| Part of a series on |
| Islam |
|---|
 |
Wetu Telu ("three times") is a sect of Islamic beliefs of the Sasak people of Lombok, Indonesia. it differs from orthodox Sunni Islam in that practitioners pray three times a day, rather than five. [1]
| Part of a series on |
| Islam |
|---|
 |
Wetu Telu ("three times") is a sect of Islamic beliefs of the Sasak people of Lombok, Indonesia. it differs from orthodox Sunni Islam in that practitioners pray three times a day, rather than five. [1]

Lombok is an island in West Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia. It forms part of the chain of the Lesser Sunda Islands, with the Lombok Strait separating it from Bali to the west and the Alas Strait between it and Sumbawa to the east. It is roughly circular, with a "tail" to the southwest, about 70 kilometres across and a total area of about 4,738.65 square kilometres. The provincial capital and largest city on the island is Mataram.

The Sasak people live mainly on the island of Lombok, Indonesia, numbering around 3.6 million. They are related to the Balinese in language and ancestry, although the Sasak are predominantly Muslim while the Balinese are predominantly Hindu. Sasak people who practice pre-Islamic beliefs are also known as Sasak Boda in reference to the name of the Sasak people's original religion, Bodha.

Joglo is a type of traditional vernacular house of the Javanese people. The word joglo refers to the shape of the roof. In the highly hierarchical Javanese culture, the type of the roof of a house reflects the social and economic status of the owners of the house; joglo houses is traditionally associated with Javanese aristocrats.

Baiturrahman Grand Mosque is a Mosque located in the center of Banda Aceh city, Aceh Province, Indonesia. The Baiturrahman Grand Mosque is a symbol of religion, culture, spirit, strength, struggle and nationalism of the Acehnese people. The mosque is a landmark of Banda Aceh and has survived the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami.
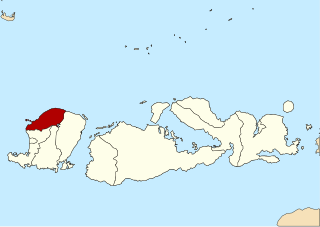
North Lombok Regency is a regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Lombok and the capital is Tanjung situated on the north coast of the island. The regency covers an area of 809.53 km2 and had a population of 199,904 at the 2010 Census and 247,400 at the 2020 Census.

A landhuis is a Dutch colonial country house, often the administrative heart of a particuliere land or private domain in the Dutch East Indies, now Indonesia. Many country houses were built by the Dutch in other colonial settlements, such as Galle, Cape Town and Curaçao, but none as extensively or elaborately as in the Residency of Batavia. Much of Batavia's reputation as "Queen of the East" rested on the grandeur of these 18th-century mansions.
Belanting is a village in northeastern Lombok, Indonesia. It lies along the main road around the island, southeast of Obel Obel and northwest of Sambelia. It belongs administratively to the kecamatan of Sambelia in East Lombok Regency, West Nusa Tenggara. As of 2010, the village had a population of 6610 people. The islands of Sulat Island and Lawang Island of the Sungian Strait just off the coast can be viewed from the village.

Javanese traditional house refers to the traditional vernacular houses of Javanese people in the island of Java, Indonesia.

Balinese traditional house refers to the traditional vernacular house of Balinese people in Bali, Indonesia. The Balinese traditional house follows a strict ancient of bali architectural guide which is a product of a blend of Hindu and Buddhist beliefs, fused with Austronesian animism, resulting in a house that is "in harmony" with the law of the cosmos of Balinese Hinduism.

Rangkiang is a granary or rice barn of the Minangkabau people used to keep rice. The rangkiang is a distinctive feature of Minangkabau architecture. The structure is traditionally found in the courtyard of a rumah gadang, the traditional house of Minangkabau people.

The Sumbanese traditional house refers to the traditional vernacular house of the Sumba people from the island of Sumba, Lesser Sunda Islands, Indonesia. Sumbanese house is characterized with its high-pitched central peak in its roof and strong connection with the spirits or marapu.

The Great Mosque of Surakarta is an 18th-century Javanese mosque in Surakarta, Central Java, Indonesia. It is the royal mosque of the Surakarta Sunanate.

Great Mosque of Banten is a historic mosque in Old Banten, 10 km north of Serang, Indonesia. The 16th-century mosque was one of the few surviving remnants of what used to be the port city of Banten, the most prosperous trading center in the Indonesian archipelago after the fall of Demak Sultanate in mid-16th century.

The National Archives Building is the building of the Government Museum in Jakarta, Indonesia. The building, formerly a late 18th-century private residence of Governor-General Reinier de Klerk, is part of the cultural heritage of Jakarta. The house is an archetypal Indies-Style house of the earliest period.

Paduraksa, also known as kori is a type of gateway covered with towering roof that can be found in the island of Java and Bali, Indonesia. This architectural feature is commonly found in buildings from the classical Hindu-Buddhist period of Indonesia. Paduraksa marks the threshold into the most sacred space within a religious compound, a cemetery, or a palace. In Balinese architecture, an elaborately decorated towering paduraksa is often built as the temple's most imposing structure.

Sandung or sandong is the ossuary of the Katingan, Ngaju and Pesaguan people native to the southern and central Kalimantan in Indonesia. The sandung is an integral part of the Tiwah ceremony of the Ngaju people, which is basically a secondary burial ritual where the bones of the deceased are taken from the cemeteries, purified and finally placed in a sandung.

A jambur is a structure that is used as a multipurpose hall by the Karo people of North Sumatra, Indonesia. The traditional jambur is a large pavilion-like structure, raised above ground, wall-less, and placed under a large Karo traditional house roof style. Karo ritual ceremonies e.g. wedding feast, funeral, or general feasts are held within the jambur. Jambur can still be found in big cities of North Sumatra, e.g. Medan, Kabanjahe, Berastagi, as well as small villages in the Karo lands.

Saka guru, or soko guru in Javanese, is the four main posts which supported certain Javanese buildings, e.g. the pendopo, the house proper and the mosque. The saka guru is the most fundamental element in Javanese architecture because it supports the entire roof of the building. Because of its importance, the saka guru is imbued with symbolism and treated with certain rituals.

Mosque architecture in Indonesia refers to the architectural traditions of mosques built in the archipelago of Indonesia. Initial forms of the mosque, for example, were predominantly built in the vernacular Indonesian architectural style mixed with Hindu, Buddhist or Chinese architectural elements, and notably didn't equip orthodox form of Islamic architectural elements such as dome and minaret. Vernacular architectural style varies depending on the island and region.

Pura Lingsar was built by Anak Agung Ngurah in 1714, located 15 km from Mataram. Lingsar origin from sasak language mean clear revelation from God, the area has a spring, which scared by Sasak people, who belief Wetu Telu.