An analog signal is any continuous-time signal representing some other quantity, i.e., analogous to another quantity. For example, in an analog audio signal, the instantaneous signal voltage varies continuously with the pressure of the sound waves.

Geotechnical engineering, also known as geotechnics, is the branch of civil engineering and Geological engineering concerned with the engineering behavior of earth materials. It uses the principles of soil mechanics and rock mechanics to solve its engineering problems. It also relies on knowledge of geology, hydrology, geophysics, and other related sciences.

A slurry wall is a civil engineering technique used to build reinforced concrete walls in areas of soft earth close to open water, or with a high groundwater table. This technique is typically used to build diaphragm (water-blocking) walls surrounding tunnels and open cuts, and to lay foundations. Slurry walls are used at Superfund sites to contain the waste or contamination and reduce potential future migration of waste constituents, often with other waste treatment methods. Slurry walls are a "well-established" technology but the decision to use slurry walls for a certain project requires geophysical and other engineering studies to develop a plan appropriate for the needs of that specific location. Slurry walls may need to be used in conjunction with other methods to meet project objectives.

The cone penetration or cone penetrometer test (CPT) is a method used to determine the geotechnical engineering properties of soils and delineating soil stratigraphy. It was initially developed in the 1950s at the Dutch Laboratory for Soil Mechanics in Delft to investigate soft soils. Based on this history it has also been called the "Dutch cone test". Today, the CPT is one of the most used and accepted soil methods for soil investigation worldwide.

Soil liquefaction occurs when a cohesionless saturated or partially saturated soil substantially loses strength and stiffness in response to an applied stress such as shaking during an earthquake or other sudden change in stress condition, in which material that is ordinarily a solid behaves like a liquid. In soil mechanics, the term "liquefied" was first used by Allen Hazen in reference to the 1918 failure of the Calaveras Dam in California. He described the mechanism of flow liquefaction of the embankment dam as:
If the pressure of the water in the pores is great enough to carry all the load, it will have the effect of holding the particles apart and of producing a condition that is practically equivalent to that of quicksand... the initial movement of some part of the material might result in accumulating pressure, first on one point, and then on another, successively, as the early points of concentration were liquefied.

In geotechnical engineering, a caisson is a watertight retaining structure used, for example, to work on the foundations of a bridge pier, for the construction of a concrete dam, or for the repair of ships.

Rock mechanics is a theoretical and applied science of the mechanical behavior of rocks and rock masses.
Norwegian Geotechnical Institute is an independent Norwegian centre for research and consultancy in engineering-related geosciences, such as the geotechnical, geological and geophysical areas. It was created in 1953 and became a private foundation in 1985.
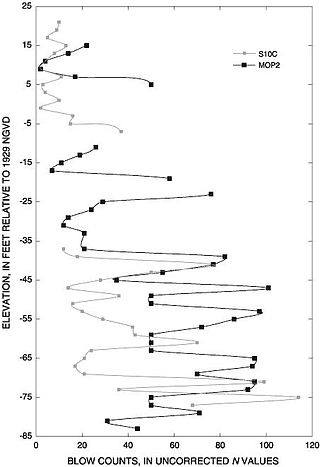
The standard penetration test (SPT) is an in-situ dynamic penetration test designed to provide information on the geotechnical engineering properties of soil. This test is the most frequently used subsurface exploration drilling test performed worldwide. The test procedure is described in ISO 22476-3, ASTM D1586 and Australian Standards AS 1289.6.3.1. The test provides samples for identification purposes and provides a measure of penetration resistance which can be used for geotechnical design purposes. Various local and widely published international correlations that relate blow count, or N-value, to the engineering properties of soils are available for geotechnical engineering purposes.
Pore water pressure refers to the pressure of groundwater held within a soil or rock, in gaps between particles (pores). Pore water pressures below the phreatic level of the groundwater are measured with piezometers. The vertical pore water pressure distribution in aquifers can generally be assumed to be close to hydrostatic.

Geotechnical investigations are performed by geotechnical engineers or engineering geologists to obtain information on the physical properties of soil earthworks and foundations for proposed structures and for repair of distress to earthworks and structures caused by subsurface conditions; this type of investigation is called a site investigation. Geotechnical investigations are also used to measure the thermal resistance of soils or backfill materials required for underground transmission lines, oil and gas pipelines, radioactive waste disposal, and solar thermal storage facilities. A geotechnical investigation will include surface exploration and subsurface exploration of a site. Sometimes, geophysical methods are used to obtain data about sites. Subsurface exploration usually involves soil sampling and laboratory tests of the soil samples retrieved.

A triaxial shear test is a common method to measure the mechanical properties of many deformable solids, especially soil and rock, and other granular materials or powders. There are several variations on the test.
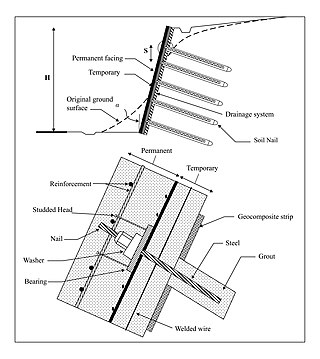
Soil nailing is a remedial construction measure to treat unstable natural soil slopes or unstable man-made (fill) slopes as a construction technique that allows the safe over-steepening of new or existing soil slopes. The technique involves the insertion of relatively slender reinforcing elements into the slope – often general purpose reinforcing bars (rebar) although proprietary solid or hollow-system bars are also available. Solid bars are usually installed into pre-drilled holes and then grouted into place using a separate grout line, whereas hollow bars may be drilled and grouted simultaneously by the use of a sacrificial drill bit and by pumping grout down the hollow bar as drilling progresses. Kinetic methods of firing relatively short bars into soil slopes have also been developed.
Ralph Brazelton Peck was a civil engineer specializing in soil mechanics. He was awarded the National Medal of Science in 1976 "for his development of the science and art of subsurface engineering, combining the contributions of the sciences of geology and soil mechanics with the practical art of foundation design"?

Lightweight expanded clay aggregate (LECA) or expanded clay (exclay) is a lightweight aggregate made by heating clay to around 1,200 °C (2,190 °F) in a rotary kiln. The heating process causes gases trapped in the clay to expand, forming thousands of small bubbles and giving the material a porous structure. LECA has an approximately round or oblong shape due to circular movement in the kiln and is available in different sizes and densities. LECA is used to make lightweight concrete products and other uses.

Cementation involves ions carried in groundwater chemically precipitating to form new crystalline material between sedimentary grains. The new pore-filling minerals forms "bridges" between original sediment grains, thereby binding them together. In this way, sand becomes sandstone, and gravel becomes conglomerate or breccia. Cementation occurs as part of the diagenesis or lithification of sediments. Cementation occurs primarily below the water table regardless of sedimentary grain sizes present. Large volumes of pore water must pass through sediment pores for new mineral cements to crystallize and so millions of years are generally required to complete the cementation process. Common mineral cements include calcite, quartz, and silica phases like cristobalite, iron oxides, and clay minerals; other mineral cements also occur.

Pressure grouting or jet grouting involves injecting a grout material into otherwise inaccessible but interconnected pore or void space of which neither the configuration or volume are known, and is often referred to simply as grouting.

Suction caissons are a form of fixed platform anchor in the form of an open bottomed tube embedded in the sediment and sealed at the top while in use so that lifting forces generate a pressure differential that holds the caisson down. They have a number of advantages over conventional offshore foundations, mainly being quicker to install than deep foundation piles and being easier to remove during decommissioning. Suction caissons are now used extensively worldwide for anchoring large offshore installations, like oil platforms, offshore drillings and accommodation platforms to the seafloor at great depths. In recent years, suction caissons have also seen usage for offshore wind turbines in shallower waters.

An oedometer test is a kind of geotechnical investigation performed in geotechnical engineering that measures a soil's consolidation properties. Oedometer tests are performed by applying different loads to a soil sample and measuring the deformation response. The results from these tests are used to predict how a soil in the field will deform in response to a change in effective stress.
Rotary-pressure sounding is a method of testing soil conditions that might be performed as part of a geotechnical investigation. A series of rods, with a specially designed tip, is forced into the ground under downward pressure. The rotation and speed of insertion are maintained at a constant rate, and the amount of force required to maintain that rate is measured. The results can be interpreted to provide information about sediment stratification, and sometimes also the type of soil and the depth to bedrock.