Related Research Articles

A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies, and autoimmune disorders.
Sexual dysfunction is difficulty experienced by an individual or partners during any stage of normal sexual activity, including physical pleasure, desire, preference, arousal, or orgasm. The World Health Organization defines sexual dysfunction as a "person's inability to participate in a sexual relationship as they would wish". This definition is broad and is subject to many interpretations. A diagnosis of sexual dysfunction under the DSM-5 requires a person to feel extreme distress and interpersonal strain for a minimum of six months. Sexual dysfunction can have a profound impact on an individual's perceived quality of sexual life. The term sexual disorder may not only refer to physical sexual dysfunction, but to paraphilias as well; this is sometimes termed disorder of sexual preference.
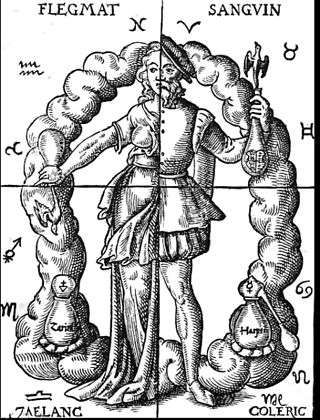
Humorism, the humoral theory, or humoralism, is a system of medicine detailing a supposed makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Ancient Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers.

In Philippine mythology, the kapre is a creature that may be described as a tree giant, being a tall, dark-coloured, hairy, and muscular creature. Kapres are also said to have a very strong body odour and to sit in tree branches to smoke.
Usog or balis is a Filipino superstition whereby an affliction or psychological disorder is attributed to a stranger's greeting or evil eye hex. It is usually attributed to afflictions of infants and toddlers.

Witchcraft has been present throughout the Philippines even before Spanish colonization, and is associated with indigenous Philippine folk religions. Its practice involves black magic, specifically a malevolent use of sympathetic magic. Today, practices are said to be centered in Siquijor, Cebu, Davao, Talalora, Western Samar, and Sorsogon, where many of the country's faith healers reside. Witchcraft also exists in many of the hinterlands, especially in Samar and Leyte; however, witchcraft is known and occurs anywhere in the country.
Hilot (/HEE-lot/) is an ancient Filipino art of healing. It uses manipulation and massage to achieve the treatment outcome, although techniques differ from one practitioner to another. It emerged from the shamanic tradition of the ancient Filipinos with healers considering their practice as derived from their calling from visions or from having been born by breech.
Albularyo or albulario is a Filipino term for a witch doctor, folk healer or medicine man, derived from Spanish herbolario (herbalist). They practice folk medicine and use medicinal plants in their trade.

Filipino shamans, commonly known as babaylan, were shamans of the various ethnic groups of the pre-colonial Philippine islands. These shamans specialized in communicating, appeasing, or harnessing the spirits of the dead and the spirits of nature. They were almost always women or feminized men. They were believed to have spirit guides, by which they could contact and interact with the spirits and deities and the spirit world. Their primary role were as mediums during pag-anito séance rituals. There were also various subtypes of babaylan specializing in the arts of healing and herbalism, divination, and sorcery.

Indigenous Philippine folk religions are the distinct native religions of various ethnic groups in the Philippines, where most follow belief systems in line with animism. Generally, these Indigenous folk religions are referred to as Anito or Anitism or the more modern and less ethnocentric Dayawism, where a set of local worship traditions are devoted to the anito or diwata, terms which translate to gods, spirits, and ancestors. 0.23% of the population of the Philippines are affiliated with the Indigenous Philippine folk religions according to the 2020 national census, an increase from the previous 0.19% from the 2010 census.
Pagtatawas is a divination ritual in pseudomedicine in Filipino Psychology, carried out by the mangtatawas. It attempts to diagnose an affliction or psychological disorder by interpreting shapes produced in water by heated alum or molten wax droppings from a burning candle. It is thus a form of both carromancy and oryctomancy.

Michael Lim Tan is a Filipino medical anthropologist, veterinarian, and writer who is currently a professor at the University of the Philippines Diliman College of Social Sciences and Philosophy. Tan served as the chancellor of UP Diliman from 2014 to 2020.
Postorgasmic illness syndrome (POIS) is a syndrome in which human males have chronic physical and cognitive symptoms following ejaculation. The symptoms usually onset within seconds, minutes, or hours, and last for up to a week. The cause and prevalence are unknown; it is considered a rare disease.
Swimming induced pulmonary edema (SIPE), also known as immersion pulmonary edema, is a life threatening condition that occurs when fluids from the blood leak abnormally from the small vessels of the lung (pulmonary capillaries) into the airspaces (alveoli).
Post-intensive care syndrome (PICS) describes a collection of health disorders that are common among patients who survive critical illness and intensive care. Generally, PICS is considered distinct from the impairments experienced by those who survive critical illness and intensive care following traumatic brain injury and stroke. The range of symptoms that PICS describes falls under three broad categories: physical impairment, cognitive impairment, and psychiatric impairment. A person with PICS may have symptoms from one or multiple of these categories.

The history of medicine in the Philippines discusses the folk medicinal practices and the medical applications used in Philippine society from the prehistoric times before the Spaniards were able to set a firm foothold on the islands of the Philippines for over 300 years, to the transition from Spanish rule to fifty-year American colonial embrace of the Philippines, and up to the establishment of the Philippine Republic of the present. Although according to Dr. José Policarpio Bantug in his book A Short History of Medicine in the Philippines During The Spanish Regime, 1565-1898 there were "no authentic monuments have come down to us that indicate with some certainty early medical practices" regarding the "beginnings of medicine in the Philippines" a historian from the United States named Edward Gaylord Borne described that the Philippines became "ahead of all the other European colonies" in providing healthcare to ill and invalid people during the start of the 17th century, a time period when the Philippines was a colony of Spain. From the 17th and 18th centuries, there had been a "state-of-the-art medical and pharmaceutical science" developed by Spanish friars based on Filipino curanderos that was "unique to the [Philippine] islands."
Mental health in the Philippines is a survey of the status of psychological, psychiatric, and emotional health care in the Philippines from both past and present programs.
Shenkui is a traditional Chinese medicinal term in which the individual suffers withdrawal like symptoms including chills, nausea, and even flu-like symptoms with anxiety, believed to be caused by an orgasm and loss of semen. The symptoms can last weeks to months after a single orgasm. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, shen (kidney) is the reservoir of vital essence in semen (ching) and k’uei signifies deficiency.
The Filipino American identity comprises principles from both the Philippines and the United States. Although the meaning of identity differs from one individual to another, the fundamental factors are the same. History, genetics, socio-economic status, culture, and education are all indirect factors that influences the identity of an ethnic group; thus, they are also reflective of a group's health beliefs and practices.

The indigenous religious beliefs of the Tagalog people were well documented by Spanish missionaries, mostly in the form of epistolary accounts (relaciones) and entries in various dictionaries compiled by missionary friars.
References
- 1 2 Jocano, F. Landa (1973). Folk Medicine in a Philippine Community. Quezon City: Punlad Research House, Inc. ISBN 971-622-015-4.
- 1 2 Tan, Michael (August 8, 2007). "'Pasma' (Part 1)". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Archived from the original on February 22, 2013.
- ↑ Tan, Michael (August 10, 2007). "'Pasma' (Part 2)". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Archived from the original on February 21, 2013.
- 1 2 de Leon, Remi (2005). Health Knowledge Processes and Flows in a Coastal Community in Victoria, Laguna Philippines (Masters thesis). University of the Philippines Los Baños Graduate School.
- ↑ Palis, F.; Flor, R.; Warburton, H.; Hossain, M. (2006). "Our farmers at risk: behavior and belief system in pesticide safety". Journal of Public Health. 28 (1): 43–48. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdi066 . PMID 16436451.