Related Research Articles
Romanian is the official and main language of Romania and Moldova. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin which separated from the Western Romance languages in the course of the period from the 5th to the 8th centuries. To distinguish it within the Eastern Romance languages, in comparative linguistics it is called Daco-Romanian as opposed to its closest relatives, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian, and Istro-Romanian. As a minority language it is spoken by stable communities in the countries surrounding Romania, and by the large Romanian diaspora. In total, it is spoken by 28–29 million people as an L1+L2 language, of whom c. 24 million are native speakers. In Europe, Romanian occupies the 10th position among 37 official languages.

Transylvania is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains and to the west the Apuseni Mountains. Broader definitions of Transylvania also include the western and northwestern Romanian regions of Crișana and Maramureș, and occasionally Banat. Historical Transylvania also includes small parts of neighbouring Western Moldavia and even a small part of south-western neighbouring Bukovina to its north east. The capital of the region is Cluj-Napoca.

The coat of arms of Romania was adopted in the Romanian Parliament on 10 September 1992 as a representative coat of arms for Romania. The current coat of arms is based on the lesser coat of arms of interwar Kingdom of Romania, which was designed in 1921 by the Transylvanian Hungarian heraldist József Sebestyén from Cluj, at the request of King Ferdinand I of Romania, it was redesigned by Victor Dima. As a central element, it shows a golden aquila holding a cross in its beak, and a mace and a sword in its claws. It also consists of the three colors which represent the colors of the national flag. The coat of arms was augmented on 11 July 2016 to add a representation of the Steel Crown of Romania.

The Transylvanian Saxons are a people of mainly German ethnicity and overall Germanic origin; mostly Luxembourgish and from the Low Countries initially during the medieval Ostsiedlung process, then also from other parts of present-day Germany who settled in Transylvania in various waves, starting from the mid and mid-late 12th century until the mid 19th century.
In the phonology of the Romanian language, the phoneme inventory consists of seven vowels, two or four semivowels, and twenty consonants. In addition, as with other languages, other phonemes can occur occasionally in interjections or recent borrowings.

The Germans of Romania represent one of the most significant historical ethnic minorities of Romania since the late modern period onwards.

The Vlach law refers to the traditional Romanian common law as well as to various special laws and privileges enjoyed or enforced upon particularly pastoralist communities of Romanian stock or origin in European states of the Late Middle Ages and Early modern period, including in the two Romanian polities of Moldavia and Wallachia, as well as in the Kingdom of Hungary, the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Serbia, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, etc.
The Early Modern Times in Romania started after the death of Michael the Brave, who ruled in a personal union, Wallachia, Transylvania, and Moldavia – three principalities in the lands that now form Romania – for three months, in 1600. The three principalities were subjected to the Ottoman Empire, and paid a yearly tribute to the Ottoman Sultans, but they preserved their internal autonomy. In contrast, Dobruja and the Banat were fully incorporated into the Ottoman Empire.

The Principality of Transylvania was a semi-independent state ruled primarily by Hungarian princes. Its territory, in addition to the traditional Transylvanian lands, also included the other major component called Partium, which was in some periods comparable in size with Transylvania proper. The establishment of the principality was connected to the Treaty of Speyer. However, Stephen Báthory's status as king of Poland also helped to phase in the name Principality of Transylvania. It was usually under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire, although the principality often had dual vassalage in the 16th and 17th centuries.
The Romanian dialects are the several regional varieties of the Romanian language (Daco-Romanian). The dialects are divided into two types, northern and southern, but further subdivisions are less clear, so the number of dialects varies between two and occasionally twenty. Most recent works seem to favor a number of three clear dialects, corresponding to the regions of Wallachia, Moldavia, and Banat, and an additional group of varieties covering the remainder of Transylvania, two of which are more clearly distinguished, in Crișana and Maramureș, that is, a total of five.
Editura Dacia is a publishing house based in Romania, located on Pavel Chinezul Street 2, Cluj-Napoca. Named after the ancient region of Dacia, it was founded in 1969 by a group of Transylvanian intellectuals, and printed works in Romanian, German and Hungarian.
The history of the Romanian language started in Roman provinces north of the Jireček Line in Classical antiquity. There are three main hypotheses around its exact territory: the autochthony thesis, the discontinuation thesis, and the "as-well-as" thesis that supports the language development on both sides of the Danube. Between the 6th and 8th centuries AD, following the accumulated tendencies inherited from the vernacular Latin and, to a much smaller degree, the influences from an unidentified substratum, and in the context of a lessened power of the Roman central authority, the language evolved into Common Romanian. This proto-language then came into close contact with the Slavic languages and subsequently divided into Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian, Istro-Romanian, and Romanian. Because of limited attestations between the 6th and 16th centuries, entire stages from its history are reconstructed by researchers, often with proposed relative chronologies and loose limits.
The Wallachian dialect is one of the several dialects of the Romanian language (Daco-Romanian). Its geographic distribution covers approximately the historical region of Wallachia, occupying the southern part of Romania, roughly between the Danube and the Southern Carpathians. Standard Romanian, in particular its phonology, is largely based on Wallachian.
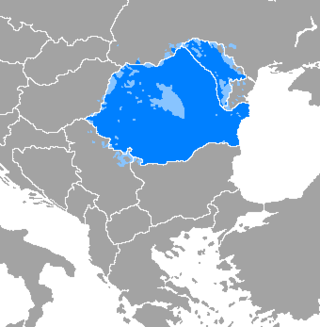
The Moldavian dialect is one of several dialects of the Romanian language (Daco-Romanian). It is spoken across the approximate area of the historical region of Moldavia, now split between the Republic of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine.
The Banat dialect is one of the dialects of the Romanian language (Daco-Romanian). Its geographic distribution extends over the Romanian Banat and parts of the Serbian Banat, but also in parts of the Timok Valley of Serbia.
The Crișana dialect is one of the dialects of the Romanian language (Daco-Romanian). Its geographic distribution covers approximately the historical region of Crișana, in western Transylvania.
The Maramureș dialect is one of the dialects of the Romanian language (Daco-Romanian). Its geographic distribution covers approximately the historical region of Maramureș, now split between Romania and Ukraine.
Giovenale Vegezzi Ruscalla, was a liberal Italian journalist, foreign honorary member of the Romanian Academy, and secretary to the Subalpine Agrarian Association. He traveled to Transylvania and Banat on a study trip in 1830 and was an honorary citizen as a Romanian diplomat. He translated poems of the Romanian poet and playwright Vasile Alecsandri and taught a history course and Romanian literature at the University of Turin. At the Congress of Paris 1856 Vegezzi Ruscalla successfully debated in favour of Romanian independence.

Hungarian has ten dialects. These are fully mutually intelligible, and do not differ significantly from standard Hungarian except for the Csángó dialect. They are mostly distinguished by pronunciation; although there are differences in vocabulary, these are usually small and do not hinder intelligibility. Due to increased internal migration and urbanization during the 20th century, most of the characteristics of the different dialects can only be observed in smaller towns and villages, and even there mostly among the elderly; the population of the larger cities and especially the capital has been mixed for generations and the dialectal differences have been lost. A notable exception is the Western Transdanubian pronunciation, which is distinctly noticeable even in Szombathely, the largest city in the region.

Moldavia, also called Romanian Moldavia, is the core historic and geographical part of the former Principality of Moldavia situated in eastern and north-eastern Romania. Until its union with Wallachia in 1859, the Principality of Moldavia also included, at various times in its history, the regions of Bessarabia, all of Bukovina, and Hertsa; the larger part of the former is nowadays the independent state of Moldova, while the rest of it, the northern part of Bukovina, and Hertsa form territories of Ukraine.
References
- ↑ Mozes Gaster, 1891
- ↑ Gustav Weigand, "Despre dialectele românești", in Convorbiri literare, XLII, 1908, 4, pp. 441–448, cited by Vasile Ursan
- ↑ Emil Petrovici, "Transilvania, vatră lingvistică a românismului nord-dunărean", in Transilvania, LXXII, 1941, 2, p. 103, cited by Vasile Ursan (in Romanian)