Colloquially known as "downers", depressants or central depressants are drugs that lower neurotransmission levels, or depress or reduce arousal or stimulation in various areas of the brain. Depressants do not change the mood or mental state of others. Stimulants, or "uppers", increase mental or physical function, hence the opposite drug class from depressants are stimulants, not antidepressants.

Azapirones are a class of drugs used as anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. They are commonly used as add-ons to other antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).

Dizocilpine (INN), also known as MK-801, is a pore blocker of the NMDA receptor, a glutamate receptor, discovered by a team at Merck in 1982. Glutamate is the brain's primary excitatory neurotransmitter. The channel is normally blocked with a magnesium ion and requires depolarization of the neuron to remove the magnesium and allow the glutamate to open the channel, causing an influx of calcium, which then leads to subsequent depolarization. Dizocilpine binds inside the ion channel of the receptor at several of PCP's binding sites thus preventing the flow of ions, including calcium (Ca2+), through the channel. Dizocilpine blocks NMDA receptors in a use- and voltage-dependent manner, since the channel must open for the drug to bind inside it. The drug acts as a potent anti-convulsant and probably has dissociative anesthetic properties, but it is not used clinically for this purpose because of the discovery of brain lesions, called Olney's lesions (see below), in laboratory rats. Dizocilpine is also associated with a number of negative side effects, including cognitive disruption and psychotic-spectrum reactions. It inhibits the induction of long term potentiation and has been found to impair the acquisition of difficult, but not easy, learning tasks in rats and primates. Because of these effects of dizocilpine, the NMDA receptor pore blocker ketamine is used instead as a dissociative anesthetic in human medical procedures. While ketamine may also trigger temporary psychosis in certain individuals, its short half-life and lower potency make it a much safer clinical option. However, dizocilpine is the most frequently used uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist in animal models to mimic psychosis for experimental purposes.

Kainic acid, or kainate, is an acid that naturally occurs in some seaweed. Kainic acid is a potent neuroexcitatory amino acid agonist that acts by activating receptors for glutamate, the principal excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Glutamate is produced by the cell's metabolic processes and there are four major classifications of glutamate receptors: NMDA receptors, AMPA receptors, kainate receptors, and the metabotropic glutamate receptors. Kainic acid is an agonist for kainate receptors, a type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. Kainate receptors likely control a sodium channel that produces excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) when glutamate binds.

Alpidem, sold under the brand name Ananxyl, is a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic medication which was briefly used to treat anxiety disorders but is no longer marketed. It was previously marketed in France, but was discontinued due to liver toxicity. Alpidem is taken by mouth.

Erythrina mulungu (Mulungu) is a Brazilian ornamental tree and medicinal plant native to the cerrado and caatinga ecoregions in Brazil, South America.
An anxiogenic or panicogenic substance is one that causes anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiolytic agents, which inhibits anxiety. Together these categories of psychoactive compounds may be referred to as anxiotropic compounds.

NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for humans and non-human animals; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia.

Eglumetad is a research drug developed by Eli Lilly and Company, which is being investigated for its potential in the treatment of anxiety and drug addiction. It is a glutamate derived compound and its mode of action implies a novel mechanism.

Zatosetron (LY-277,359) is a drug which acts as an antagonist at the 5HT3 receptor It is orally active and has a long duration of action, producing antinauseant effects but without stimulating the rate of gastrointestinal transport. It is also an effective anxiolytic in both animal studies and human trials, although with some side effects at higher doses.

TPA-023 (MK-0777) is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic. It is a mixed, subtype-selective ligand of the benzodiazepine site of α1, α2, α3, and α5-containing GABAA receptors, where it acts as a partial agonist at benzodiazepine sites of the α2 and α3-containing subtypes, but as a silent antagonist at α1 and α5-containing subtypes. It has primarily anxiolytic and anticonvulsant effects in animal tests, but with no sedative effects even at 50 times the effective anxiolytic dose.

SB-399885 is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as a potent, selective and orally active 5-HT6 receptor antagonist, with a Ki of 9.0nM. SB-399885 and other 5-HT6 antagonists show nootropic effects in animal studies, as well as antidepressant and anxiolytic effects which are comparable to and synergistic with drugs such as imipramine and diazepam, and have been proposed as potential novel treatments for cognitive disorders such as schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease.
A convulsant is a drug which induces convulsions and/or epileptic seizures, the opposite of an anticonvulsant. These drugs generally act as stimulants at low doses, but are not used for this purpose due to the risk of convulsions and consequent excitotoxicity. Most convulsants are antagonists at either the GABAA or glycine receptors, or ionotropic glutamate receptor agonists. Many other drugs may cause convulsions as a side effect at high doses but only drugs whose primary action is to cause convulsions are known as convulsants. Nerve agents such as sarin, which were developed as chemical weapons, produce convulsions as a major part of their toxidrome, but also produce a number of other effects in the body and are usually classified separately. Dieldrin which was developed as an insecticide blocks chloride influx into the neurons causing hyperexcitability of the CNS and convulsions. The Irwin observation test and other studies that record clinical signs are used to test the potential for a drug to induce convulsions. Camphor, and other terpenes given to children with colds can act as convulsants in children who have had febrile seizures.

GR-159897 is a potent and selective NK2 receptor antagonist drug. It has anxiolytic effects in animal models, and also inhibits bronchoconstriction of the airways, which may potentially make it useful in the treatment of asthma.

2-Methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)pyridine (MPEP) is a research drug which was one of the first compounds found to act as a selective antagonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. After being originally patented as a liquid crystal for LCDs, it was developed by the pharmaceutical company Novartis in the late 1990s. It was found to produce neuroprotective effects following acute brain injury in animal studies, although it was unclear whether these results were purely from mGluR5 blockade as it also acts as a weak NMDA antagonist, and as a positive allosteric modulator of another subtype mGlu4, and there is also evidence for a functional interaction between mGluR5 and NMDA receptors in the same populations of neurons. It was also shown to produce antidepressant and anxiolytic effects in animals, and to reduce the effects of morphine withdrawal, most likely due to direct interaction between mGluR5 and the μ-opioid receptor.

3-( ethynyl)pyridine (MTEP) is a research drug that was developed by Merck & Co. as a selective allosteric antagonist of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. Identified through structure-activity relationship studies on an older mGluR5 antagonist MPEP, MTEP has subsequently itself acted as a lead compound for newer and even more improved drugs.
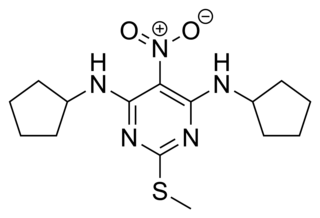
GS-39783 is a compound used in scientific research which acts as a positive allosteric modulator at the GABAB receptor. It has been shown to produce anxiolytic effects in animal studies, and reduces self-administration of alcohol, cocaine and nicotine.

BNC210 is an anxiolytic drug that acts via negative allosteric modulation of the α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, by Bionomics Limited. It is currently being investigated for the treatment of post traumatic stress disorder. The drug has demonstrated clinically significant anxiety reduction in both animal models and in Phase I trials.

SB-206553 is a drug which acts as a mixed antagonist for the 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C serotonin receptors. It has anxiolytic properties in animal studies and interacts with a range of other drugs. It has also been shown to act as a positive allosteric modulator of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Modified derivatives of SB-206553 have been used to probe the structure of the 5-HT2B receptor.

Willardiine (correctly spelled with two successive i's) or (S)-1-(2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)pyrimidine-2,4-dione is a chemical compound that occurs naturally in the seeds of Mariosousa willardiana and Acacia sensu lato. The seedlings of these plants contain enzymes capable of complex chemical substitutions that result in the formation of free amino acids (See:#Synthesis). Willardiine is frequently studied for its function in higher level plants. Additionally, many derivates of willardiine are researched for their potential in pharmaceutical development. Willardiine was first discovered in 1959 by R. Gmelin, when he isolated several free, non-protein amino acids from Acacia willardiana (another name for Mariosousa willardiana) when he was studying how these families of plants synthesize uracilyalanines. A related compound, Isowillardiine, was concurrently isolated by a different group, and it was discovered that the two compounds had different structural and functional properties. Subsequent research on willardiine has focused on the functional significance of different substitutions at the nitrogen group and the development of analogs of willardiine with different pharmacokinetic properties. In general, Willardiine is the one of the first compounds studied in which slight changes to molecular structure result in compounds with significantly different pharmacokinetic properties.

















