
The United States Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit is a federal court located in Richmond, Virginia, with appellate jurisdiction over the district courts in the following districts:

The United States District Court for the Eastern District of Pennsylvania is one of the original 13 federal judiciary districts created by the Judiciary Act of 1789. It originally sat in Independence Hall in Philadelphia as the United States District Court for the District of Pennsylvania, and is now located at the James Byrne Courthouse at 601 Market Street in Philadelphia. There are five Eastern District federal courtrooms in Pennsylvania: Philadelphia, Lancaster, Allentown, Reading, and Easton.

The United States District Court for the Northern District of California is the federal United States district court whose jurisdiction comprises the following counties of California: Alameda, Contra Costa, Del Norte, Humboldt, Lake, Marin, Mendocino, Monterey, Napa, San Benito, San Francisco, San Mateo, Santa Clara, Santa Cruz, and Sonoma. The court hears cases in its courtrooms in Eureka, Oakland, San Francisco, and San Jose. It is headquartered in San Francisco.

The United States District Court for the Northern District of Illinois is the federal trial-level court with jurisdiction over the northern counties of Illinois.

The United States District Court for the District of South Carolina is the federal district court whose jurisdiction is the state of South Carolina. Court is held in the cities of Aiken, Anderson, Beaufort, Charleston, Columbia, Florence, Greenville, and Spartanburg.

The United States District Court for the District of Rhode Island is the federal district court whose jurisdiction is the state of Rhode Island. The District Court was created in 1790 when Rhode Island ratified the Constitution. The Federal Courthouse was built in 1908.

The United States District Court for the Western District of Virginia is a United States district court.

The United States District Court for the Eastern District of North Carolina is the United States district court that serves the eastern 44 counties in North Carolina. Appeals from the Eastern District of North Carolina are taken to the United States Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit.

The United States District Court for the Western District of North Carolina is a federal district court which covers the western third of North Carolina.

The United States District Court for the Southern District of Ohio is one of two United States district courts in Ohio and includes forty-eight of the state's eighty-eight counties—everything from the Columbus area southward. Appeals from the court are taken to the United States Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit at Cincinnati.

The United States District Court for the Eastern District of Michigan is the federal district court with jurisdiction over of the eastern half of the Lower Peninsula of the State of Michigan. The Court is based in Detroit, with courthouses also located in Ann Arbor, Bay City, Flint, and Port Huron. The United States Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit has appellate jurisdiction over the court.
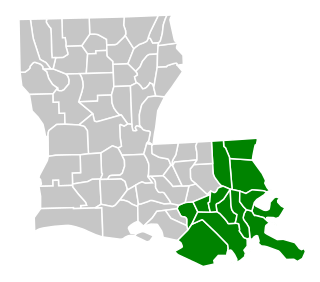
The United States District Court for the Eastern District of Louisiana is a United States federal court based in New Orleans.
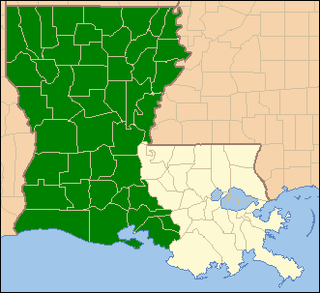
The United States District Court for the Western District of Louisiana is a United States federal court with jurisdiction over approximately two thirds of the state of Louisiana, with courts in Alexandria, Lafayette, Lake Charles, Monroe, and Shreveport. These cities comprise the Western District of Louisiana.

The United States District Court for the Eastern District of Tennessee is the federal court in the Sixth Circuit whose jurisdiction covers most of East Tennessee and a portion of Middle Tennessee. The court has jurisdiction over 41 counties with 4 divisions. Based in Knoxville, Tennessee, it maintains branch facilities in Chattanooga, Tennessee; Greeneville, Tennessee; and Winchester, Tennessee.

Henry Potter was the longest-serving United States federal judge to sit on a single court and the longest-serving judge in active service. Potter served as a United States circuit judge of the United States Circuit Court for the Fifth Circuit and as a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the Albemarle, Cape Fear and Pamptico Districts of North Carolina.

George Washington Brooks was a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the Albemarle, Cape Fear and Pamptico Districts of North Carolina and the United States District Court for the Eastern District of North Carolina.
Robert Paine Dick was a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the Western District of North Carolina.

John Sitgreaves was a delegate to the Congress of the Confederation, a United States Attorney for the District of North Carolina and a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the District of North Carolina, the United States District Court for the Edenton, New Bern & Wilmington Districts of North Carolina and the United States District Court for the Albemarle, Cape Fear & Pamptico Districts of North Carolina.


















