
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine.

Sodium hypochlorite, commonly known in a dilute solution as (chlorine) bleach, is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula NaOCl, consisting of a sodium cation and a hypochlorite anion. It may also be viewed as the sodium salt of hypochlorous acid. The anhydrous compound is unstable and may decompose explosively. It can be crystallized as a pentahydrate NaOCl·5H
2O, a pale greenish-yellow solid which is not explosive and is stable if kept refrigerated.

A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than sterilization, which is an extreme physical or chemical process that kills all types of life. Disinfectants are generally distinguished from other antimicrobial agents such as antibiotics, which destroy microorganisms within the body, and antiseptics, which destroy microorganisms on living tissue. Disinfectants are also different from biocides—the latter are intended to destroy all forms of life, not just microorganisms. Disinfectants work by destroying the cell wall of microbes or interfering with their metabolism. It is also a form of decontamination, and can be defined as the process whereby physical or chemical methods are used to reduce the amount of pathogenic microorganisms on a surface.

Hypochlorous acid is an acid that forms when chlorine dissolves in water, and itself partially dissociates, forming hypochlorite, ClO−. HClO and ClO− are oxidizers, and the primary disinfection agents of chlorine solutions. HClO cannot be isolated from these solutions due to rapid equilibration with its precursor, chlorine.

In organic chemistry, an acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.

In chemistry, hypochlorite, or chloroxide is an anion with the chemical formula ClO−. It combines with a number of cations to form hypochlorite salts. Common examples include sodium hypochlorite and calcium hypochlorite. The Cl-O distance in ClO− is 1.69 Å.

Nitrogen trichloride, also known as trichloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula NCl3. This yellow, oily, pungent-smelling and explosive liquid is most commonly encountered as a byproduct of chemical reactions between ammonia-derivatives and chlorine (for example, in swimming pools). Alongside monochloramine and dichloramine, trichloramine is responsible for the distinctive 'chlorine smell' associated with swimming pools, where the compound is readily formed as a product from hypochlorous acid reacting with ammonia and other nitrogenous substances in the water, such as urea from urine.
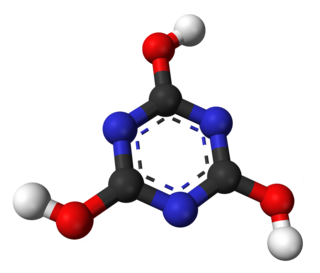
Cyanuric acid or 1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triol is a chemical compound with the formula (CNOH)3. Like many industrially useful chemicals, this triazine has many synonyms. This white, odorless solid finds use as a precursor or a component of bleaches, disinfectants, and herbicides. In 1997, worldwide production was 160 000 tonnes.

Sodium chlorite (NaClO2) is a chemical compound used in the manufacturing of paper and as a disinfectant.

Cyanuric chloride is an organic compound with the formula (NCCl)3. This white solid is the chlorinated derivative of 1,3,5-triazine. It is the trimer of cyanogen chloride. Cyanuric chloride is the main precursor to the popular but controversial herbicide atrazine.
Calcium hypochlorite is an inorganic compound with formula Ca(ClO)2. It is a white solid, although commercial samples appear yellow. It strongly smells of chlorine, owing to its slow decomposition in moist air. This compound is relatively stable as a solid and solution and has greater available chlorine than sodium hypochlorite. "Pure" samples have 99.2% active chlorine. Given common industrial purity, an active chlorine content of 65-70% is typical. It is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, used for water treatment and as a bleaching agent.
1,3,5-Triazine, also called s-triazine, is an organic chemical compound with the formula (HCN)3. It is a six-membered heterocyclic aromatic ring, one of several isomeric triazines. S-triazine—the "symmetric" isomer—and its derivatives are useful in a variety of applications.
Benzyl chloride, or α-chlorotoluene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2Cl. This colorless liquid is a reactive organochlorine compound that is a widely used chemical building block.

Sodium dichloroisocyanurate is a chemical compound widely used as a cleansing agent and disinfectant. It is a colorless, water-soluble solid, produced as a result of reaction of cyanuric acid with chlorine. The dihydrate is also known as is the potassium salt.
Monochloramine, often called chloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula NH2Cl. Together with dichloramine (NHCl2) and nitrogen trichloride (NCl3), it is one of the three chloramines of ammonia. It is a colorless liquid at its melting point of −66 °C (−87 °F), but it is usually handled as a dilute aqueous solution, in which form it is sometimes used as a disinfectant. Chloramine is too unstable to have its boiling point measured.

Rongalite is a chemical compound with the molecular formula Na+HOCH2SO2−. This salt has many additional names, including Rongalit, sodium hydroxymethylsulfinate, sodium formaldehyde sulfoxylate, and Bruggolite. It is listed in the European Cosmetics Directive as sodium oxymethylene sulfoxylate (INCI). It is water-soluble and generally sold as the dihydrate. The compound and its derivatives are widely used in the dye industry. The structure of this salt has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography.
Chloramines refer to derivatives of ammonia and organic amines wherein one or more N−H bonds have been replaced by N−Cl bonds. Two classes of compounds are considered: inorganic chloramines and organic chloramines.
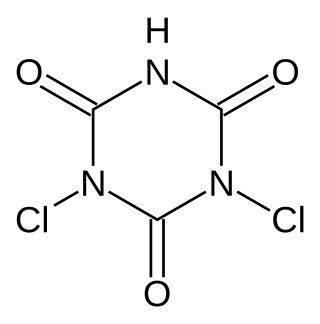
Dichloroisocyanuric acid, also known as dichlor or dichloro-s-triazinetrione and is marketed under many names (e.g. troclosene), is a chemical compound with the formula (C(O)NCl)2(C(O)NH).

Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove colour (whitening) from fabric or fiber or to clean or to remove stains in a process called bleaching. It often refers specifically to a dilute solution of sodium hypochlorite, also called "liquid bleach".

Chlorine-releasing compounds, also known as chlorine base compounds, is jargon to describe certain chlorine-containing substances that are used as disinfectants and bleaches. They include the following chemicals: sodium hypochlorite, chloramine, halazone, and sodium dichloroisocyanurate. They are widely used to disinfect water and medical equipment, and surface areas as well as bleaching materials such as cloth. The presence of organic matter can make them less effective as disinfectants. They come as a liquid solution, or as a powder that is mixed with water before use.



















