A body cavity is any space or compartment, or potential space, in an animal body. Cavities accommodate organs and other structures; cavities as potential spaces contain fluid.

The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines, among other functions.

In human anatomy, the groin also known as the inguinal region or iliac region, is the junctional area between the torso and the thigh. The groin is at the front of the body on either side of the pubic tubercle, where the lower part of the abdominal wall meets the thigh. A fold or crease is formed at this junction known as the inguinal groove, or crease. This is also the area of the medial compartment of the thigh that contains attachments of the adductor muscles of the hip or the groin muscles. The groin is the common site for a hernia.

The lesser omentum is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach, and to the first part of the duodenum. The lesser omentum is usually divided into these two connecting parts: the hepatogastric ligament, and the hepatoduodenal ligament.

In the anatomy of humans and homologous primates, the ascending colon is the part of the colon located between the cecum and the transverse colon.

The internal iliac artery is the main artery of the pelvis.

In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath, then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath.

In anatomy, the abdominal wall represents the boundaries of the abdominal cavity. The abdominal wall is split into the anterolateral and posterior walls.

In human anatomy, the falciform ligament is a ligament that attaches the liver to the front body wall and divides the liver into the left lobe and right lobe. The falciform ligament is a broad and thin fold of peritoneum, its base being directed downward and backward and its apex upward and forward. It droops down from the hilum of the liver.
In human anatomy, the inguinal region refers to either the groin or the lower lateral regions of the abdomen. It may also refer to:

The pelvic cavity is a body cavity that is bounded by the bones of the pelvis. Its oblique roof is the pelvic inlet. Its lower boundary is the pelvic floor.

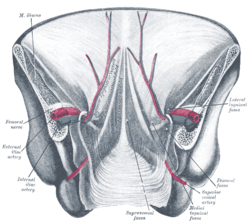
The lateral umbilical fold is an elevation of the peritoneum lining the inner/posterior surface of the lower anterior abdominal wall formed by the underlying inferior epigastric artery and inferior epigastric vein which the peritoneum covers. Superiorly, the lateral umbilical fold ends where the vessels reach and enter the rectus sheath at the arcuate line of rectus sheath; in spite of the name, the lateral umbilical folds do not extend as far superiorly as the umbilicus. Inferiorly, it extends to just medial to the deep inguinal ring.

In human anatomy, the median umbilical ligament is an unpaired midline ligamentous structure upon the lower inner surface of the anterior abdominal wall. It is covered by the median umbilical fold.

The medial umbilical ligament is a paired structure found in human anatomy. It is on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall, and is covered by the medial umbilical folds. It is different from the median umbilical ligament, a structure that represents the remnant of the embryonic urachus.

The lateral inguinal fossa is a structure described in human anatomy. It is a shallow concave stretch of peritoneum on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall and is best seen from the greater peritoneal cavity, looking anteriorly.

The medial umbilical fold is an elevation of the peritoneum lining the inner surface of the lower anterior abdominal wall formed by the underlying medial umbilical ligament which the peritoneum covers. Superiorly, the two medial umbilical folds converge towards the midline to meet and terminate at the umbilicus.

The medial inguinal fossa is a depression located within the inguinal triangle on the peritoneal surface of the anterior abdominal wall between the ridges formed by the lateral umbilical fold and the medial umbilical ligament, corresponding to the superficial inguinal ring.

The peritoneum of the anterior pelvic wall covers the superior surface of the bladder, and on either side of this viscus forms a depression, termed the paravesical fossa, which is limited laterally by the fold of peritoneum covering the ductus deferens.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
The development of the digestive system in the human embryo concerns the epithelium of the digestive system and the parenchyma of its derivatives, which originate from the endoderm. Connective tissue, muscular components, and peritoneal components originate in the mesoderm. Different regions of the gut tube such as the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, etc. are specified by a retinoic acid gradient that causes transcription factors unique to each region to be expressed. Differentiation of the gut and its derivatives depends upon reciprocal interactions between the gut endoderm and its surrounding mesoderm. Hox genes in the mesoderm are induced by a Hedgehog signaling pathway secreted by gut endoderm and regulate the craniocaudal organization of the gut and its derivatives. The gut system extends from the oropharyngeal membrane to the cloacal membrane and is divided into the foregut, midgut, and hindgut.