
A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that includes the Linux kernel and often a package management system. They are often obtained from the website of each distribution, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to servers and powerful supercomputers.
Darwin is the core Unix-like operating system of macOS, iOS, watchOS, tvOS, iPadOS, visionOS, and bridgeOS. It previously existed as an independent open-source operating system, first released by Apple Inc. in 2000. It is composed of code derived from NeXTSTEP, FreeBSD, other BSD operating systems, Mach, and other free software projects' code, as well as code developed by Apple.
Cray Inc., a subsidiary of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, is an American supercomputer manufacturer headquartered in Seattle, Washington. It also manufactures systems for data storage and analytics. Several Cray supercomputer systems are listed in the TOP500, which ranks the most powerful supercomputers in the world.
This article presents a timeline of events in the history of computer operating systems from 1951 to the current day. For a narrative explaining the overall developments, see the History of operating systems.
OSF/1 is a variant of the Unix operating system developed by the Open Software Foundation during the late 1980s and early 1990s. OSF/1 is one of the first operating systems to have used the Mach kernel developed at Carnegie Mellon University, and is probably best known as the native Unix operating system for DEC Alpha architecture systems.

The Cray X-MP was a supercomputer designed, built and sold by Cray Research. It was announced in 1982 as the "cleaned up" successor to the 1975 Cray-1, and was the world's fastest computer from 1983 to 1985 with a quad-processor system performance of 800 MFLOPS. The principal designer was Steve Chen.
MkLinux is an open-source software computer operating system begun by the Open Software Foundation Research Institute and Apple Computer in February 1996, to port Linux to the PowerPC platform, and Macintosh computers. The name refers to the Linux kernel being adapted to run as a server hosted on the Mach microkernel, version 3.0.
The T3D was Cray Research's first attempt at a massively parallel supercomputer architecture. Launched in 1993, it also marked Cray's first use of another company's microprocessor. The T3D consisted of between 32 and 2048 Processing Elements (PEs), each comprising a 150 MHz DEC Alpha 21064 (EV4) microprocessor and either 16 or 64 MB of DRAM. PEs were grouped in pairs, or nodes, which incorporated a 6-way processor interconnect switch. These switches had a peak bandwidth of 300 MB/second in each direction and were connected to form a three-dimensional torus network topology.
The Cray Time Sharing System, also known in the Cray user community as CTSS, was developed as an operating system for the Cray-1 or Cray X-MP line of supercomputers in 1978. CTSS was developed by the Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory in conjunction with the Lawrence Livermore Laboratory. CTSS was popular with Cray sites in the United States Department of Energy (DOE), but was used by several other Cray sites, such as the San Diego Supercomputing Center.

Linux is both an open-source Unix-like kernel and a generic name for a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses and recommends the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the use and importance of GNU software in many distributions, causing some controversy.
The Cray SV1 is a vector processor supercomputer from the Cray Research division of Silicon Graphics introduced in 1998. The SV1 has since been succeeded by the Cray X1 and X1E vector supercomputers. Like its predecessor, the Cray J90, the SV1 used CMOS processors, which lowered the cost of the system, and allowed the computer to be air-cooled. The SV1 was backwards compatible with J90 and Y-MP software, and ran the same UNIX-derived UNICOS operating system. The SV1 used Cray floating point representation, not the IEEE 754 floating point format used on the Cray T3E and some Cray T90 systems.

The Cray XT3 is a distributed memory massively parallel MIMD supercomputer designed by Cray Inc. with Sandia National Laboratories under the codename Red Storm. Cray turned the design into a commercial product in 2004. The XT3 derives much of its architecture from the previous Cray T3E system, and also from the Intel ASCI Red supercomputer.

The Cray XT4 is an updated version of the Cray XT3 supercomputer. It was released on November 18, 2006. It includes an updated version of the SeaStar interconnect router called SeaStar2, processor sockets for Socket AM2 Opteron processors, and 240-pin unbuffered DDR2 memory. The XT4 also includes support for FPGA coprocessors that plug into riser cards in the Service and IO blades. The interconnect, cabinet, system software and programming environment remain unchanged from the Cray XT3. It was superseded in 2007 by the Cray XT5.

Cray XMT is a scalable multithreaded shared memory supercomputer architecture by Cray, based on the third generation of the Tera MTA architecture, targeted at large graph problems. Presented in 2005, it supersedes the earlier unsuccessful Cray MTA-2. It uses the Threadstorm3 CPUs inside Cray XT3 blades. Designed to make use of commodity parts and existing subsystems for other commercial systems, it alleviated the shortcomings of Cray MTA-2's high cost of fully custom manufacture and support. It brought various substantial improvements over Cray MTA-2, most notably nearly tripling the peak performance, and vastly increased maximum CPU count to 8,192 and maximum memory to 128 TB, with a data TLB of maximal 512 TB.

The Cray XT5 is an updated version of the Cray XT4 supercomputer, launched on November 6, 2007. It includes a faster version of the XT4's SeaStar2 interconnect router called SeaStar2+, and can be configured either with XT4 compute blades, which have four dual-core AMD Opteron processor sockets, or XT5 blades, with eight sockets supporting dual or quad-core Opterons. The XT5 uses a 3-dimensional torus network topology.
The Cray CX1 is a deskside workstation designed by Cray Inc., based on the x86-64 processor architecture. It was launched on September 16, 2008, and was discontinued in early 2012. It comprises a single chassis blade server design that supports a maximum of eight modular single-width blades, giving up to 96 processor cores. Computational load can be run independently on each blade and/or combined using clustering techniques.
Compute Node Linux (CNL) is a runtime environment based on the Linux kernel for the Cray XT3, Cray XT4, Cray XT5, Cray XT6, Cray XE6 and Cray XK6 supercomputer systems based on SUSE Linux Enterprise Server. CNL forms part of the Cray Linux Environment. As of November 2011 systems running CNL were ranked 3rd, 6th and 8th among the fastest supercomputers in the world.
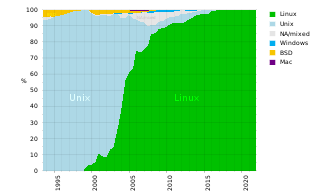
A supercomputer operating system is an operating system intended for supercomputers. Since the end of the 20th century, supercomputer operating systems have undergone major transformations, as fundamental changes have occurred in supercomputer architecture. While early operating systems were custom tailored to each supercomputer to gain speed, the trend has been moving away from in-house operating systems and toward some form of Linux, with it running all the supercomputers on the TOP500 list in November 2017. In 2021, top 10 computers run for instance Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), or some variant of it or other Linux distribution e.g. Ubuntu.
SHMEM is a family of parallel programming libraries, providing one-sided, RDMA, parallel-processing interfaces for low-latency distributed-memory supercomputers. The SHMEM acronym was subsequently reverse engineered to mean "Symmetric Hierarchical MEMory”. Later it was expanded to distributed memory parallel computer clusters, and is used as parallel programming interface or as low-level interface to build partitioned global address space (PGAS) systems and languages. “Libsma”, the first SHMEM library, was created by Richard Smith at Cray Research in 1993 as a set of thin interfaces to access the CRAY T3D's inter-processor-communication hardware. SHMEM has been implemented by Cray Research, SGI, Cray Inc., Quadrics, HP, GSHMEM, IBM, QLogic, Mellanox, Universities of Houston and Florida; there is also open-source OpenSHMEM.







