
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) is a type of mass spectrometry that uses an inductively coupled plasma to ionize the sample. It atomizes the sample and creates atomic and small polyatomic ions, which are then detected. It is known and used for its ability to detect metals and several non-metals in liquid samples at very low concentrations. It can detect different isotopes of the same element, which makes it a versatile tool in isotopic labeling.

High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify specific components in mixtures. The mixtures can originate from food, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, biological, environmental and agriculture, etc, which have been dissolved into liquid solutions.

Valdecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used in the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and painful menstruation and menstrual symptoms. It is a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. It was patented in 1995.

Aniracetam, also known as N-anisoyl-2-pyrrolidinone, is a racetam which is sold in Europe as a prescription drug. It is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the United States as a prescription medication or dietary supplement. Despite the FDA's lack of approval, the drug is readily available over-the-counter in misbranded dietary supplements.

Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites, the small molecule substrates, intermediates, and products of cell metabolism. Specifically, metabolomics is the "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerprints that specific cellular processes leave behind", the study of their small-molecule metabolite profiles. The metabolome represents the complete set of metabolites in a biological cell, tissue, organ, or organism, which are the end products of cellular processes. Messenger RNA (mRNA), gene expression data, and proteomic analyses reveal the set of gene products being produced in the cell, data that represents one aspect of cellular function. Conversely, metabolic profiling can give an instantaneous snapshot of the physiology of that cell, and thus, metabolomics provides a direct "functional readout of the physiological state" of an organism. There are indeed quantifiable correlations between the metabolome and the other cellular ensembles, which can be used to predict metabolite abundances in biological samples from, for example mRNA abundances. One of the ultimate challenges of systems biology is to integrate metabolomics with all other -omics information to provide a better understanding of cellular biology.
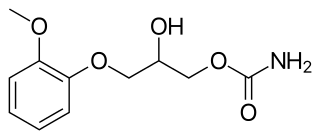
Methocarbamol, sold under the brand name Robaxin among others, is a medication used for short-term musculoskeletal pain. It may be used together with rest, physical therapy, and pain medication. It is less preferred in low back pain. It has limited use for rheumatoid arthritis and cerebral palsy. Effects generally begin within half an hour. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein.

Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) is an analytical chemistry technique that combines the physical separation capabilities of liquid chromatography with the mass analysis capabilities of mass spectrometry (MS). Coupled chromatography – MS systems are popular in chemical analysis because the individual capabilities of each technique are enhanced synergistically. While liquid chromatography separates mixtures with multiple components, mass spectrometry provides spectral information that may help to identify each separated component. MS is not only sensitive, but provides selective detection, relieving the need for complete chromatographic separation. LC–MS is also appropriate for metabolomics because of its good coverage of a wide range of chemicals. This tandem technique can be used to analyze biochemical, organic, and inorganic compounds commonly found in complex samples of environmental and biological origin. Therefore, LC–MS may be applied in a wide range of sectors including biotechnology, environment monitoring, food processing, and pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and cosmetic industries. Since the early 2000s, LC–MS has also begun to be used in clinical applications.

Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) is an ionization method used in mass spectrometry which utilizes gas-phase ion-molecule reactions at atmospheric pressure (105 Pa), commonly coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). APCI is a soft ionization method similar to chemical ionization where primary ions are produced on a solvent spray. The main usage of APCI is for polar and relatively less polar thermally stable compounds with molecular weight less than 1500 Da. The application of APCI with HPLC has gained a large popularity in trace analysis detection such as steroids, pesticides and also in pharmacology for drug metabolites.

Thermospray is a soft ionization source by which a solvent flow of liquid sample passes through a very thin heated column to become a spray of fine liquid droplets. As a form of atmospheric pressure ionization in mass spectrometry these droplets are then ionized via a low-current discharge electrode to create a solvent ion plasma. A repeller then directs these charged particles through the skimmer and acceleration region to introduce the aerosolized sample to a mass spectrometer. It is particularly useful in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS).
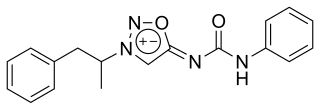
Mesocarb is a drug that is currently being developed for Parkinson's disease.

Adrenosterone, also known as Reichstein's substance G , as well as 11-ketoandrostenedione (11-KA4), 11-oxoandrostenedione (11-OXO), and androst-4-ene-3,11,17-trione, is a steroid hormone with an extremely weak androgenic effect, and an intermediate/prohormone of 11-ketotestosterone. It was first isolated in 1936 from the adrenal cortex by Tadeus Reichstein at the Pharmaceutical Institute in the University of Basel. Originally, adrenosterone was called Reichstein's substance G. Adrenosterone occurs in trace amounts in humans as well as most mammals and in larger amounts in fish, where it is a precursor to the primary androgen, 11-ketotestosterone.

Flutazolam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It was invented in Japan, and this is the main country in which it has been used medically. It has sedative, muscle relaxant, anticonvulsant, and anxiolytic effects similar to those produced by other benzodiazepine derivatives, and though it is around the same potency as diazepam, it produces a more marked sedation and impaired coordination. It is indicated for the treatment of insomnia. Its major active metabolite is n-desalkylflurazepam, also known as norflurazepam, which is also a principal metabolite of flurazepam. While flutazolam has a very short half-life of only 3.5 hours, n-desalkylflurazepam has a long half-life of between 47–100 hours.
Blood plasma fractionation are the general processes separating the various components of blood plasma, which in turn is a component of blood obtained through blood fractionation. Plasma-derived immunoglobulins are giving a new narrative to healthcare across a wide range of autoimmune inflammatory diseases. This widespread applicability is anticipated to leverage market prospects for plasma fractionation, pegged to witness a noteworthy 7% CAGR. COVID-19 pandemic is expected to generate growth opportunities for the plasma fractionation market.
A monolithic HPLC column, or monolithic column, is a column used in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The internal structure of the monolithic column is created in such a way that many channels form inside the column. The material inside the column which separates the channels can be porous and functionalized. In contrast, most HPLC configurations use particulate packed columns; in these configurations, tiny beads of an inert substance, typically a modified silica, are used inside the column. Monolithic columns can be broken down into two categories, silica-based and polymer-based monoliths. Silica-based monoliths are known for their efficiency in separating smaller molecules while, polymer-based are known for separating large protein molecules.
Bioanalysis is a sub-discipline of analytical chemistry covering the quantitative measurement of xenobiotics and biotics in biological systems.

A direct electron ionization liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry interface is a technique for coupling liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry (LC-MS) based on the direct introduction of the liquid effluent into an electron ionization (EI) source. Library searchable mass spectra are generated. Gas-phase EI has many applications for the detection of HPLC amenable compounds showing minimal adverse matrix effects. The direct-EI LC-MS interface provides access to well-characterized electron ionization data for a variety of LC applications and readily interpretable spectra from electronic libraries for environmental, food safety, pharmaceutical, biomedical, and other applications.
Interchim is a privately owned French company specialized in manufacturing and distribution of reagents, consumables and dedicated instruments for the R&D and industry laboratory in the fields of fine chemistry, chromatography and bio-analysis. It has become a provider of reference methods, products for analytics serving research and quality control in the biomedical field, pharmaceutical industry, but also cosmetics and environment.
Host cell proteins (HCPs) are process-related protein impurities that are produced by the host organism during biotherapeutic manufacturing and production. During the purification process, a majority of produced HCPs are removed from the final product. However, residual HCPs still remain in the final distributed pharmaceutical drug. Examples of HCPs that may remain in the desired pharmaceutical product include: monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), antibody-drug-conjugates (ADCs), therapeutic proteins, vaccines, and other protein-based biopharmaceuticals.

Laser diode thermal desorption (LDTD) is an ionization technique that is coupled to mass spectrometry to analyze samples with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI). It uses a laser to thermally desorb analytes that are deposited on a stainless steel sheet sample holder, called LazWell. The coupling of LDTD and APCI is considered to be a soft-ionization technique. With LDTD-APCI, it is possible to analyze samples in forensics, pharmaceuticals, environment, food and clinical studies. LDTD is suitable for small molecules between 0 and 1200 Da and some peptides such as cyclosporine.














