
Rhineland-Palatinate is a western state of Germany. It covers 19,846 km2 (7,663 sq mi) and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the sixteen states. Mainz is the capital and largest city. Other cities are Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Koblenz, Trier, Kaiserslautern, Worms and Neuwied. It is bordered by North Rhine-Westphalia, Saarland, Baden-Württemberg and Hesse and by the countries France, Luxembourg and Belgium.

Hoppstädten-Weiersbach is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Birkenfeld, whose seat is in the like-named town.

Mörschied is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Herrstein-Rhaunen, whose seat is in Herrstein.
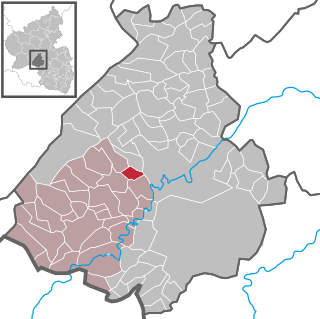
Rötsweiler-Nockenthal is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Birkenfeld, whose seat is in the like-named town.
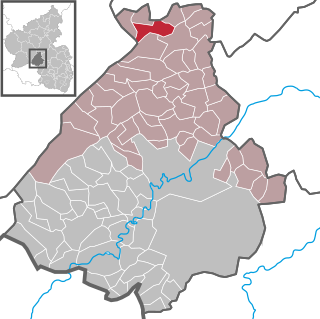
Weitersbach is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Herrstein-Rhaunen, whose seat is in Herrstein.
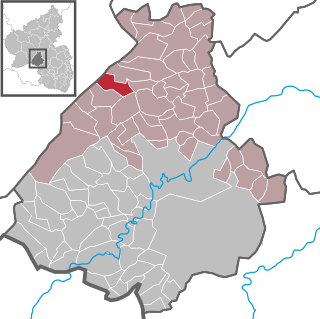
Schauren is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Herrstein-Rhaunen, whose seat is in Herrstein.
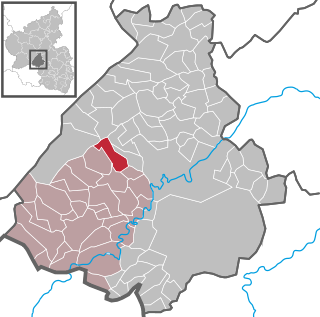
Siesbach is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Birkenfeld, whose seat is in the like-named town.

The Mannheim–Saarbrücken railway is a railway in the German states of Baden-Württemberg, Rhineland-Palatinate and the Saarland that runs through Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Neustadt an der Weinstraße, Kaiserslautern, Homburg and St. Ingbert. It is the most important railway line that runs through the Palatinate. It serves both passenger and freight transport and carries international traffic.
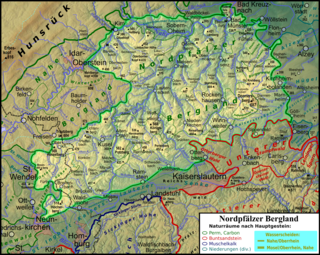
The North Palatine Uplands, sometimes shortened to Palatine Uplands, is a low mountain range and landscape unit in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate and belongs mainly to the Palatinate region. It is part of the Saar-Nahe Uplands.

Worms Hauptbahnhof is, along with Worms Pfeddersheim station, one of two operational passenger stations in the Rhenish Hesse city of Worms, Germany. The station with its pedestrian underpass is also an essential link between the eastern and the western parts of central Worms. Every day it is used by about 15,000 people.

The Nahe Valley Railway is a two-track, partially electrified main line railway in the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland, which runs for almost 100 kilometres along the Nahe. It was built by the Rhine-Nahe Railway Company and connects Bingen am Rhein on the Left Rhine line with Saarbrücken. It was opened between 1858 and 1860 and is one of the oldest railways in Germany. The section south of Bad Kreuznach is part of the regionally important transport corridor between the two major cities of Mainz and Saarbrücken.

Neustadt (Weinstr) Hauptbahnhof – called Neustadt a/d. Haardt until 1935 and from 1945 until 1950 – is the central station of in the city of Neustadt in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. In addition to the Hauptbahnhof, Rhine-Neckar S-Bahn services stop at Neustadt (Weinstr) Böbig halt (Haltepunkt). Mußbach station and Neustadt (Weinstr) halt, opened on 19 November 2013, are also located in Neustadt.
The Heimbach (Nahe)–Baumholder Railway was opened in 1912. It was formerly used exclusively for freight and military transport, but passenger services were reactivated in February 2015. It links to the Nahe Valley Railway west of Heimbach (Nahe).

Bad Münster am Stein station is a station at a railway junction in Bad Münster am Stein-Ebernburg, a district of Bad Kreuznach in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. The station building, dating from about 1910, is protected as a monument. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 4 station. The station is located in the network of the Rhein-Nahe-Nahverkehrsverbund and belongs to fare zone 401. Its address is: Berliner Straße 20.
The Saar-Nahe Hills or Saar-Nahe Uplands is a major natural region in the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and the Saarland. The region of hills and mountains covers an area of 4,185 km² running from Saarbrücken, Kaiserslautern and the Palatine Forest in the south to the Hunsrück in the northeast. It contains the catchment area of the Nahe as far as Bad Kreuznach as well as small sections of the Middle Saar in the west.

Alzey station is, along with the stations Alzey Süd and Alzey West, one of three stations in the urban area of the Rhenish Hesse town of Alzey in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 3 station.
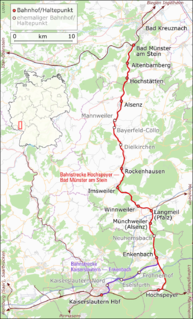
The Alsenz Valley Railway is a line that runs from Hochspeyer via Winnweiler and Alsenz to Bad Munster am Stein in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. The line closely follows the Alsenz river from the Enkenbach district and crosses it several times. It was originally built primarily as a long-distance route, but it has lost this function since 1990 and is now exclusively used for local transport.

Staudernheim station is a through station, located 35.3 km from Bingen on the Nahe Valley Railway (Bingen–Saarbrücken), in Staudernheim in the district of Bad Kreuznach in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. It was opened with this line on 15 December 1859 and was the first and only station in the Meisenheim exclave of the Landgraviate of Hesse-Homburg, which was absorbed by Prussia in 1866. The station is located in the network area of the Rhein-Nahe-Nahverkehrsverbund and it is in fare zone 420. Its address is Bahnhofstraße 1.

Vectus Verkehrsgesellschaft mbH was a German transport company based in Limburg an der Lahn. In 2004, it took over the operation of a regional rail network located in the Lahn valley, the Westerwald and the Taunus, which is called the Westerwald-Taunus network. The operations of the network focused on Limburg. In 2014, the contract for these services were awarded to its main shareholder, Hessische Landesbahn (HLB) and Vectus Verkehrsgesellschaft was subsequently taken over by HLB.

Neubrücke (Nahe) station is a station in the town of Neubrücke (Nahe) in the municipality of Hoppstädten-Weiersbach in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. It is on the Nahe Valley Railway (Nahetalbahn) and was the terminus of the Birkenfeld District Railway to the district seat of Birkenfeld from 1880 to 1991. It was opened with the extension of the Nahe Valley Railway from Idar-Oberstein to Neunkirchen (Saar) on 26 May 1860.
























