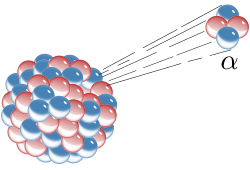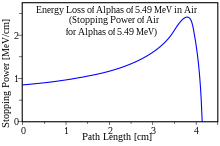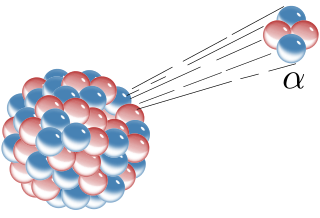
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle and thereby transforms or 'decays' into a different atomic nucleus, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an atomic number that is reduced by two. An alpha particle is identical to the nucleus of a helium-4 atom, which consists of two protons and two neutrons. It has a charge of +2 e and a mass of 4 Da. For example, uranium-238 decays to form thorium-234.

The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol
n
or
n0
, which has a neutral charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons behave similarly within the nucleus, they are both referred to as nucleons. Nucleons have a mass of approximately one atomic mass unit, or dalton, symbol Da. Their properties and interactions are described by nuclear physics. Protons and neutrons are not elementary particles; each is composed of three quarks.

Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.

Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactive decay.
Particle radiation is the radiation of energy by means of fast-moving subatomic particles. Particle radiation is referred to as a particle beam if the particles are all moving in the same direction, similar to a light beam.

In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nuclide the decay rate, and thus the half-life (t1/2) for that collection, can be calculated from their measured decay constants. The range of the half-lives of radioactive atoms has no known limits and spans a time range of over 55 orders of magnitude.

A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation, is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and β+ decay, which produce electrons and positrons respectively.

Nuclear technology is technology that involves the nuclear reactions of atomic nuclei. Among the notable nuclear technologies are nuclear reactors, nuclear medicine and nuclear weapons. It is also used, among other things, in smoke detectors and gun sights.

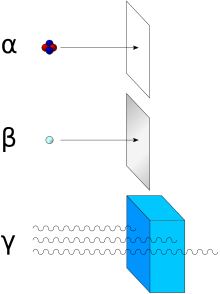
Radioactive decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha, beta, and gamma decay. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetism and nuclear force.
Ionizing radiation, including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.

Neutron emission is a mode of radioactive decay in which one or more neutrons are ejected from a nucleus. It occurs in the most neutron-rich/proton-deficient nuclides, and also from excited states of other nuclides as in photoneutron emission and beta-delayed neutron emission. As only a neutron is lost by this process the number of protons remains unchanged, and an atom does not become an atom of a different element, but a different isotope of the same element.

Neutron radiation is a form of ionizing radiation that presents as free neutrons. Typical phenomena are nuclear fission or nuclear fusion causing the release of free neutrons, which then react with nuclei of other atoms to form new nuclides—which, in turn, may trigger further neutron radiation. Free neutrons are unstable, decaying into a proton, an electron, plus an electron antineutrino. Free neutrons have a mean lifetime of 887 seconds.

In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another. If a nucleus interacts with another nucleus or particle and they then separate without changing the nature of any nuclide, the process is simply referred to as a type of nuclear scattering, rather than a nuclear reaction.

Uranium-238 is the most common isotope of uranium found in nature, with a relative abundance of 99%. Unlike uranium-235, it is non-fissile, which means it cannot sustain a chain reaction in a thermal-neutron reactor. However, it is fissionable by fast neutrons, and is fertile, meaning it can be transmuted to fissile plutonium-239. 238U cannot support a chain reaction because inelastic scattering reduces neutron energy below the range where fast fission of one or more next-generation nuclei is probable. Doppler broadening of 238U's neutron absorption resonances, increasing absorption as fuel temperature increases, is also an essential negative feedback mechanism for reactor control.

Radioluminescence is the phenomenon by which light is produced in a material by bombardment with ionizing radiation such as alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma rays. Radioluminescence is used as a low level light source for night illumination of instruments or signage. Radioluminescent paint is occasionally used for clock hands and instrument dials, enabling them to be read in the dark. Radioluminescence is also sometimes seen around high-power radiation sources, such as nuclear reactors and radioisotopes.
Radionuclides which emit gamma radiation are valuable in a range of different industrial, scientific and medical technologies. This article lists some common gamma-emitting radionuclides of technological importance, and their properties.
In radiobiology, the relative biological effectiveness is the ratio of biological effectiveness of one type of ionizing radiation relative to another, given the same amount of absorbed energy. The RBE is an empirical value that varies depending on the type of ionizing radiation, the energies involved, the biological effects being considered such as cell death, and the oxygen tension of the tissues or so-called oxygen effect.
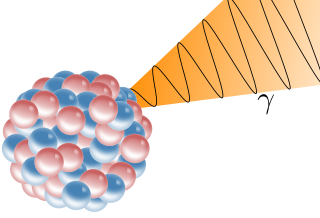
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequencies above 30 exahertz (3×1019 Hz), it imparts the highest photon energy. Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation gamma rays based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900 he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha rays and beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power.
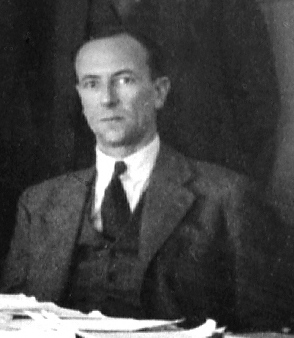
The discovery of the neutron and its properties was central to the extraordinary developments in atomic physics in the first half of the 20th century. Early in the century, Ernest Rutherford developed a crude model of the atom, based on the gold foil experiment of Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden. In this model, atoms had their mass and positive electric charge concentrated in a very small nucleus. By 1920, isotopes of chemical elements had been discovered, the atomic masses had been determined to be (approximately) integer multiples of the mass of the hydrogen atom, and the atomic number had been identified as the charge on the nucleus. Throughout the 1920s, the nucleus was viewed as composed of combinations of protons and electrons, the two elementary particles known at the time, but that model presented several experimental and theoretical contradictions.