
Adobe Photoshop is a raster graphics editor developed and published by Adobe for Windows and macOS. It was originally created in 1987 by Thomas and John Knoll. Since then, the software has become the most used tool for professional digital art, especially in raster graphics editing. Owing to its fame, the program's name has become genericised as a verb although Adobe disapproves of such use.
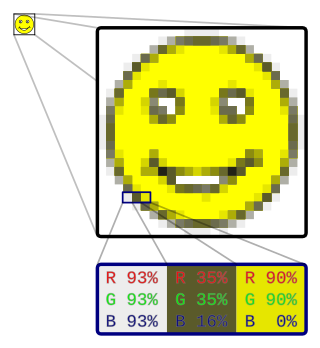
In computer graphics and digital photography, a raster graphic represents a two-dimensional picture as a rectangular matrix or grid of pixels, viewable via a computer display, paper, or other display medium. A raster is technically characterized by the width and height of the image in pixels and by the number of bits per pixel. Raster images are stored in image files with varying dissemination, production, generation, and acquisition formats.

Vector graphics are a form of computer graphics in which visual images are created directly from geometric shapes defined on a Cartesian plane, such as points, lines, curves and polygons. The associated mechanisms may include vector display and printing hardware, vector data models and file formats, as well as the software based on these data models. Vector graphics is an alternative to raster or bitmap graphics, with each having advantages and disadvantages in specific situations.

2D computer graphics is the computer-based generation of digital images—mostly from two-dimensional models and by techniques specific to them. It may refer to the branch of computer science that comprises such techniques or to the models themselves.
A raster graphics editor is a computer program that allows users to create and edit images interactively on the computer screen and save them in one of many raster graphics file formats such as JPEG, PNG, and GIF.

A vector graphic editor is a computer program that enables its users to create, compose and edit images with the use of mathematical and geometrical commands rather than individual pixels. This software is used in creating high-definition vector graphic images that can be scaled indefinitely without losing their quality. The output is saved in vector graphic formats, such as EPS, PDF, WMF, SVG, or VML.

An illustrator is an artist who specializes in enhancing writing or elucidating concepts by providing a visual representation that corresponds to the content of the associated text or idea. The illustration may be intended to clarify complicated concepts or objects that are difficult to describe textually, which is the reason illustrations are often found in children's books.

Digital painting is an art medium created with computer technologies. It employs pixels which are assigned a color to create imagery. It is also known as raster graphics. It is called digital painting because it initially distinguished itself from vector graphics in its ability to render gradiated or blended colors in imagery which mimicked traditional drawing and painting media.
Corel Painter is a raster-based digital art application created to simulate as accurately as possible the appearance and behavior of traditional media associated with drawing, painting, and printmaking. It is intended to be used in real-time by professional digital artists as a functional creative tool.

A category of fine art, graphic art covers a broad range of visual artistic expression, typically two-dimensional, i.e. produced on a flat surface. The term usually refers to the arts that rely more on line, color or tone, especially drawing and the various forms of engraving; it is sometimes understood to refer specifically to printmaking processes, such as line engraving, aquatint, drypoint, etching, mezzotint, monotype, lithography, and screen printing. Graphic art mostly includes calligraphy, photography, painting, typography, computer graphics, and bindery. It also encompasses drawn plans and layouts for interior and architectural designs.
A computer font is implemented as a digital data file containing a set of graphically related glyphs. A computer font is designed and created using a font editor. A computer font specifically designed for the computer screen, and not for printing, is a screen font.
A number of vector graphics editors exist for various platforms. Potential users of these editors will make a comparison of vector graphics editors based on factors such as the availability for the user's platform, the software license, the feature set, the merits of the user interface (UI) and the focus of the program. Some programs are more suitable for artistic work while others are better for technical drawings. Another important factor is the application's support of various vector and bitmap image formats for import and export.
An image file format is a file format for a digital image. There are many formats that can be used, such as JPEG, PNG, and GIF. Most formats up until 2022 were for storing 2D images, not 3D ones. The data stored in an image file format may be compressed or uncompressed. If the data is compressed, it may be done so using lossy compression or lossless compression. For graphic design applications, vector formats are often used. Some image file formats support transparency.
In computer graphics, image tracing, raster-to-vector conversion or raster vectorization is the conversion of raster graphics into vector graphics.

Graphic art software is a subclass of application software used for graphic design, multimedia development, stylized image development, technical illustration, general image editing, or simply to access graphic files. Art software uses either raster or vector graphic reading and editing methods to create, edit, and view art.
In computing, a bitmap is a mapping from some domain to bits. It is also called a bit array or bitmap index.

Computer graphics deals with by generating images and art with the aid of computers. Today, computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great deal of specialized hardware and software has been developed, with the displays of most devices being driven by computer graphics hardware. It is a vast and recently developed area of computer science. The phrase was coined in 1960 by computer graphics researchers Verne Hudson and William Fetter of Boeing. It is often abbreviated as CG, or typically in the context of film as computer generated imagery (CGI). The non-artistic aspects of computer graphics are the subject of computer science research.

Image editing encompasses the processes of altering images, whether they are digital photographs, traditional photo-chemical photographs, or illustrations. Traditional analog image editing is known as photo retouching, using tools such as an airbrush to modify photographs or editing illustrations with any traditional art medium. Graphic software programs, which can be broadly grouped into vector graphics editors, raster graphics editors, and 3D modelers, are the primary tools with which a user may manipulate, enhance, and transform images. Many image editing programs are also used to render or create computer art from scratch. The term "image editing" usually refers only to the editing of 2D images, not 3D ones.

Boxy SVG is a vector graphics editor for creating illustrations, as well as logos, icons, and other elements of graphic design. It is primarily focused on editing drawings in the SVG file format. The program is available as both a web app and a desktop application for Windows, macOS, ChromeOS, and Linux-based operating systems.















