
SKF-82,958 is a synthetic compound of the benzazepine class that acts as a D1/D5 receptor full agonist. SKF-82,958 and similar D1-like-selective full agonists like SKF-81,297 and 6-Br-APB produce characteristic anorectic effects, hyperactivity and self-administration in animals, with a similar but not identical profile to that of dopaminergic stimulants such as amphetamine. SKF-82,958 was also subsequently found to act as an agonist of ERα with negligible activity at ERβ, making it a subtype-selective estrogen.

SB-277,011A is a drug which acts as a potent and selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, which is around 80–100 times selective for D3 over D2, and lacks any partial agonist activity.

The serotonin 1A receptor is a subtype of serotonin receptors, or 5-HT receptors, that binds serotonin, also known as 5-HT, a neurotransmitter. 5-HT1A is expressed in the brain, spleen, and neonatal kidney. It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), coupled to the Gi protein, and its activation in the brain mediates hyperpolarization and reduction of firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron. In humans, the serotonin 1A receptor is encoded by the HTR1A gene.

8-OH-DPAT is a research chemical of the aminotetralin chemical class which was developed in the 1980s and has been widely used to study the function of the 5-HT1A receptor. It was one of the first major 5-HT1A receptor full agonists to have been discovered.

Dopamine receptor D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD3 gene.

WAY-100635 is a piperazine drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It was originally believed to act as a selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, but subsequent research showed that it also acts as potent full agonist at the D4 receptor. It is sometimes referred to as a silent antagonist at the former receptor. It is closely related to WAY-100135.

UH-232 ((+)-UH232) is a drug which acts as a subtype selective mixed agonist-antagonist for dopamine receptors, acting as a weak partial agonist at the D3 subtype, and an antagonist at D2Sh autoreceptors on dopaminergic nerve terminals. It causes dopamine release in the brain and has a stimulant effect, as well as blocking the behavioural effects of cocaine. It may also serve as a 5-HT2A receptor agonist, based on animal studies. It was investigated in clinical trials for the treatment of schizophrenia, but unexpectedly caused symptoms to become worse.
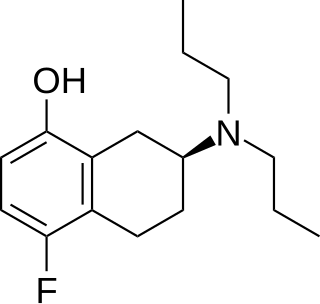
(S)-UH-301 is a drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It acts as a selective 5-HT1A receptor silent antagonist. It is structurally related to 8-OH-DPAT. UH-301 was found to produce a head-twitch response in mice which is usually typical of 5-HT2A agonist drugs, and has subsequently been used to investigate how 5-HT1A receptor activity modulates 5-HT2A receptors downstream.

6-Br-APB is a synthetic compound that acts as a selective D1 agonist, with the (R)-enantiomer being a potent full agonist, while the (S) enantiomer retains its D1 selectivity but is a weak partial agonist. (R)-6-Br-APB and similar D1-selective full agonists like SKF-81,297 and SKF-82,958 produce characteristic anorectic effects, stereotyped behaviour and self-administration in animals, with a similar but not identical profile to that of dopaminergic stimulants such as amphetamine.
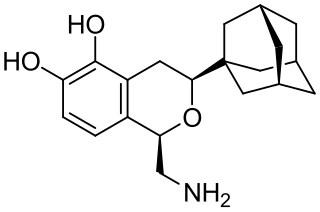
A-77636 is a synthetic drug which acts as a selective D1 receptor full agonist. It has nootropic, anorectic, rewarding and antiparkinsonian effects in animal studies, but its high potency and long duration of action causes D1 receptor downregulation and tachyphylaxis, and unlike other D1 full agonists such as SKF-82,958, it does not produce place preference in animals. A-77636 partially substituted for cocaine in animal studies, and has been suggested for use as a possible substitute drug in treating addiction, but it is better known for its use in studying the role of D1 receptors in the brain.

SKF-81,297 is a synthetic drug of the benzazepine chemical class that acts as a selective dopamine D1/D5 receptor full agonist, and produces a characteristic stimulant-like pattern of anorexia, hyperactivity and self-administration in animals. This profile is shared with several related drugs such as 6-Br-APB and SKF-82,958, but not with certain other D1 full agonists such as A-77,636, reflecting functional selectivity of D1 activation. Newer findings reveal that SKF-81,297 additionally acts as a partial agonist at D1-D2 receptor heteromers.

A-86929 is a synthetic compound that acts as a selective dopamine receptor D1 agonist. It was developed as a possible treatment for Parkinson's disease, as well as for other applications such as treatment of cocaine addiction, but while it had reasonable efficacy in humans it also caused dyskinesias and has not been continued. It has mainly been used as its diacetate ester prodrug adrogolide (ABT-431), which has better bioavailability.

PD-128,907 is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the dopamine D2 and D3 receptors. It is used for studying the role of these receptors in the brain, in roles such as inhibitory autoreceptors that act to limit further dopamine release, as well as release of other neurotransmitters. In animal studies, it has been shown to reduce toxicity from cocaine overdose.
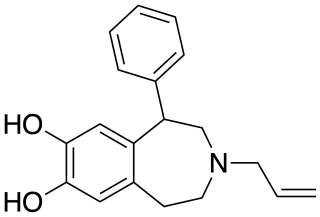
SKF-77,434 is a drug which acts as a selective dopamine D1 receptor partial agonist, and has stimulant and anorectic effects. Unlike other D1 agonists with higher efficacy such as SKF-81,297 and 6-Br-APB, SKF-77,434 does not maintain self-administration in animal studies, and so has been researched as a potential treatment for cocaine addiction.
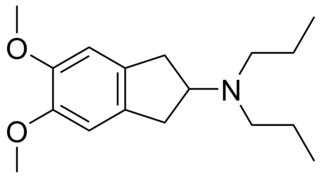
PNU-99,194(A) (or U-99,194(A)) is a drug which acts as a moderately selective D3 receptor antagonist with ~15-30-fold preference for D3 over the D2 subtype. Though it has substantially greater preference for D3 over D2, the latter receptor does still play some role in its effects, as evidenced by the fact that PNU-99,194 weakly stimulates both prolactin secretion and striatal dopamine synthesis, actions it does not share with the more selective (100-fold) D3 receptor antagonists S-14,297 and GR-103,691.

BP-897 is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a potent selective dopamine D3 receptor partial agonist with an in vitro intrinsic activity of ~0.6 and ~70x greater affinity for D3 over D2 receptors and is suspected to have partial agonist or antagonist activity in vivo. It has mainly been used in the study of treatments for cocaine addiction. A study comparing BP-897 with the potent, antagonistic, and highly D3 selective SB-277,011-A found, "SB 277011-A (1–10 mg/kg) was able to block cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking, indicating that DRD3 selective antagonism may be an effective approach to prevent relapse for nicotine. In contrast, BP 897 did not block the cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking or nicotine-taking under the FR5 schedule."
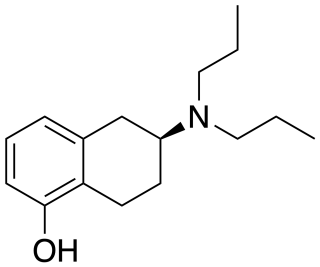
5-OH-DPAT is a synthetic compound that acts as a dopamine receptor agonist with selectivity for the D2 receptor and D3 receptor subtypes. Only the (S)-enantiomer is active as an agonist, with the (R)-enantiomer being a weak antagonist at D2 receptors. Radiolabelled 11C-5-OH-DPAT is used as an agonist radioligand for mapping the distribution and function of D2 and D3 receptors in the brain, and the drug is also being studied in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.

L-741,626 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the dopamine receptor D2. It has good selectivity over the related D3 and D4 subtypes and other receptors. L-741,626 is used for laboratory research into brain function and has proved particularly useful for distinguishing D2 mediated responses from those produced by the closely related D3 subtype, and for studying the roles of these subtypes in the action of cocaine and amphetamines in the brain.

PF-592,379 is a drug developed by Pfizer which acts as a potent, selective and orally active agonist for the dopamine D3 receptor, which was under development as a potential medication for the treatment of female sexual dysfunction and male erectile dysfunction. Unlike some other less selective D3 agonists, a research study showed that PF-592,379 has little abuse potential in animal studies, and so was selected for further development and potentially human clinical trials. Development has since been discontinued.

5-Chloro-α-methyltryptamine (5-Chloro-αMT), also known as PAL-542, is a tryptamine derivative related to α-methyltryptamine (αMT) and one of only a few known specific serotonin-dopamine releasing agents (SDRAs). It has been investigated in animals as a potential treatment for cocaine dependence. The EC50 values of 5-chloro-αMT in evoking the in vitro release of serotonin (5-HT), dopamine (DA), and norepinephrine (NE) in rat synaptosomes were reported as 16 nM, 54 nM, and 3434 nM, with an NE/DA ratio of 63.6 and a DA/5-HT ratio of 3.38, indicating that it is a highly specific and well-balanced SDRA. However, 5-chloro-αMT has also been found to act as a potent full agonist of the 5-HT2A receptor, with an EC50 value of 6.27 nM and an efficacy of 105%. It is likely to act as a potent agonist of other serotonin receptors as well.




















