External links
| Overview | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disasters |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preparation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Countermeasures | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Media | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Organizations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pakistan articles | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
The following is a list of natural disasters that have affected Pakistan.
| Event | Disaster | Location | Date | Affected | Death Toll |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earthquake/Tsunami | Makran | 325 BC | |||
| 1935 Quetta earthquake | Earthquake | Quetta | May 31, 1935 | 60,000 | |
| 1945 Balochistan earthquake | Earthquake/Tsunami | Makran | Nov 27, 1945 | 4,000 | |
| Flood | 1950 | 2,900 | |||
| Wind storm | Karachi | Dec 15, 1965 | 10,000 | ||
| Flood | Aug 1973 | 4,800,000 | |||
| 1974 Hunza earthquake | Earthquake | Northern Areas | Dec 28, 1974 | 97,000 | 5,300 |
| Flood | Aug 2, 1976 | 5,566,000 | |||
| Flood | Jun 1977 | 1,022,000 | 848 | ||
| Flood | Jul 1978 | 2,246,000 | |||
| Flood | Aug 1988 | 1,000,000 | |||
| Extreme Temperature | Jun 11, 1991 | 961 | |||
| Flood | Aug 9, 1992 | 6,184,418 | |||
| Flood | Sep 1992 | 12,324,024 | 1,334 | ||
| Wind storm | Nov 14, 1993 | 609 | |||
| Flood | Jul 22, 1995 | 1,255,000 | |||
| Flood | Aug 24, 1996 | 1,186,131 | |||
| Flood | Mar 3, 1998 | 1,000 | |||
| Drought | Mar 2000 | 2,200,000 | |||
| 2005 Kashmir earthquake | Earthquake | Muzaffarabad | Oct 8, 2005 | 2,500,000 | 87,351 |
| Flood | Jul/Aug 2010 | 20,000,000 |

A disaster is a serious problem occurring over a period of time that causes widespread human, material, economic or environmental loss which exceeds the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own resources. Disasters are routinely divided into either "natural disasters" caused by natural hazards or "human-instigated disasters" caused from anthropogenic hazards. However, in modern times, the divide between natural, human-made and human-accelerated disasters is difficult to draw.

A natural disaster is the highly harmful impact on a society or community following a natural hazard event. Some examples of natural hazard events include: flooding, drought, earthquake, tropical cyclone, lightning, tsunami, volcanic activity, wildfire. A natural disaster can cause loss of life or damage property, and typically leaves economic damage in its wake. The severity of the damage depends on the affected population's resilience and on the infrastructure available. Scholars have been saying that the term natural disaster is unsuitable and should be abandoned. Instead, the simpler term disaster could be used, while also specifying the category of hazard. A disaster is a result of a natural or human-made hazard impacting a vulnerable community. It is the combination of the hazard along with exposure of a vulnerable society that results in a disaster.
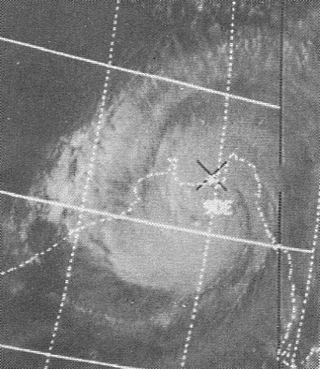
The 1970 Bhola cyclone was a devastating tropical cyclone in the Bengal region, that struck East Pakistan and India's West Bengal on November 12, 1970. It remains the deadliest tropical cyclone ever recorded and one of the world's deadliest humanitarian disasters. At least 300,000 people died in the storm, possibly as many as 500,000, primarily as a result of the storm surge that flooded much of the low-lying islands of the Ganges Delta. Bhola was the sixth and strongest cyclonic storm of the 1970 North Indian Ocean cyclone season.

Emergency management or disaster management is a science and a system charged with creating the framework within which communities reduce vulnerability to hazards and cope with disasters. Emergency management, despite its name, does not actually focus on the management of emergencies, which can be understood as minor events with limited impacts and are managed through the day-to-day functions of a community. Instead, emergency management focuses on the management of disasters, which are events that produce more impacts than a community can handle on its own. The management of disasters tends to require some combination of activity from individuals and households, organizations, local, and/or higher levels of government. Although many different terminologies exist globally, the activities of emergency management can be generally categorized into preparedness, response, mitigation, and recovery, although other terms such as disaster risk reduction and prevention are also common. The outcome of emergency management is to prevent disasters and where this is not possible, to reduce their harmful impacts.
Environmental issues in Pakistan include air pollution, water pollution, noise pollution, climate change, pesticide misuse, soil erosion, natural disasters, desertification and flooding. According to the 2020 edition of the environmental performance index (EPI) ranking released by Yale Center for Environmental Law & Policy, Pakistan ranks 142 with an EPI score of 33.1, an increase of 6.1 over a 10-year period. It ranked 180 in terms of air quality. The climatic changes and global warming are the most alarming issues risking millions of lives across the country. The major reasons of these environmental issues are carbon emissions, population explosion, and deforestation.
Events from the year 1970 in Pakistan.
Focus Humanitarian Assistance is an international group of agencies established in Europe, North America and South Asia to complement the provision of emergency relief, principally in the developing world. It helps people in need reduce their dependence on humanitarian aid and facilitates their transition to sustainable self-reliant, long-term development.

Climate change in South Asia is having significant impacts already which are expected to intensify as global temperatures rise due to climate change. The South Asia region consists of the eight countries: Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, the Maldives and Sri Lanka. In the 2017 edition of Germanwatch's Climate Risk Index, Bangladesh and Pakistan ranked sixth and seventh respectively as the countries most affected by climate change in the period from 1996 to 2015, while India ranked fourth among the list of countries most affected by climate change in 2015. The Indian subcontinent is one of the most vulnerable regions globally to a number of direct and indirect effects of climate change, including sea level rise, cyclonic activity, and changes in ambient temperature and precipitation patterns. Ongoing sea level rise has already submerged several low-lying islands in the Sundarbans region, displacing thousands of people.

The Pakistan Meteorological Department (PMD) (Urdu: محکمہ موسمیات پاکستان, also known as Pakistan Met Office), is an autonomous and independent institution tasked with providing weather forecasts and public warnings concerning weather for protection, safety and general information.

Thoise or Thoise Airbase is a military airfield and small village in Nubra region of Ladakh, India, occupying the only large piece of flat land in the area. The airstrip is a critical facility enabling a quick inflow of men and material from the Indian interior to Siachen, a glacier, helipad and battleground near the Actual Ground Position Line between India and Pakistan.
The U.S. Central Intelligence Agency deals with activities related to human survival issues, emphasizing disease and basic needs such as water and agriculture as a part of its function across the world.

The following are lists of disasters.
China plans to launch eleven Huanjing satellites for disaster and environmental monitoring. The satellites will be capable of visible, infrared, multi-spectral and synthetic-aperture radar imaging.
Electricity in Pakistan is generated, transmitted, distributed, and retail supplied by two vertically integrated public sector companies, Water and Power Development Authority (WAPDA) responsible for the production of hydroelectricity and supplied to the consumers by the power distribution companies (DISCOS) under the Pakistan Electric Power Company (PEPCO). Currently, there are 11 distribution companies and one National Transmission And Dispatch Company (NTDC) all in the public sector, and the Karachi Electric (K-Electric) for the city of Karachi and its surrounding areas. There are around 42 independent power producers (IPPs) that contribute significantly in electricity generation in Pakistan.

The following is a summary of significant earthquakes during the 21st century. In terms of fatalities, the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake was the most destructive event with 227,898 confirmed fatalities, followed by the 2010 Haiti earthquake with about 160,000 fatalities, the 2008 Sichuan earthquake with 87,587 fatalities, the 2005 Kashmir earthquake with 87,351 fatalities, and the 2023 Turkey–Syria earthquakes with at least 59,259 fatalities.

The floods in Pakistan began in late July 2010, resulting from heavy monsoon rains in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Sindh, Punjab and, Balochistan regions of Pakistan, which affected the Indus River basin. Approximately one-fifth of Pakistan's total land area was affected by floods, with the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province facing the brunt of the damage and casualties. Nationwide, there were 1,985 deaths. According to Pakistani government data, the floods directly affected about 20 million people, mostly by destruction of property, livelihood and infrastructure.

The Civil Armed Forces (CAF) are a group of nine paramilitary, uniformed organisations, separate and distinct from the regular "military" Pakistan Armed Forces. They are responsible for maintaining internal security, helping law enforcement agencies, border control, counter-insurgency and counter-terrorism, riot control, and anti-smuggling under the Ministry of Interior. They frequently operate alongside the Pakistani military in response to natural disasters. During times of war they can have their command transferred to the Ministry of Defence, and effectively combined to form a reserve force for the Pakistani military.