Related Research Articles

Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is "the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients." The aim of EBM is to integrate the experience of the clinician, the values of the patient, and the best available scientific information to guide decision-making about clinical management. The term was originally used to describe an approach to teaching the practice of medicine and improving decisions by individual physicians about individual patients.
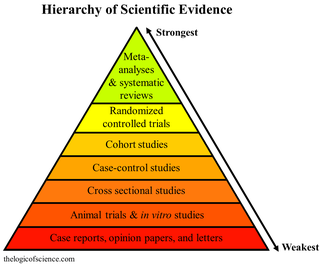
Meta-analysis is the statistical combination of the results of multiple studies addressing a similar research question. An important part of this method involves computing an effect size across all of the studies; this involves extracting effect sizes and variance measures from various studies. Meta-analyses are integral in supporting research grant proposals, shaping treatment guidelines, and influencing health policies. They are also pivotal in summarizing existing research to guide future studies, thereby cementing their role as a fundamental methodology in metascience. Meta-analyses are often, but not always, important components of a systematic review procedure. For instance, a meta-analysis may be conducted on several clinical trials of a medical treatment, in an effort to obtain a better understanding of how well the treatment works.

A randomized controlled trial is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical techniques, medical devices, diagnostic procedures or other medical treatments.

Cochrane is a British international charitable organisation formed to synthesize medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professionals, patients and policy makers. It includes 53 review groups that are based at research institutions worldwide. Cochrane has approximately 30,000 volunteer experts from around the world.

The Cochrane Library is a collection of databases in medicine and other healthcare specialties provided by Cochrane and other organizations. At its core is the collection of Cochrane Reviews, a database of systematic reviews and meta-analyses which summarize and interpret the results of medical research. The Cochrane Library aims to make the results of well-conducted controlled trials readily available and is a key resource in evidence-based medicine.
In a blind or blinded experiment, information which may influence the participants of the experiment is withheld until after the experiment is complete. Good blinding can reduce or eliminate experimental biases that arise from a participants' expectations, observer's effect on the participants, observer bias, confirmation bias, and other sources. A blind can be imposed on any participant of an experiment, including subjects, researchers, technicians, data analysts, and evaluators. In some cases, while blinding would be useful, it is impossible or unethical. For example, it is not possible to blind a patient to their treatment in a physical therapy intervention. A good clinical protocol ensures that blinding is as effective as possible within ethical and practical constraints.
In published academic research, publication bias occurs when the outcome of an experiment or research study biases the decision to publish or otherwise distribute it. Publishing only results that show a significant finding disturbs the balance of findings in favor of positive results. The study of publication bias is an important topic in metascience.

A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on the topic, then analyzes, describes, critically appraises and summarizes interpretations into a refined evidence-based conclusion. For example, a systematic review of randomized controlled trials is a way of summarizing and implementing evidence-based medicine.

In fields such as epidemiology, social sciences, psychology and statistics, an observational study draws inferences from a sample to a population where the independent variable is not under the control of the researcher because of ethical concerns or logistical constraints. One common observational study is about the possible effect of a treatment on subjects, where the assignment of subjects into a treated group versus a control group is outside the control of the investigator. This is in contrast with experiments, such as randomized controlled trials, where each subject is randomly assigned to a treated group or a control group. Observational studies, for lacking an assignment mechanism, naturally present difficulties for inferential analysis.
Peter Christian Gøtzsche is a Danish physician, medical researcher, and former leader of the Nordic Cochrane Center at Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen, Denmark. He is a co-founder of the Cochrane Collaboration and has written numerous reviews for the organization. His membership in Cochrane was terminated by its Governing Board of Trustees on 25 September 2018. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Gøtzsche was criticised for spreading disinformation about COVID-19 vaccines.
The Jadad scale, sometimes known as Jadad scoring or the Oxford quality scoring system, is a procedure to assess the methodological quality of a clinical trial by objective criteria. It is named after Canadian-Colombian physician Alex Jadad who in 1996 described a system for allocating such trials a score of between zero and five (rigorous). It is the most widely used such assessment in the world, and as of 2022, its seminal paper has been cited in over 23,000 scientific works.

John P. A. Ioannidis is a Greek-American physician-scientist, writer and Stanford University professor who has made contributions to evidence-based medicine, epidemiology, and clinical research. Ioannidis studies scientific research itself, meta-research primarily in clinical medicine and the social sciences.
Funding bias, also known as sponsorship bias, funding outcome bias, funding publication bias, and funding effect, refers to the tendency of a scientific study to support the interests of the study's financial sponsor. This phenomenon is recognized sufficiently that researchers undertake studies to examine bias in past published studies. Funding bias has been associated, in particular, with research into chemical toxicity, tobacco, and pharmaceutical drugs. It is an instance of experimenter's bias.
Tom Jefferson is a British epidemiologist, based in Rome, Italy, who works for the Cochrane Collaboration. Jefferson is an author and editor of the Cochrane Collaboration's acute respiratory infections group, as well as part of four other Cochrane groups. He was also an advisor to the Italian National Agency for Regional Health Services.
Isabelle Boutron is a professor of epidemiology at the Université Paris Cité and head of the INSERM- METHODS team within the Centre of Research in Epidemiology and Statistics (CRESS). She was originally trained in rheumatology and later switched to a career in epidemiology and public health. She is also deputy director of the French EQUATOR Centre, member of the SPIRIT-CONSORT executive committee, director of Cochrane France and co-convenor of the Bias Methods group of the Cochrane Collaboration.
Kay Dickersin is an academic who trained first in cell biology and subsequently epidemiology. She went on to a career studying factors that influence research integrity, in particular publication bias and outcome reporting bias. She is retired Professor Emerita in the Department of Epidemiology at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health where she was Director of the Center for Clinical Trials and Evidence Synthesis there. She was also Director of the US Cochrane Center and the US Satellite of the Cochrane Eyes and Vision Group within the Cochrane Collaboration. Dickersin received multiple awards for her research.
Allegiance bias in behavioral sciences is a bias resulted from the investigator's or researcher's allegiance to a specific school of thought. Researchers/investigators have been exposed to many types of branches of psychology or schools of thought. Naturally they adopt a school or branch that fits with their paradigm of thinking. More specifically, allegiance bias is when this leads therapists, researchers, etc. believing that their school of thought or treatment is superior to others. Their superior belief to these certain schools of thought can bias their research in effective treatments trials or investigative situations leading to allegiance bias. Reason being is that they may have devoted their thinking to certain treatments they have seen work in their past experiences. This can lead to errors in interpreting the results of their research. Their “pledge” to stay within their own paradigm of thinking may affect their ability to find more effective treatments to help the patient or situation they are investigating.
Preregistration is the practice of registering the hypotheses, methods, and/or analyses of a scientific study before it is conducted. Clinical trial registration is similar, although it may not require the registration of a study's analysis protocol. Finally, registered reports include the peer review and in principle acceptance of a study protocol prior to data collection.
Outcome switching is the practice of changing the primary or secondary outcomes of a clinical trial after its initiation. Outcome switching can lead to bias and undermine the reliability of the trial, for instance when outcomes are switched after researchers already have access to trial data. That way, researchers can cherry pick an outcome which is statistically significant.
References
- ↑ Porta M, ed. (5 June 2008). A Dictionary of Epidemiology. Oxford University Press. p. 275. ISBN 978-0-19-157844-1 . Retrieved 27 March 2013.
- 1 2 Gordon J, Van Durme B (2013). "Reporting bias and knowledge acquisition". Proceedings of the 2013 workshop on Automated knowledge base construction - AKBC '13. pp. 25–30. doi:10.1145/2509558.2509563. hdl:1802/28266. ISBN 978-1-4503-2411-3. S2CID 16567195.
- ↑ McGauran N, Wieseler B, Kreis J, Schüler YB, Kölsch H, Kaiser T (April 2010). "Reporting bias in medical research - a narrative review". Trials. 11 (1): 37. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-11-37 . PMC 2867979 . PMID 20388211.
- ↑ JP, Green S, eds. (24 November 2008). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-69951-5.[ page needed ]
- ↑ Rosenthal R (1979). "The file drawer problem and tolerance for null results". Psychological Bulletin. 86 (3): 638–641. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.86.3.638.
- 1 2 Vedula SS, Goldman PS, Rona IJ, Greene TM, Dickersin K (August 2012). "Implementation of a publication strategy in the context of reporting biases. A case study based on new documents from Neurontin litigation". Trials. 13 (136): 136. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-13-136 . PMC 3439687 . PMID 22888801.
- 1 2 Vedula SS, Bero L, Scherer RW, Dickersin K (November 2009). "Outcome reporting in industry-sponsored trials of gabapentin for off-label use". The New England Journal of Medicine. 361 (20): 1963–71. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa0906126 . PMID 19907043.
- ↑ Stempel J (2 June 2014). "Pfizer to pay $325 million in Neurontin settlement". Reuters. Retrieved 24 August 2014.
- ↑ "The Reporting of Unsuccessful Cases — Hand Disinfection in Out-Patient Clinics — Training of Parents in the Care of Children — Medical Notes". The Boston Medical and Surgical Journal. 161 (8): 263–266. 19 August 1909. doi:10.1056/nejm190908191610809.
- 1 2 Dickersin K (2006). "Publication Bias: Recognizing the Problem, Understanding Its Origins and Scope, and Preventing Harm". Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis. pp. 9–33. doi:10.1002/0470870168.ch2. ISBN 978-0-470-87016-7.
- ↑ Godlee F, Dickersin K (2003). "Bias, Subjectivity, Chance, and Conflict of Interest in Editorial Decisions". In Godlee F, Jefferson T (eds.). Peer review in health sciences (2nd ed.). London: BMJ Books. pp. 91–117. hdl:10822/1004354. ISBN 978-0-7279-1685-3.
- ↑ Olson CM, Rennie D, Cook D, Dickersin K, Flanagin A, Hogan JW, et al. (June 2002). "Publication bias in editorial decision making". JAMA. 287 (21): 2825–8. doi:10.1001/jama.287.21.2825. PMID 12038924.
- ↑ Song F, Parekh S, Hooper L, Loke YK, Ryder J, Sutton AJ, et al. (February 2010). "Dissemination and publication of research findings: an updated review of related biases". Health Technology Assessment. 14 (8): iii, ix–xi, 1–193. doi: 10.3310/hta14080 . PMID 20181324.
- ↑ Scherer RW, Langenberg P, von Elm E (April 2007). "Full publication of results initially presented in abstracts". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): MR000005. doi:10.1002/14651858.MR000005.pub3. PMID 17443628.
- 1 2 3 Hopewell S, Clarke M, Stewart L, Tierney J (April 2007). "Time to publication for results of clinical trials". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2010 (2): MR000011. doi:10.1002/14651858.MR000011.pub2. PMC 7437393 . PMID 17443632.
- ↑ Hopewell S, Loudon K, Clarke MJ, Oxman AD, Dickersin K (January 2009). "Publication bias in clinical trials due to statistical significance or direction of trial results". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2010 (1): MR000006. doi:10.1002/14651858.MR000006.pub3. hdl: 1893/22314 . PMC 8276556 . PMID 19160345.
- ↑ Lundh A, Lexchin J, Mintzes B, Schroll JB, Bero L (February 2017). "Industry sponsorship and research outcome" (PDF). The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (2): MR000033. doi:10.1002/14651858.MR000033.pub3. PMC 8132492 . PMID 28207928.
- ↑ von Elm E, Poglia G, Walder B, Tramèr MR (February 2004). "Different patterns of duplicate publication: an analysis of articles used in systematic reviews". JAMA. 291 (8): 974–80. doi:10.1001/jama.291.8.974. PMID 14982913.
- ↑ Easterbrook PJ, Berlin JA, Gopalan R, Matthews DR (April 1991). "Publication bias in clinical research". Lancet. 337 (8746): 867–72. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90201-y . PMID 1672966. S2CID 36570135.
- ↑ Hopewell S, McDonald S, Clarke M, Egger M (April 2007). "Grey literature in meta-analyses of randomized trials of health care interventions". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2010 (2): MR000010. doi:10.1002/14651858.MR000010.pub3. PMC 8973936 . PMID 17443631.
- ↑ Gøtzsche PC (September 1987). "Reference bias in reports of drug trials". British Medical Journal. 295 (6599): 654–6. doi:10.1136/bmj.295.6599.654. PMC 1257776 . PMID 3117277.
- ↑ Kjaergard LL, Gluud C (April 2002). "Citation bias of hepato-biliary randomized clinical trials". Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 55 (4): 407–10. doi:10.1016/s0895-4356(01)00513-3. PMID 11927210.
- ↑ Schmidt LM, Gotzsche PC (April 2005). "Of mites and men: reference bias in narrative review articles: a systematic review". The Journal of Family Practice. 54 (4): 334–8. PMID 15833223. Gale A131501020.
- ↑ Nieminen P, Rucker G, Miettunen J, Carpenter J, Schumacher M (September 2007). "Statistically significant papers in psychiatry were cited more often than others". Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 60 (9): 939–46. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.11.014. PMID 17689810.
- ↑ Pham B, Klassen TP, Lawson ML, Moher D (August 2005). "Language of publication restrictions in systematic reviews gave different results depending on whether the intervention was conventional or complementary". Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 58 (8): 769–76. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.08.021. PMID 16086467.
- ↑ Jüni P, Holenstein F, Sterne J, Bartlett C, Egger M (February 2002). "Direction and impact of language bias in meta-analyses of controlled trials: empirical study" (PDF). International Journal of Epidemiology. 31 (1): 115–23. doi: 10.1093/ije/31.1.115 . PMID 11914306.
- ↑ Misra I, Lawrence Zitnick C, Mitchell M, Girshick R (2016). "Seeing through the Human Reporting Bias: Visual Classifiers from Noisy Human-Centric Labels". 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). pp. 2930–2939. arXiv: 1512.06974 . doi:10.1109/CVPR.2016.320. ISBN 978-1-4673-8851-1. S2CID 3039286.
- ↑ Sterne JA, Egger M, Moher D (2008). "Addressing Reporting Biases". Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. pp. 297–333. doi:10.1002/9780470712184.ch10. ISBN 978-0-470-71218-4.
- ↑ Chan AW, Krleza-Jerić K, Schmid I, Altman DG (September 2004). "Outcome reporting bias in randomized trials funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research". CMAJ. 171 (7): 735–40. doi:10.1503/cmaj.1041086. PMC 517858 . PMID 15451835.
- ↑ Hemminki E (March 1980). "Study of information submitted by drug companies to licensing authorities". British Medical Journal. 280 (6217): 833–6. doi:10.1136/bmj.280.6217.833. PMC 1601011 . PMID 7370687.