Related Research Articles

In computing, load balancing refers to the process of distributing a set of tasks over a set of resources, with the aim of making their overall processing more efficient. Load balancing can optimize the response time and avoid unevenly overloading some compute nodes while other compute nodes are left idle.

In computer networking, a proxy server is a server application that acts as an intermediary between a client requesting a resource and the server providing that resource.
An application server is a server that hosts applications.

Internet Information Services is an extensible web server software created by Microsoft for use with the Windows NT family. IIS supports HTTP, HTTP/2, HTTPS, FTP, FTPS, SMTP and NNTP. It has been an integral part of the Windows NT family since Windows NT 4.0, though it may be absent from some editions, and is not active by default.
Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA) is a term associated with Microsoft products that refers to the SPNEGO, Kerberos, and NTLMSSP authentication protocols with respect to SSPI functionality introduced with Microsoft Windows 2000 and included with later Windows NT-based operating systems. The term is used more commonly for the automatically authenticated connections between Microsoft Internet Information Services, Internet Explorer, and other Active Directory aware applications.

An application firewall is a form of firewall that controls input/output or system calls of an application or service. It operates by monitoring and blocking communications based on a configured policy, generally with predefined rule sets to choose from. The application firewall can control communications up to the application layer of the OSI model, which is the highest operating layer, and where it gets its name. The two primary categories of application firewalls are network-based and host-based.
The Internet Server Application Programming Interface (ISAPI) is an N-tier API of Internet Information Services (IIS), Microsoft's collection of Windows-based web server services. The most prominent application of IIS and ISAPI is Microsoft's web server.
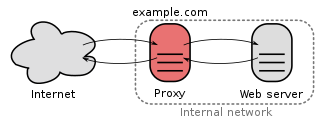
In computer networks, a reverse proxy is a type of proxy server that retrieves resources on behalf of a client from one or more servers. These resources are then returned to the client, appearing as if they originated from the reverse proxy server itself. It is mainly used to balance load.

Windows Server 2008 is the fourth release of the Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of the operating systems, based on Windows Vista. It was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and generally to retail on February 27, 2008. Windows Server 2008 is the successor of Windows Server 2003, which is derived from the Windows XP codebase, released nearly five years earlier.

Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway, formerly known as Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server, is a network router, firewall, antivirus program, VPN server and web cache from Microsoft Corporation. It runs on Windows Server and works by inspecting all network traffic that passes through it.
Network load balancing is the ability to balance traffic across two or more WAN links without using complex routing protocols like BGP.
HTTP compression is a capability that can be built into web servers and web clients to improve transfer speed and bandwidth utilization.
An application delivery network (ADN) is a suite of technologies that, when deployed together, provide availability, security, visibility, and acceleration for Internet applications such as websites. ADN components provide supporting functionality that enables website content to be delivered to visitors and other users of that website, in a fast, secure, and reliable way.
Nginx, stylized as NGINX, nginx or NginX, is a web server that can also be used as a reverse proxy, load balancer, mail proxy and HTTP cache. The software was created by Igor Sysoev and publicly released in 2004. Nginx is free and open-source software, released under the terms of the 2-clause BSD license. A large fraction of web servers use NGINX, often as a load balancer.

SharePoint is a web-based collaborative platform that integrates with Microsoft Office. Launched in 2001, SharePoint is primarily sold as a document management and storage system, but the product is highly configurable and its usage varies substantially among organizations.

Web Platform Installer is a freeware, closed-source package management system that installs non-commercial development tools and their dependencies that are part of Microsoft Web Platform, including:
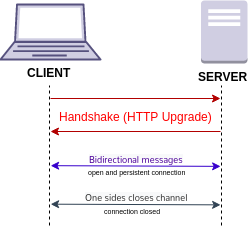
WebSocket is a computer communications protocol, providing full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection. The WebSocket protocol was standardized by the IETF as RFC 6455 in 2011, and the WebSocket API in Web IDL is being standardized by the W3C.
IBM WebSphere Edge Components is a set of web server/application server components that are intended to improve the performance of web-based systems, particularly as edge servers. It is part of the IBM WebSphere product suite. Current version is version 9.0. It consists of two independent products:
Server Core is a minimalistic Microsoft Windows Server installation option, debuted in Windows Server 2008. Server Core provides a server environment with functionality scaled back to core server features, and because of limited features, it has reduced servicing and management requirements, attack surface, disk and memory usage. Andrew Mason, a program manager on the Windows Server team, noted that a primary motivation for producing a Server Core variant of Windows Server 2008 was to reduce the attack surface of the operating system, and that about 70% of the security vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows from the prior five years would not have affected Server Core. Most notably, no Windows Explorer shell is installed. All configuration and maintenance is done entirely through command-line interface windows, or by connecting to the machine remotely using Microsoft Management Console (MMC), remote server administration tools, and PowerShell.
Azure Web Apps is a cloud computing based platform for hosting websites, created and operated by Microsoft. It is a platform as a service (PaaS) which allows publishing Web apps running on multiple frameworks and written in different programming languages, including Microsoft proprietary ones and 3rd party ones. Microsoft Azure Web Sites became available in its first preview version in June 2012, and an official version was announced in June 2013. Microsoft Azure Web Sites was originally named Windows Azure Web Sites, but was renamed as part of a re-branding move across Azure in March 2014. It was subsequently renamed "App Service" in March 2015.
References
- ↑ "Application Request Routing".
- ↑ Schaefer, Ken; Cochran, Jeff; Forsyth, Scott; Glendenning, Dennis; Perkins, Benjamin (2012). "Chapter 17: IIS Scalability II: Load Balancing and ARR". Professional Microsoft IIS 8. UK: Wrox. p. 558. ISBN 978-1118388044.