
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jérôme Balard, its name was derived from the Ancient Greek βρῶμος (bromos) meaning "stench", referring to its sharp and pungent smell.

The halogens are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would exclude tennessine as its chemistry is unknown and is theoretically expected to be more like that of gallium. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is known as group 17.
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications.

Hydrogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula HBr. It is a hydrogen halide consisting of hydrogen and bromine. A colorless gas, it dissolves in water, forming hydrobromic acid, which is saturated at 68.85% HBr by weight at room temperature. Aqueous solutions that are 47.6% HBr by mass form a constant-boiling azeotrope mixture that boils at 124.3 °C. Boiling less concentrated solutions releases H2O until the constant-boiling mixture composition is reached.
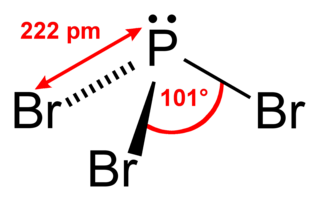
Phosphorus tribromide is a colourless liquid with the formula PBr3. The liquid fumes in moist air due to hydrolysis and has a penetrating odour. It is used in the laboratory for the conversion of alcohols to alkyl bromides.

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of n, the material is either a dense brown solid or a soluble reddish salt. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis, notably for the industrial production of acetic acid and hydroformylation.

Iron(III) bromide is the chemical compound with the formula FeBr3. Also known as ferric bromide, this red-brown odorless compound is used as a Lewis acid catalyst in the halogenation of aromatic compounds. It dissolves in water to give acidic solutions.

Zinc bromide (ZnBr2) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ZnBr2. It is a colourless salt that shares many properties with zinc chloride (ZnCl2), namely a high solubility in water forming acidic solutions, and good solubility in organic solvents. It is hygroscopic and forms a dihydrate ZnBr2·2H2O.

Tantalum(V) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula Ta2Br10. Its name comes from the compound's empirical formula, TaBr5. It is a diamagnetic, orange solid that hydrolyses readily. The compound adopts an edge-shared bioctahedral structure, which means that two TaBr5 units are joined by a pair of bromide bridges. There is no bond between the Ta centres. Niobium(V) chloride, niobium(V) bromide, niobium(V) iodide, tantalum(V) chloride, and tantalum(V) iodide all share this structural motif.
In inorganic chemistry, sulfonyl halide groups occur when a sulfonyl functional group is singly bonded to a halogen atom. They have the general formula RSO2X, where X is a halogen. The stability of sulfonyl halides decreases in the order fluorides > chlorides > bromides > iodides, all four types being well known. The sulfonyl chlorides and fluorides are of dominant importance in this series.
There are three sets of Indium halides, the trihalides, the monohalides, and several intermediate halides. In the monohalides the oxidation state of indium is +1 and their proper names are indium(I) fluoride, indium(I) chloride, indium(I) bromide and indium(I) iodide.

Barium bromide is the chemical compound with the formula BaBr2. It is ionic in nature.

Beryllium bromide is the chemical compound with the formula BeBr2. It is very hygroscopic and dissolves well in water. The compound is a polymer with tetrahedral coordinated Be centres.

Neodymium(III) bromide is an inorganic salt of bromine and neodymium the formula NdBr3. The anhydrous compound is an off-white to pale green solid at room temperature, with an orthorhombic PuBr3-type crystal structure. The material is hygroscopic and forms a hexahydrate in water (NdBr3· 6H2O), similar to the related neodymium(III) chloride.

Rhodium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula RhI3. It is a black solid.
Praseodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal praseodymium (Pr). In these compounds, praseodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as PrCl3, Pr(NO3)3 and Pr(CH3COO)3. However, compounds with praseodymium in the +2 and +4 oxidation states, and unlike other lanthanides, the +5 oxidation state, are also known.

Dysprosium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound of bromine and dysprosium, with the chemical formula of DyBr3.
Lutetium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal lutetium (Lu). In these compounds, lutetium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as LuCl3, Lu2O3 and Lu2(SO4)3. Aqueous solutions of most lutetium salts are colorless and form white crystalline solids upon drying, with the common exception of the iodide. The soluble salts, such as nitrate, sulfate and acetate form hydrates upon crystallization. The oxide, hydroxide, fluoride, carbonate, phosphate and oxalate are insoluble in water.
Protactinium compounds are compounds containing the element protactinium. These compounds usually have protactinium in the +5 oxidation state, although these compounds can also exist in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states.













