In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula HCO−
3.

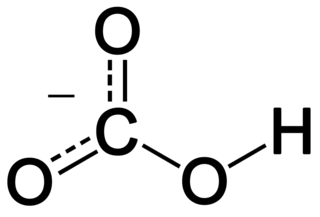
Citric acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2. It is a colorless weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism of all aerobic organisms.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.

In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word "base": Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century.

Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda, is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt composed of a sodium cation (Na+) and a bicarbonate anion (HCO3−). Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline, but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda (sodium carbonate). The natural mineral form is nahcolite. It is a component of the mineral natron and is found dissolved in many mineral springs.

Sodium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants grown in sodium-rich soils, and because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood, sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process, as well as by carbonating sodium hydroxide which is made using the Chlor-alkali process.

An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base. "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion typically found in aqueous solution and written with the chemical formula C
2H
3O−
2. The neutral molecules formed by the combination of the acetate ion and a positive ion are also commonly called "acetates". The simplest of these is hydrogen acetate with corresponding salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion CH
3CO−
2, or CH
3COO−
.
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image into a visible image, makes this permanent and renders it insensitive to light.

Sodium hypochlorite is an alkaline inorganic chemical compound with the formula NaOCl. It is commonly known in a dilute aqueous solution as bleach or chlorine bleach. It is the sodium salt of hypochlorous acid, consisting of sodium cations and hypochlorite anions.

Collodion is a flammable, syrupy solution of nitrocellulose in ether and alcohol. There are two basic types: flexible and non-flexible. The flexible type is often used as a surgical dressing or to hold dressings in place. When painted on the skin, collodion dries to form a flexible nitrocellulose film. While it is initially colorless, it discolors over time. Non-flexible collodion is often used in theatrical make-up. Collodion was also the basis of most wet-plate photography until it was superseded by modern gelatin emulsions.

In the processing of photographic films, plates or papers, the photographic developer is one or more chemicals that convert the latent image to a visible image. Developing agents achieve this conversion by reducing the silver halides, which are pale-colored, into silver metal, which is black when in the form of fine particles. The conversion occurs within the gelatine matrix. The special feature of photography is that the developer acts more quickly on those particles of silver halide that have been exposed to light. When left in developer, all the silver halides will eventually be reduced and turn black. Generally, the longer a developer is allowed to work, the darker the image.

In chemistry, neutralization or neutralisation is a chemical reaction in which acid and a base react with an equivalent quantity of each other. In a reaction in water, neutralization results in there being no excess of hydrogen or hydroxide ions present in the solution. The pH of the neutralized solution depends on the acid strength of the reactants.

Copper electroplating is the process of electroplating a layer of copper onto the surface of a metal object. Copper is used both as a standalone coating and as an undercoat onto which other metals are subsequently plated. The copper layer can be decorative, provide corrosion resistance, increase electrical and thermal conductivity, or improve the adhesion of additional deposits to the substrate.

Sodium acetate, CH3COONa, also abbreviated NaOAc, is the sodium salt of acetic acid. This colorless deliquescent salt has a wide range of uses.
Pickling is a metal surface treatment used to remove impurities, such as stains, inorganic contaminants, and rust or scale from ferrous metals, copper, precious metals and aluminum alloys. A solution called pickle liquor, which usually contains acid, is used to remove the surface impurities. It is commonly used to descale or clean steel in various steelmaking processes.

Bromocresol purple (BCP) or 5′,5″-dibromo-o-cresolsulfophthalein, is a dye of the triphenylmethane family and a pH indicator. It is colored yellow below pH 5.2, and violet above pH 6.8. In its cyclic sulfonate ester form, it has a pKa value of 6.3, and is usually prepared as a 0.04% aqueous solution.

Cleaning agents or hard-surface cleaners are substances used to remove dirt, including dust, stains, foul odors, and clutter on surfaces. Purposes of cleaning agents include health, beauty, removing offensive odor, and avoiding the spread of dirt and contaminants to oneself and others. Some cleaning agents can kill bacteria and clean at the same time. Others, called degreasers, contain organic solvents to help dissolve oils and fats.

The blue bottle experiment is a color-changing redox chemical reaction. An aqueous solution containing glucose, sodium hydroxide, methylene blue is prepared in a closed bottle containing some air. Upon standing, it spontaneously turns from blue to colorless due to reduction of methylene blue by the alkaline glucose solution. However, shaking the bottle oxidizes methylene blue back into its blue form. With further shaking, this color-change cycle can be repeated many times. This experiment is a classic chemistry demonstration that can be used in laboratory courses as a general chemistry experiment to study chemical kinetics and reaction mechanism. The reaction also works with other reducing agents besides glucose and other redox indicator dyes besides methylene blue.

Mordançage is an alternative photographic process that alters silver gelatin prints to give them a degraded effect. The mordançage solution works in two ways: it chemically bleaches the print so that it can be redeveloped, and it lifts the black areas of the emulsion away from the paper giving the appearance of veils. Once the emulsion is lifted, it can then be removed or manipulated depending on the desired outcome. Areas where the emulsion was removed appear to be in relief. These prints can become oxidized during their creation, further altering the tonality of the image.

The dry ice color show is a demonstration of the chemical formation of carbonic acid by the dissolution of dry ice in water. The dry ice color show is usually performed in classrooms to demonstrate the properties of acids and bases, their effect on pH indicators, and the sublimation of dry ice. Setup is simple and generally involves only minor hazards, the main one being the low temperature of dry ice, which can cause frostbite upon skin contact. The carbonic acid formed in the demonstration is a weak acid and is not hazardous, being present in numerous consumer products including tonic water, soda, and beer.


















