Related Research Articles
In linguistics, morphology is the study of words, including the principles by which they are formed, and how they relate to one another within a language. Most approaches to morphology investigate the structure of words in terms of morphemes, which are the smallest units in a language with some independent meaning. Morphemes include roots that can exist as words by themselves, but also categories such as affixes that can only appear as part of a larger word. For example, in English the root catch and the suffix -ing are both morphemes; catch may appear as its own word, or it may be combined with -ing to form the new word catching. Morphology also analyzes how words behave as parts of speech, and how they may be inflected to express grammatical categories including number, tense, and aspect. Concepts such as productivity are concerned with how speakers create words in specific contexts, which evolves over the history of a language.
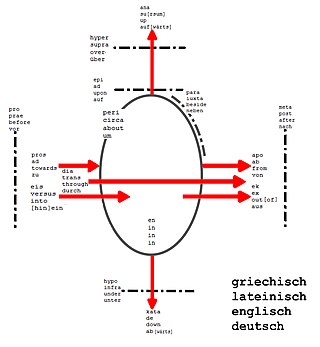
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the word to which it is affixed.
Morphological derivation, in linguistics, is the process of forming a new word from an existing word, often by adding a prefix or suffix, such as un- or -ness. For example, unhappy and happiness derive from the root word happy.

Crow is a Missouri Valley Siouan language spoken primarily by the Crow Nation in present-day southeastern Montana. The word Apsáalooke translates to "Children of the Large Beaked Bird", which was later incorrectly translated into English as 'Crow'. It is one of the larger populations of American Indian languages with 4,160 speakers according to the 2015 US Census.
In linguistics, a word stem is a part of a word responsible for its lexical meaning. Typically, a stem remains unmodified during inflection with few exceptions due to apophony

A word is a basic element of language that carries meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consensus among linguists on its definition and numerous attempts to find specific criteria of the concept remain controversial. Different standards have been proposed, depending on the theoretical background and descriptive context; these do not converge on a single definition. Some specific definitions of the term "word" are employed to convey its different meanings at different levels of description, for example based on phonological, grammatical or orthographic basis. Others suggest that the concept is simply a convention used in everyday situations.
Syntax is concerned with the way sentences are constructed from smaller parts, such as words and phrases. Two steps can be distinguished in the study of syntax. The first step is to identify different types of units in the stream of speech and writing. In natural languages, such units include sentences, phrases, and words. The second step is to analyze how these units build up larger patterns, and in particular to find general rules that govern the construction of sentences.http://people.dsv.su.se/~vadim/cmnew/chapter2/ch2_21.htm
In generative morphology, the righthand head rule is a rule of grammar that specifies that the rightmost morpheme in a morphological structure is almost always the head in certain languages. What this means is that it is the righthand element that provides the primary syntactic and/or semantic information. The projection of syntactic information from the righthand element onto the output word is known as feature percolation. The righthand head rule is considered a broadly general and universal principle of morphology. In certain other languages it is proposed that rather than a righthand head rule, a lefthand head rule applies, where the lefthand element provides this information.

Tuscarora, sometimes called Skarò˙rə̨ˀ, was the Iroquoian language of the Tuscarora people, spoken in southern Ontario, Canada, North Carolina and northwestern New York around Niagara Falls, in the United States, before becoming extinct in late 2020. The historic homeland of the Tuscarora was in eastern North Carolina, in and around the Goldsboro, Kinston, and Smithfield areas.
Onondaga language is the language of the Onondaga First Nation, one of the original five constituent tribes of the League of the Iroquois (Haudenosaunee).
The grammar of Classical Nahuatl is agglutinative, head-marking, and makes extensive use of compounding, noun incorporation and derivation. That is, it can add many different prefixes and suffixes to a root until very long words are formed. Very long verbal forms or nouns created by incorporation, and accumulation of prefixes are common in literary works. New words can thus be easily created.
German verbs may be classified as either weak, with a dental consonant inflection, or strong, showing a vowel gradation (ablaut). Both of these are regular systems. Most verbs of both types are regular, though various subgroups and anomalies do arise; however, textbooks for learners often class all strong verbs as irregular. The only completely irregular verb in the language is sein. There are more than 200 strong and irregular verbs, but just as in English, there is a gradual tendency for strong verbs to become weak.
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns and adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry grammatical information or lexical information . Inflection changes the grammatical properties of a word within its syntactic category. Derivational suffixes fall into two categories: class-changing derivation and class-maintaining derivation.
English prefixes are affixes that are added before either simple roots or complex bases consisting of (a) a root and other affixes, (b) multiple roots, or (c) multiple roots and other affixes. Examples of these follow:

The Nukak language is a language of uncertain classification, perhaps part of the macrofamily Puinave-Maku. It is very closely related to Kakwa.
Odia grammar is the study of the morphological and syntactic structures, word order, case inflections, verb conjugation and other grammatical structures of Odia, an Indo-Aryan language spoken in South Asia.

Pashto is an S-O-V language with split ergativity. Adjectives come before nouns. Nouns and adjectives are inflected for gender (masc./fem.), number (sing./plur.), and case. The verb system is very intricate with the following tenses: Present; simple past; past progressive; present perfect; and past perfect. In any of the past tenses, Pashto is an ergative language; i.e., transitive verbs in any of the past tenses agree with the object of the sentence. The dialects show some non-standard grammatical features, some of which are archaisms or descendants of old forms.

In linguistic morphology, inflection is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical categories such as tense, case, voice, aspect, person, number, gender, mood, animacy, and definiteness. The inflection of verbs is called conjugation, and one can refer to the inflection of nouns, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, determiners, participles, prepositions and postpositions, numerals, articles, etc., as declension.
Daga is a non-Austronesian language of Papua New Guinea. Daga is spoken by about 9,000 people as of 2007. The peoples that speak Daga are located in the Rabaraba subdistrict of Milne Bay district, and in the Abau subdistrict of the Central district of Papua New Guinea.
Mekéns (Mekem), or Amniapé, is a nearly extinct Tupian language of the state of Rondônia, in the Amazon region of Brazil.
References
- ↑ "agent noun". Oxford Learner's Dictionaries. Retrieved December 11, 2014.
- ↑ Panther, Klaus-Uwe; Thornburg, Linda L.; Barcelona, Antonio (2009). Metonymy and metaphor in grammar. Vol. 25. John Benjamins Publishing Company. p. 101. ISBN 978-90-272-2379-1.
- ↑ Delvaux, Martine; Melançon, Benoit (2019-08-21). "Pour ou contre le mot « autrice » ?" [For or against the word "author"?]. Radio-Canada (in French). Québec. Retrieved 2024-03-20. See also wikt:fr:-eure.
- ↑ Aronson, Howard I. (1990). Georgian: A Reading Grammar. Corrected edition. Columbus, Ohio: Slavica Publishers. pp. 119–120.
- ↑ ""Agent noun-اسم فاعل" in Dehkhoda Dictionary". Parsi Wiki.
- ↑ "Suffixes of Russian Nouns - Examples and Translation of Russian Suffixes". masterrussian.com. Retrieved 2017-02-15.