
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral to caudal axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets.

A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers in the peripheral nervous system.
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The field of neural development draws on both neuroscience and developmental biology to describe and provide insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which complex nervous systems develop, from nematodes and fruit flies to mammals.

The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiovascular center, the respiratory center, vomiting and vasomotor centers, responsible for the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. "Medulla" is from Latin, ‘pith or marrow’. And "oblongata" is from Latin, ‘lengthened or longish or elongated'.

In the developing chordate, the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural folds become elevated, and ultimately the folds meet and coalesce in the middle line and convert the groove into the closed neural tube. In humans, neural tube closure usually occurs by the fourth week of pregnancy.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The brainstem is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem.

Sonic hedgehog protein (SHH) is encoded for by the SHH gene. The protein is named after the video game character Sonic the Hedgehog.

The grey columns are three regions of the somewhat ridge-shaped mass of grey matter in the spinal cord. These regions present as three columns: the anterior grey column, the posterior grey column, and the lateral grey column, all of which are visible in cross-section of the spinal cord.
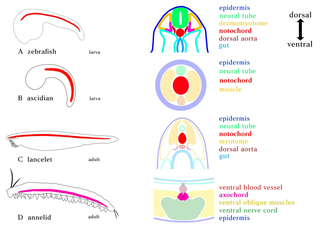
In zoology and developmental anatomy, the notochord is an elastic, rod-like anatomical structure found in many deuterostomal animals. A notochord is one of five synapomorphies, or characteristics used to define a species as a chordate.

The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

Neurulation refers to the folding process in vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube. The embryo at this stage is termed the neurula.

Neuromeres are distinct groups of neural crest cells, forming segments in the neural tube of the early embryonic development of the brain. There are three classes of neuromeres in the central nervous system – prosomeres, mesomeres and rhombomeres that will develop the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain respectively.
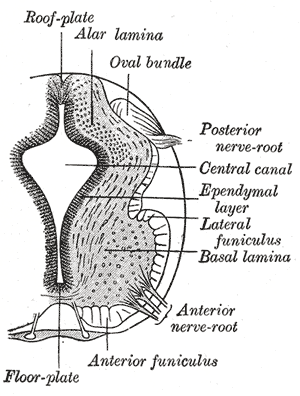
The floor plate is a structure integral to the developing nervous system of vertebrate organisms. Located on the ventral midline of the embryonic neural tube, the floor plate is a specialized glial structure that spans the anteroposterior axis from the midbrain to the tail regions. It has been shown that the floor plate is conserved among vertebrates, such as zebrafish and mice, with homologous structures in invertebrates such as the fruit fly Drosophila and the nematode C. elegans. Functionally, the structure serves as an organizer to ventralize tissues in the embryo as well as to guide neuronal positioning and differentiation along the dorsoventral axis of the neural tube.

Alpha (α) motor neurons (also called alpha motoneurons), are large, multipolar lower motor neurons of the brainstem and spinal cord. They innervate extrafusal muscle fibers of skeletal muscle and are directly responsible for initiating their contraction. Alpha motor neurons are distinct from gamma motor neurons, which innervate intrafusal muscle fibers of muscle spindles.

The glia limitans, or the glial limiting membrane, is a thin barrier of astrocyte foot processes associated with the parenchymal basal lamina surrounding the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost layer of neural tissue, and among its responsibilities is the prevention of the over-migration of neurons and neuroglia, the supporting cells of the nervous system, into the meninges. The glia limitans also plays an important role in regulating the movement of small molecules and cells into the brain tissue by working in concert with other components of the central nervous system (CNS) such as the blood–brain barrier (BBB).
The Allothalamus is a division used by some researchers in describing the thalamus.
The development of the nervous system in humans, or neural development, or neurodevelopment involves the studies of embryology, developmental biology, and neuroscience. These describe the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which the complex nervous system forms in humans, develops during prenatal development, and continues to develop postnatally.
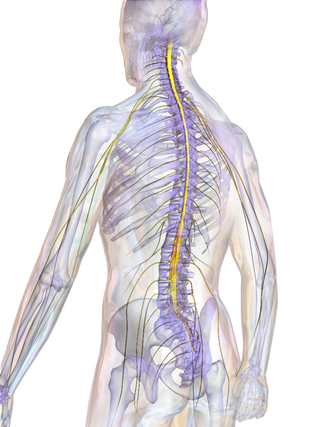
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.

The following diagram is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the human nervous system:
















