the high coordination number characteristic of barium.

Europium acetylacetonate is a compound with formula Eu(C5H7O2)3(H2O)2. It is a europium(III) complex with three acetylacetonate and two aquo ligands. The electronic structure of the Eu3+
core gives the complex an unusual charge-transfer band absent in other lanthanide acetylacetonates. The photoluminescent emission lines occur near 465 (blue), 525 (green), and 579 nm (yellow), and are unusually sharp, especially the yellow doublet. Doping a blend of polyacrylate and polycarbonate with europium acetylacetonate enhances photoluminescence over a broad range of ultraviolet wavelengths. EuFOD is a substituted derivative.
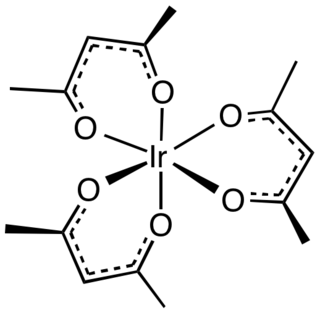
Iridium acetylacetonate is the iridium coordination complex with the formula Ir(O2C5H7)3, which is sometimes known as Ir(acac)3. The molecule has D3-symmetry. It is a yellow-orange solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
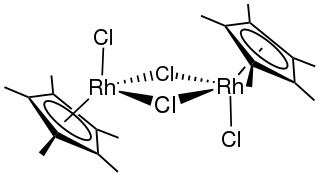
Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl rhodium dichloride dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula [(C5(CH3)5RhCl2)]2, commonly abbreviated [Cp*RhCl2]2 This dark red air-stable diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry.

Dicarbonyl(acetylacetonato)rhodium(I) is an organorhodium compound with the formula Rh(O2C5H7)(CO)2. The compound consists of two CO ligands and an acetylacetonate. It is a dark green solid that dissolves in acetone and benzene, giving yellow solutions. The compound is used as a precursor to homogeneous catalysts.

Hydridotetrakis(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I) is the coordination complex with the formula HRh[P(C6H5)3]4. It consists of a Rh(I) center complexed to four triphenylphosphine (PPh3) ligands and one hydride. The molecule has idealized C3v symmetry. The compound is a homogeneous catalyst for hydrogenation and related reactions. It is a yellow solid that dissolves in aromatic solvents.
Rhodium(III) nitrate is a inorganic compound, a salt of rhodium and nitric acid with the formula Rh(NO3)3. This anhydrous complex has been the subject of theoretical analysis but has not been isolated. However, a dihydrate and an aqueous solution are known with similar stoichiometry; they contain various hexacoordinated rhodium(III) aqua and nitrate complexes. A number of other rhodium nitrates have been characterized by X-ray crystallography: Rb4[trans-[Rh(H2O)2(NO3)4][Rh(NO3)6] and Cs2[-[Rh(NO3)5]. Rhodium nitrates are of interest because nuclear wastes, which contain rhodium, are recycled by dissolution in nitric acid.

















