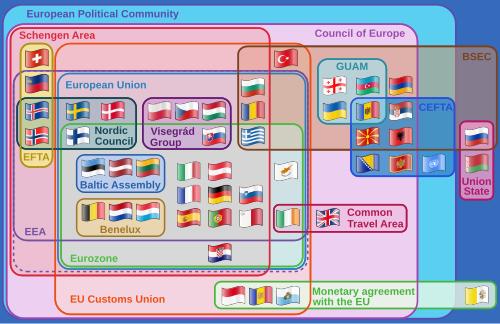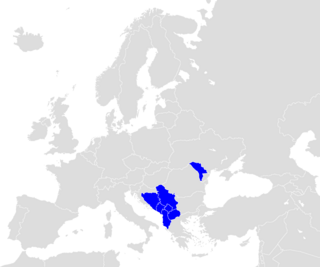
The Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA) is an international trade agreement between countries mostly located in Southeastern Europe. Founded by representatives of Poland, Hungary and Czechoslovakia, CEFTA in 2006 expanded to Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia and the UNMIK.

The European Banking Federation (EBF) is a trade association representing national banking associations in countries of the European Union and the European Free Trade Association. It represents over 3,500 banks and about 2.6 million employees. It was established in 1960 as the Fédération bancaire européenne.

Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the cultural region of Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of the region, due to political, economic, historical, cultural, and geographical considerations.

EuroVoc is a multilingual thesaurus maintained by the Publications Office of the European Union and hosted on the portal Europa. It exists in the 24 official languages of the European Union plus Albanian, Macedonian and Serbian, although the user interface is not yet available in these languages.
As a member of FIFA and UEFA, the Montenegro national football team has been playing official matches since March 2007. Montenegro plays in the qualifiers for the FIFA World Cup and UEFA European Championship, as well as partaking in the UEFA Nations League. Apart from that, the team participates in friendly matches.

The following is an alphabetical list of subregions in the United Nations geoscheme for Europe, created by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD). The scheme subdivides the continent into Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, Southern Europe, and Western Europe. The UNSD notes that "the assignment of countries or areas to specific groupings is for statistical convenience and does not imply any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories".
AMC Networks International Central and Northern Europe is a Budapest, Hungary-based television company, owned by AMC Networks International.
East-Central Europe is the region between German-, Hungarian-, and West Slavic-speaking Europe and the East Slavic countries of Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine. Those lands are described as situated "between two": "between two worlds, between two stages, between two futures".

The 29th and final SPAR European Cup took place in June 2008. Track and field events were held on 21 and 22 June 2008 at the Parc des Sports Stadium in Annecy, France. Other event venues included Estádio Dr. Magalhães Pessoa in Portugal and facilities in Istanbul, Turkey, Kadriorg Stadium in Estonia and SNP Stadium in Slovakia, and facilities in Eindhoven, Netherlands. The Parc des Sports Annecy Stadium was also stadium for 1998 World Junior Championships in Athletics. It was the last edition of the European Cup which from 2009 has been replaced by European Team Championships combining the men and women competitions.

The European Chess Union (ECU) is an independent association for the interests of European chess.
The 2011 European Junior Swimming Championships were held from 6–10 July 2011 in Belgrade, Serbia. The Championships were organized by Ligue Européenne de Natation (LEN), the European Swimming League, and were held in a 50-meter pool. Per LEN rules, competitors were aged 15 or 16 for girls and 17 or 18 for boys.

This is a list of the Romania national football team results from 2000 to 2019:
This article provides details of international football games played by the Israel national football team from 1990 to 2019.
The 2019 FIBA Basketball World Cupqualification for the FIBA Europe region, began in August 2017 and concluded in February 2019. Contrary to previous years, no teams were automatically placed into the World Cup, so all FIBA Europe nations had to participate in qualification.
The Slovenia national football team represents Slovenia in association football and is controlled by the Football Association of Slovenia, the governing body for football in Slovenia. It competes as a member of the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA), which encompasses the countries of Europe. Slovenia joined UEFA and the International Federation of Association Football (FIFA) in 1992, a year after the country gained independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.
This page describes the qualification procedure for FIBA Women's EuroBasket 2021. 14 teams joined the co-hosts France and Spain.

The Lithuania national football team represents Lithuania in association football and is controlled by the Lithuanian Football Federation (LFF), the governing body of the sport in the country.

This is a list of the Poland national football team results from 2000 to 2019.
The EuroBasket Women 2023 qualification was held from November 2021 to February 2023 to decide the 14 teams to join the co-hosts Israel and Slovenia. It featured 38 teams split in ten groups of three or four teams. The ten group winners and the four best second-ranked teams qualified for the final tournament.

This article provides details of international football games played by the Hungary national football team from 2000 to 2009.