Articles related to anatomy include:

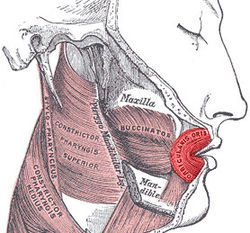
The buccinator is a thin quadrilateral muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral wall of the oral cavity.

The lips are a horizontal pair of soft appendages attached to the jaws and are the most visible part of the mouth of many animals, including humans. Vertebrate lips are soft, movable and serve to facilitate the ingestion of food and the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are also a somatosensory organ, and can be an erogenous zone when used in kissing and other acts of intimacy.

The platysma muscle is a superficial muscle of the human neck that overlaps the sternocleidomastoid. It covers the anterior surface of the neck superficially. When it contracts, it produces a slight wrinkling of the neck, and a "bowstring" effect on either side of the neck.

The depressor labii inferioris is a facial muscle. It helps to lower the bottom lip.

The orbicularis oculi is a muscle in the face that closes the eyelids. It arises from the nasal part of the frontal bone, from the frontal process of the maxilla in front of the lacrimal groove, and from the anterior surface and borders of a short fibrous band, the medial palpebral ligament.

The levator labii superioris is a muscle of the human body used in facial expression. It is a broad sheet, the origin of which extends from the side of the nose to the zygomatic bone.

The levator anguli oris (caninus) is a facial muscle of the mouth arising from the canine fossa, immediately below the infraorbital foramen. It elevates angle of mouth medially. Its fibers are inserted into the angle of the mouth, intermingling with those of the zygomaticus, triangularis, and orbicularis oris. Specifically, the levator anguli oris is innervated by the buccal branches of the facial nerve.

The depressor anguli oris muscle is a facial muscle. It originates from the mandible and inserts into the angle of the mouth. It is associated with frowning, as it depresses the corner of the mouth.

The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.
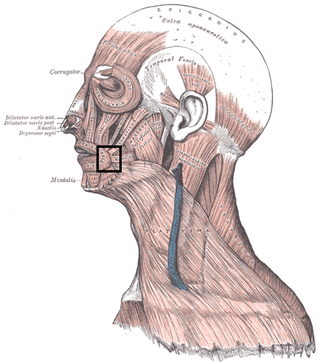
In facial anatomy, the modiolus is a dense, compact, mobile, fibromuscular tissue mass of facial muscles formed by the interlacing of a number of muscles just lateral to the angle of the mouth opposite the second upper premolar tooth.

The frontal process of the maxilla is a strong plate, which projects upward, medialward, and backward from the maxilla, forming part of the lateral boundary of the nose.

The angular artery is an artery of the face. It is the terminal part of the facial artery. It ascends to the medial angle of the eye's orbit. It is accompanied by the angular vein. It ends by anastomosing with the dorsal nasal branch of the ophthalmic artery. It supplies the lacrimal sac, the orbicularis oculi muscle, and the outer side of the nose.

The buccal branches of the facial nerve, are of larger size than the rest of the branches, pass horizontally forward to be distributed below the orbit and around the mouth.
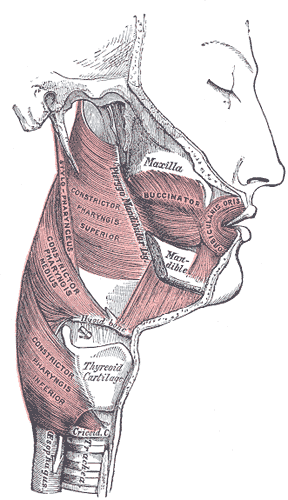
The buccal space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the cheek, and is paired on each side. The buccal space is superficial to the buccinator muscle and deep to the platysma muscle and the skin. The buccal space is part of the subcutaneous space, which is continuous from head to toe.

The facial muscles are a group of striated skeletal muscles supplied by the facial nerve that, among other things, control facial expression. These muscles are also called mimetic muscles. They are only found in mammals, although they derive from neural crest cells found in all vertebrates. They are the only muscles that attach to the dermis.

The human nose is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum, which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
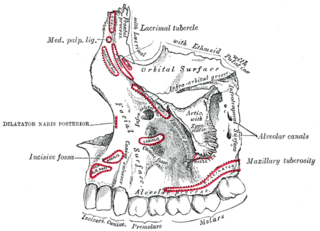
The canine space, is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a thin potential space on the face, and is paired on either side. It is located between the levator anguli oris muscle inferiorly and the levator labii superioris muscle superiorly. The term is derived from the fact that the space is in the region of the canine fossa, and that infections originating from the maxillary canine tooth may spread to involve the space. Infra-orbital is derived from infra- meaning below and orbit which refers to the eye socket.