The Aedui or Haedui were a Gallic tribe dwelling in what is now the region of Burgundy during the Iron Age and the Roman period.

Vercingetorix was a Gallic king and chieftain of the Arverni tribe who united the Gauls in a failed revolt against Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. After surrendering to Caesar and spending almost six years in prison, he was executed in Rome.

This article concerns the period 59 BC – 50 BC.
Year 52 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Pompeius and Scipio. The denomination 52 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul. Gallic, Germanic, and Brittonic tribes fought to defend their homelands against an aggressive Roman campaign. The Wars culminated in the decisive Battle of Alesia in 52 BC, in which a complete Roman victory resulted in the expansion of the Roman Republic over the whole of Gaul. Though the collective Gallic armies were as strong as the Roman forces, the Gallic tribes' internal divisions eased victory for Caesar. Gallic chieftain Vercingetorix's attempt to unite the Gauls under a single banner came too late. Caesar portrayed the invasion as being a preemptive and defensive action, but historians agree that he fought the wars primarily to boost his political career and to pay off his debts. Still, Gaul was of significant military importance to the Romans. Native tribes in the region, both Gallic and Germanic, had attacked Rome several times. Conquering Gaul allowed Rome to secure the natural border of the river Rhine.

The Arverni were a Gallic people dwelling in the modern Auvergne region during the Iron Age and the Roman period. They were one of the most powerful tribes of ancient Gaul, contesting primacy over the region with the neighbouring Aedui.

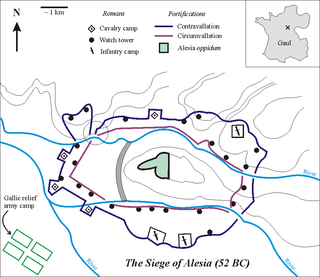
The Battle of Alesia or siege of Alesia was the climactic military engagement of the Gallic Wars, fought around the Gallic oppidum of Alesia in modern France, a major centre of the Mandubii tribe. It was fought by the Roman army of Julius Caesar against a confederation of Gallic tribes united under the leadership of Vercingetorix of the Arverni. It was the last major engagement between Gauls and Romans, and is considered one of Caesar's greatest military achievements and a classic example of siege warfare and investment; the Roman army built dual lines of fortifications—an inner wall to keep the besieged Gauls in, and an outer wall to keep the Gallic relief force out. The Battle of Alesia marked the end of Gallic independence in the modern day territory of France and Belgium.

The Bituriges Cubi were a Gallic tribe dwelling in a territory corresponding to the later province of Berry, which is named after them, during the Iron Age and the Roman period. They had a homonym tribe, the Bituriges Vivisci, in the Bordelais region, which could indicate a common origin, although there is no direct evidence of this.

Gergovia was a Gaulish town in modern Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes in the upper part of the basin of the Allier, near present-day Clermont-Ferrand. It was the capital of the Averni. The city of Gergovia had strong walls and was located on a giant raised plateau surrounded by hills.
The Battle of Gergovia took place in 52 BC in Gaul at Gergovia, the chief oppidum of the Arverni. The battle was fought between a Roman Republican army, led by proconsul Julius Caesar, and Gallic forces led by Vercingetorix, who was also the Arverni chieftain. The Romans attempted to besiege Gergovia, but miscommunication ruined the Roman plan. The Gallic cavalry counterattacked the confused Romans and sent them to flight, winning the battle.

Dumnorix was a chieftain of the Aedui, a Celtic tribe in Gaul in the 1st century B.C. He was the younger brother of Divitiacus, the Aedui druid and statesman.

Druids is a 2001 epic historical drama film directed by Jacques Dorfmann. It stars Christopher Lambert, Klaus Maria Brandauer, Inés Sastre, Maria Kavardjikova, Bernard-Pierre Donnadieu, and Max von Sydow.

The Battle of the Axona was fought in 57 BC, between the Roman army of Gaius Julius Caesar and the Belgae. The Belgae, led by King Galba of the Suessiones, attacked, only to be repelled by Caesar. Fearing an ambush, the Romans delayed their pursuit. Caesar's Commentarii de Bello Gallico describes this battle at 2.7 - 2.11.

Alesia was the capital of the Mandubii, one of the Gallic tribes allied with the Aedui. The Celtic oppidum was conquered by Julius Caesar during the Gallic Wars and afterwards became a Gallo-Roman town. Modern understanding of its location was controversial for a long time; however, it is now thought to have been located on Mont-Auxois, near Alise-Sainte-Reine in Burgundy, France.

Caesar, subtitled "Epic Battle of Alesia", is a board wargame self-published as "Alesia" by Robert Bradley in 1970, and then republished by Avalon Hill in 1976. The game simulates the ancient Battle of Alesia.
Gorgobina was a Celtic oppidum on the territory of the Aedui tribe. After the defeat of the Helvetii in 58 BC at nearby Bibracte, the Helvetians' Boii allies settled there. Whether this really was an act of clemency on Julius Caesar's part may be disputed. With the Aedui being allies of Rome, Vercingetorix besieged Gorgobina in the course of his campaign:
Hac re cognita Vercingetorix rursus in Bituriges exercitum reducit atque inde profectus Gorgobinam, Boiorum oppidum, quos ibi Helvetico proelio victos Caesar collocaverat Haeduisque attribuerat, oppugnare instituit.
(Translation:) With this in mind, Vercingetorix led his army back to the territory of the Bituriges and advanced from there to Gorgobina, the oppidum of the Boii – whom, defeated in the battle of the Helvetians, Caesar had installed there and assigned to the Aedui –, and laid siege to it.
Cenabum, Gaul was the name of the capital city of the Carnutes, located near the present French city of Orléans. Cenabum was an oppidum and a thriving commercial town on the Loire river.

Lucterius was a leader of the Cadurci, a Celtic people whose territory was located around Cahors in the modern French department of Lot. In the 50s BC, the Cadurci were under the rule of the Arverni, the civitas of Vercingetorix, under whom Lucterius served during the last stages of the Gallic Wars. In his memoirs, Julius Caesar calls him a man of unsurpassed boldness.

The siege of Uxellodunum was one of the last battles of the Gallic Wars. It took place in 51 BC at Uxellodunum. It was the last major military confrontation of the Gallic Wars and marked the pacification of Gaul under Roman rule. The battle resulted in a decisive Roman victory.
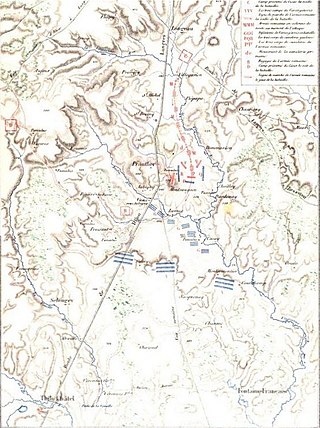
The Battle of the Vingeanne was mainly cavalry engagement between Roman legions, under the command of Gaius Julius Caesar and the coalition of Gaulic tribes led by Vercingetorix near the river of Vingeanne, as one of the major battles of the Gallic Wars. The battle was won by the Romans.