Related Research Articles

Anesthesia or anaesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia, paralysis, amnesia, and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized.
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure. Examples of drugs which can be used for sedation include isoflurane, diethyl ether, propofol, etomidate, ketamine, pentobarbital, lorazepam and midazolam.

General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a method of medically inducing loss of consciousness that renders a patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general anaesthetic medications, which often act in combination with an analgesic and neuromuscular blocking agent. Spontaneous ventilation is often inadequate during the procedure and intervention is often necessary to protect the airway. General anaesthesia is generally performed in an operating theater to allow surgical procedures that would otherwise be intolerably painful for a patient, or in an intensive care unit or emergency department to facilitate endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients. Regardless of whether a patient may prefer to be unconscious or not, certain pain stimuli could result in involuntary responses from the patient that may make an operation extremely difficult. Thus, for many procedures, general anaesthesia is required from a practical perspective.
Postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) is the phenomenon of nausea, vomiting, or retching experienced by a patient in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) or within 24 hours following a surgical procedure. PONV affects about 10% of the population undergoing general anaesthesia each year. PONV can be unpleasant and lead to a delay in mobilization and food, fluid, and medication intake following surgery.
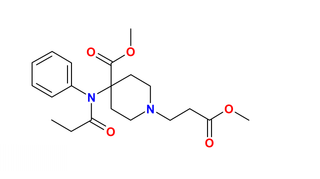
Remifentanil, marketed under the brand name Ultiva is a potent, short-acting synthetic opioid analgesic drug. It is given to patients during surgery to relieve pain and as an adjunct to an anaesthetic. Remifentanil is used for sedation as well as combined with other medications for use in general anesthesia. The use of remifentanil has made possible the use of high-dose opioid and low-dose hypnotic anesthesia, due to synergism between remifentanil and various hypnotic drugs and volatile anesthetics.
Perioperative mortality has been defined as any death, regardless of cause, occurring within 30 days after surgery in or out of the hospital. Globally, 4.2 million people are estimated to die within 30 days of surgery each year. An important consideration in the decision to perform any surgical procedure is to weigh the benefits against the risks. Anesthesiologists and surgeons employ various methods in assessing whether a patient is in optimal condition from a medical standpoint prior to undertaking surgery, and various statistical tools are available. ASA score is the most well known of these.
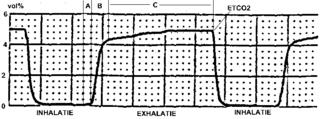
Capnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide (CO
2) in the respiratory gases. Its main development has been as a monitoring tool for use during anesthesia and intensive care. It is usually presented as a graph of CO
2 (measured in kilopascals, "kPa" or millimeters of mercury, "mmHg") plotted against time, or, less commonly, but more usefully, expired volume (known as volumetric capnography). The plot may also show the inspired CO
2, which is of interest when rebreathing systems are being used. When the measurement is taken at the end of a breath (exhaling), it is called "end tidal" CO
2 (PETCO2).
Antibiotic prophylaxis refers to, for humans, the prevention of infection complications using antimicrobial therapy. Antibiotic prophylaxis in domestic animal feed mixes has been employed in America since at least 1970.
The perioperative period is the period of a patient's surgical procedure. It commonly includes ward admission, anesthesia, surgery, and recovery. Perioperative may refer to the three phases of surgery: preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative, though it is a term most often used for the first and third of these only - a term which is often specifically utilized to imply 'around' the time of the surgery. The primary concern of perioperative care is to provide better conditions for patients before an operation and after an operation.
The ASA physical status classification system is a system for assessing the fitness of patients before surgery. In 1963 the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) adopted the five-category physical status classification system; a sixth category was later added. These are:
- Healthy person.
- Mild systemic disease.
- Severe systemic disease.
- Severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life.
- A moribund person who is not expected to survive without the operation.
- A declared brain-dead person whose organs are being removed for donor purposes.

Neurocritical care is a medical field that treats life-threatening diseases of the nervous system and identifies, prevents, and treats secondary brain injury.
Cardiothoracic anesthesiology is a subspeciality of the medical practice of anesthesiology, devoted to the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care of adult and pediatric patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery and related invasive procedures.

Clevidipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker indicated for the reduction of blood pressure when oral therapy is not feasible or not desirable. Clevidipine is used IV only and practitioners titrate this drug to lower blood pressure. It has a half-life of approximately one minute. It is rapidly inactivated by esterases.
David L. Reich is an American academic anesthesiologist, who has been President & Chief Operating Officer of The Mount Sinai Hospital, and President of Mount Sinai Queens, since October 2013.
Procedural sedation and analgesia (PSA) is a technique in which a sedating/dissociative medication is given, usually along with an analgesic medication, in order to perform non-surgical procedures on a patient. The overall goal is to induce a decreased level of consciousness while maintaining the patient's ability to breathe on their own. Airway protective reflexes are not compromised by this process and therefore endotracheal intubation is not required. PSA is commonly used in the emergency department, in addition to the operating room.
Emergence delirium is a condition in which emergence from general anesthesia is accompanied by psychomotor agitation. Some see a relation to pavor nocturnus while others see a relation to the excitement stage of anesthesia.

Postoperative residual curarization (PORC) or residual neuromuscular blockade (RNMB) is a residual paresis after emergence from general anesthesia that may occur with the use of neuromuscular-blocking drugs. Today residual neuromuscular blockade is defined as a train of four ratio of less than 0.9 when measuring the response to ulnar nerve stimulation at the adductor pollicis muscle using mechanomyography or electromyography. A meta-analysis reported that the incidence of residual neuromuscular paralysis was 41% in patients receiving intermediate neuromuscular blocking agents during anaesthesia. It is possible that > 100,000 patients annually in the USA alone, are at risk of adverse events associated with undetected residual neuromuscular blockade. Neuromuscular function monitoring and the use of the appropriate dosage of sugammadex to reverse blockade produced by rocuronium can reduce the incidence of postoperative residual curarization. In this study, with usual care group receiving reversal with neostigmine resulted in a residual blockade rate of 43%.

Peter Kranke is anesthetist and professor of anesthesiology at the University of Würzburg, Germany. Kranke is known for the design and conduct of clinical studies and for performing systematic reviews in the context of perioperative medicine. He published numerous papers on research focussed on evidence-based medicine and interventional and observational trials on postoperative nausea and vomiting and other issues in conjunction with perioperative medicine and associated topics including patient blood management. The area of his clinical responsibility and interest, among others, is the safe provision of anesthesia and analgesia in obstetrics and gynecology.
Total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA) refers to the intravenous administration of anesthetic agents to induce a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. The first study of TIVA was done in 1872 using chloral hydrate, and the common anesthetic agent propofol was licensed in 1986. TIVA is currently employed in various procedures as an alternative technique of general anesthesia in order to improve post-operative recovery.
Alex Macario is an American anesthesiologist, academic and author. He is a vice-chair for education, a professor in the Department of Anesthesiology, Perioperative and Pain Medicine, and program director for the anesthesiology residency at Stanford University School of Medicine.
References
- 1 2 "Post Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) | Renaissance School of Medicine at Stony Brook University". renaissance.stonybrookmedicine.edu. Retrieved 2022-03-23.
- 1 2 Simpson JC, Moonesinghe SR (March 2013). "Introduction to the postanaesthetic care unit". Perioperative Medicine. 2 (1): 5. doi: 10.1186/2047-0525-2-5 . PMC 3964324 . PMID 24472674.
- 1 2 Chang J (2019). Global reconstructive surgery. Edinburgh. ISBN 978-0-323-56860-9. OCLC 1053860785.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ↑ Chekol B, Eshetie D, Temesgen N (2021). "Assessment of Staffing and Service Provision in the Post-Anesthesia Care Unit of Hospitals Found in Amhara Regional State, 2020". Drug, Healthcare and Patient Safety. 13: 125–131. doi: 10.2147/DHPS.S302303 . PMC 8180306 . PMID 34104000.
- 1 2 3 Hines R, Barash PG, Watrous G, O'Connor T (April 1992). "Complications occurring in the postanesthesia care unit: a survey". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 74 (4): 503–509. doi: 10.1213/00000539-199204000-00006 . PMID 1554116. S2CID 28978751.