
The Kingdom of the East Saxons, referred to as the Kingdom of Essex, was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was founded in the 6th century and covered the territory later occupied by the counties of Essex, Middlesex, much of Hertfordshire and west Kent. The last king of Essex was Sigered of Essex, who in 825 ceded the kingdom to Ecgberht, King of Wessex.

Ilford is a large town in east London, England, 9 miles (14 km) north-east of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Redbridge, Ilford is within the ceremonial county of Greater London. It had a population of 168,168 in 2011, compared to 303,858 for the entire borough.

Upminster is a suburban town in East London, England, within the London Borough of Havering. Located 16.5 miles (26.6 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross, it is one of the locally important district centres identified in the London Plan.

West Ham is an area in East London, located 6.1 mi (9.8 km) east of Charing Cross in the west of the modern London Borough of Newham.

The London Borough of Waltham Forest is an outer London borough formed in 1965 from the merger of the municipal boroughs of Leyton, Walthamstow and Chingford.

Epping Forest District is a local government district in Essex, England. It is named after the ancient woodland of Epping Forest, a large part of which lies within the district. The council is based in the town of Epping. The district also includes the towns of Loughton, Waltham Abbey, Chigwell, Buckhurst Hill, as well as rural areas. The district is situated in the west of the county, bordering north-eastern Greater London.

The Borough of Brentwood is a local government district with borough status in Essex, England. The borough is named after its main town of Brentwood, where the council is based; it includes several villages and the surrounding rural area.

East London is the northeastern part of London, England, east of the ancient City of London and north of the River Thames as it begins to widen. East London developed as London's docklands and the primary industrial centre. The expansion of railways in the 19th century encouraged the eastward expansion of the East End of London and a proliferation of new suburbs. The industrial lands of East London are today an area of regeneration, which are well advanced in places such as Canary Wharf and ongoing elsewhere.

Shenfield is a town in the Borough of Brentwood in Essex, England. In 2020, the ward was estimated to have a population of 5,396.

East Ham was a local government district in the far south west of Essex from 1878 to 1965. It extended from Wanstead Flats in the north to the River Thames in the south and from Green Street in the west to Barking Creek in the east. It was part of the London postal district and Metropolitan Police District.

Chingford was a local government district in south west Essex, England from 1894 to 1965, around the town of Chingford. It was within the London suburbs, forming part of the London postal district and Metropolitan Police District. Its former area now corresponds to the northern part of the London Borough of Waltham Forest in Greater London.

Leyton was a local government district in southwest Essex, England, from 1873 to 1965. It included the neighbourhoods of Leyton, Leytonstone and Cann Hall. It was suburban to London, forming part of the London postal district and Metropolitan Police District. It now forms the southernmost part of the London Borough of Waltham Forest in Greater London.

Ilford was a civil parish and local government district in south west Essex, England from 1888 to 1965, covering the town Ilford. The district saw a considerable rise in population throughout its life, caused by the expansion of the built-up area of London, and became one of the most populous districts of its type in England. The district now corresponds to the greater part of the London Borough of Redbridge in Greater London.

The London Government Act 1963 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which created Greater London and a new local government structure within it. The Act significantly reduced the number of local government districts in the area, resulting in local authorities responsible for larger areas and populations. The upper tier of local government was reformed to cover the whole of the Greater London area and with a more strategic role; and the split of functions between upper and lower tiers was recast. The Act classified the boroughs into inner and outer London groups. The City of London and its corporation were essentially unreformed by the legislation. Subsequent amendments to the Act have significantly amended the upper tier arrangements, with the Greater London Council abolished in 1986, and the Greater London Authority introduced in 2000. As of 2016, the London boroughs are more or less identical to those created in 1965, although with some enhanced powers over services such as waste management and education.

The Diocese of Chelmsford is a Church of England diocese, part of the Province of Canterbury. It was created on 23 January 1914 from part of the Diocese of St Albans. It covers Essex and part of East London. Since 1984 it is divided into three episcopal areas, each with its own area bishop. The diocese covers around 1,500 square miles (3,900 km2) with a population of more than 3 million. It has 463 parishes and 588 churches.

Essex County Council is the county council that governs the non-metropolitan county of Essex in England. It has 75 councillors, elected from 70 divisions, and has been under Conservative majority control since 2001. The council meets at County Hall in the centre of Chelmsford. It is a member of the East of England Local Government Association.

The Archdeacons in the Diocese of Chelmsford are senior ecclesiastical officers in the Church of England in Essex and East London. They currently include: the Archdeacon of West Ham, the Archdeacon of Colchester and the archdeacons of Chelmsford, of Harlow, of Barking, of Stansted and of Southend. Each one has responsibility over a geographical area within the diocese.
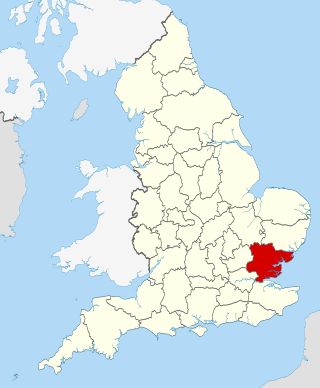
Essex is a ceremonial county in the East of England and one of the home counties. It is bordered by Cambridgeshire and Suffolk to the north, the North Sea to the east, Kent across the Thames Estuary to the south, Greater London to the south-west, and Hertfordshire to the west. The largest settlement is Southend-on-Sea, and the county town is Chelmsford.


















