
Vijayawada, formerly known as Bezawada, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the NTR district. Its Metropolitan agglomeration comprises NTR, Krishna and Guntur districts.

Eluru is a city and the district headquarters of Eluru district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the 14 municipal corporations in the state and the mandal headquarters of Eluru mandal in the Eluru revenue division. The city is on the Tammileru river. The city is well known for its wool-pile carpets and hand woven products. As of 2011 Census of India, the city had a population of 214,414. Its history dates back to the second century CE.

Gannavaram is a suburb of Vijayawada in Krishna district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is also the mandal headquarters of Gannavaram mandal which is administered under Gudivada revenue division. It is a Major Suburb of Vijayawada in the North East side, Vijayawada International Airport, Medha IT Park, IT companies like HCLTech are located here.
Gudivada is a city in Krishna district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is a municipality and the headquarters of Gudivada mandal in Gudivada revenue division. It is one of the cities in the state to be a part of Andhra Pradesh Capital Region. It is the twenty-seventh most populous city in Andhra Pradesh and the three-hundredth most populous city in India with a population of 118,167 according to the 2011 Census of India.

Delhi has significant reliance on its transport infrastructure. The city has developed a highly efficient public transport system with the introduction of the Delhi Metro, which is undergoing a rapid modernization and expansion since 2006. There are 16.6 million registered vehicles in the city as of 30 June 2014, which is the highest in the world among all cities, most of which do not follow any pollution emission norm, while the Delhi metropolitan region has 11.2 million vehicles. Delhi and NCR lose nearly 42 crore man-hours every month while commuting between home and office through public transport, due to the traffic congestion. Therefore, serious efforts, including a number of transport infrastructure projects, are under way to encourage usage of public transport in the city.

Vijayawada International Airport, is an international airport serving the city of Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh, India. The airport is located at Gannavaram, where National Highway 16 connecting Chennai to Kolkata passes through. The Government of India granted international status to the airport on 3 May 2017. The airport is internationally connected to the Middle Eastern countries of United Arab Emirates, Oman and Kuwait.
Rayapudi is a neighbourhood and a part of Urban Notified Area of Amaravati, the state capital of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It was a village in Thullur mandal of in Guntur district, prior to its denotification as gram panchayat.

Kesarapalle is a Locality and major IT hub in Vijayawada city in Krishna district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located in Gannavaram mandal of Gudivada revenue division.

The Pandit Nehru Bus Station (PNBS), also known as the Telugu Satavahana Prayana Pranganam, is a bus station in Vijayawada, situated on the southern side of the main city and adjacent to the Krishna River. It is owned by the Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (APSRTC). This Bus station is spread over an area of 28 acres of land and it is one of the largest Bus station in India preceding by Mofussil Bus Terminus in Chennai (36.5 acres) and following by Mahatma Gandhi Bus Station in Hyderabad (20 acres). It consists of four blocks, two main blocks serving departure terminal with 48 platforms and arrival terminal with 12 platforms, one RTC House serving as a NTR Administrative block headquarters of APSRTC and one block namely City Bus Port serving city buses. There are four entrances to the bus station, each serving as entrance and exit. The entries are from North Side (City Bus Port), East Side (Main entrances) and two on South Side (in front of NH-65 in Krishna Lanka).
Andhra Pradesh is well connected with various destinations in India, as well as other countries. It has road, rail, airways. With a long coast of Bay of Bengal and many sea ports, it flourishes in sea trade as well. The state has one of the largest railway junctions at Vijayawada and Visakhapatnam Port being one of the largest cargo handling seaport.

Amaravati is the capital of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located on the banks of the river Krishna in Guntur district.

Undavalli is a southern neighbourhood of Vijayawada city of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It was a village in Tadepalle mandal of Guntur district, prior to its de-notification as gram panchayat. 5th century Buddhist and Hindu Undavalli Caves which signify Monolithic Indian rock-cut architecture are present at this place. It is a part of Vijayawada Urban Agglomeration.

Vykuntapuram, also spelled as Vaikuntapuram, is a village in Guntur district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located in Amaravathi mandal of Guntur revenue division. The village forms a part of Andhra Pradesh Capital Region, under the jurisdiction of APCRDA.

There are various modes of transportation available in Eluru, a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh, and its region. It includes auto rickshaws, bicycles to mass transit systems – such as buses and trains. The city was once famed for its traffic problems with the railway gates at Vatluru, Venkatraopet, Powerpet, Old bus stand and Eastern Locks areas. When the National Highway passed through the city, the traffic hurried to pass over the railway gates in the city and outskirts, which makes traffic worse.
Transport in Visakhapatnam is the network of roads, railways, rapid transit system in the largest city of Andhra Pradesh. The city of Visakhapatnam also serves as the central hub of transport and logistics on the East coast of India and hence it is called as City Of Destiny.

There are various modes of transportation available in Nellore and its region. It includes auto rickshaws, bicycles to mass transit systems - such as buses, trains and ships.
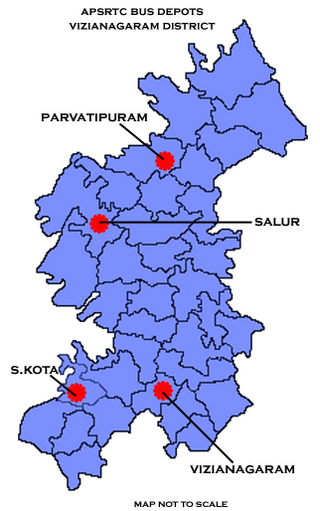
There are various modes of transportation available in Vizianagaram and its Neighbourhoods. It includes auto rickshaws, bicycles to mass transit systems - such as buses, trains and flights.

There are various modes of transportation available in Rajahmundry and its region in India. Although Auto rickshaws, bicycles are mostly used, mass transit systems – such as buses and trains. It is home for a domestic airport located near Madhurapudi and is named as Rajahmundry Airport.
Transport in Bangalore consists of several intracity commute modes such as BMTC buses, Namma Metro rail services, taxis and auto rickshaws, as well as several intercity forms of transport: Government operated KSRTC, NWKRTC, KKRTC, other states RTC buses, Private bus operators, trains, and flights.
The Vijayawada Municipal Corporation is in charge of the civic administration and infrastructure of the city of Vijayawada. The corporation was formed in 1981 by upgrading from municipality status. Many other neighbourhoods were later merged into the corporation limits to a total area of 61.88 km2 (23.89 sq mi), located in Krishna district. It is adjoined by the Legislative capital of Andhra Pradesh, Amaravati. It was also been part of Andhra Pradesh Capital Region. The Vijayawada Municipal Corporation is divided into 77 wards. Each ward is headed by a corporator, elected by popular vote. The corporators elect The City Mayor who is the titular head of the corporation. Its executive powers lie with the Municipal Commissioner appointed by the Government of Andhra Pradesh. The Andhra Pradesh State Election Commission monitors the municipal elections that are held in the city once in every five years. The last elections were held on 10 March 2021.















