
The COVID-19 pandemic in Scotland is part of the COVID-19 pandemic of coronavirus disease-2019, caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2. The first case of COVID-19 was confirmed in Scotland on 1 March 2020. Community transmission was first reported on 11 March 2020, and the first confirmed death was on 13 March 2020.
The first case relating to the COVID-19 pandemic in London, England, was confirmed on 12 February 2020 in a woman who had recently arrived from China. By March 2020, there had been almost 500 confirmed cases in the city, and 23 deaths; a month later, the number of deaths had topped 4,000.
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have spread to Wales on 28 February 2020, with a case being reported in the Swansea area; this first known case was a person who had recently returned from Italy. The first known case of community transmission was reported on 11 March in the Caerphilly area.
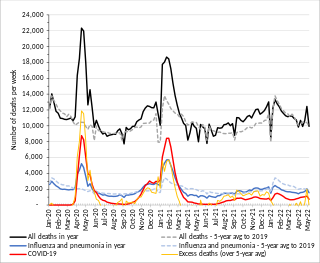
The COVID-19 pandemic was first confirmed to have spread to England with two cases among Chinese nationals staying in a hotel in York on 31 January 2020. The two main public bodies responsible for health in England are NHS England and Public Health England (PHE). NHS England oversees the budget, planning, delivery and day-to-day operation of the commissioning side of the NHS in England, while PHE's mission is "to protect and improve the nation's health and to address inequalities". As of 14 September 2021, there have been 6,237,505 total cases and 117,955 deaths in England. In January 2021, it was estimated around 22% of people in England have had COVID-19.

In response to the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom, the UK Government introduced various public health and economic measures to mitigate its impact. Devolution meant that the four nations' administrative responses to the pandemic differed; the Scottish Government, the Welsh Government, and the Northern Ireland Executive produced different policies to those that apply in England. Numerous laws were enacted or introduced throughout the crisis.
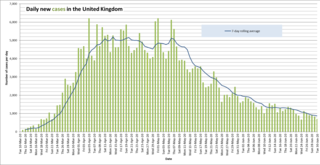
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom from January 2020 to June 2020.

NHS Test and Trace is a government-funded service in England, established in 2020 to track and help prevent the spread of COVID-19. The programme is part of the UK Health Security Agency; the service and the agency are headed by Jenny Harries.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in Northern Ireland during 2020. There are significant differences in the legislation and the reporting between the countries of the UK: England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Wales.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in Wales during 2020. There are significant differences in the legislation and the reporting between the countries of the UK: England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Wales.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in Scotland during 2020. There are significant differences in the legislation and the reporting between the countries of the UK: England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Wales.
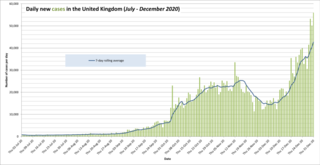
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom from July 2020 to December 2020.
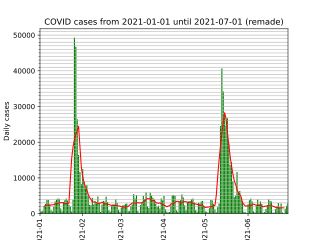
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom from January 2021 to June 2021.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in England during 2021. There are significant differences in the legislation and the reporting between the countries of the UK: England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Wales.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in England from July 2020 to December 2020. There are significant differences in the legislation and the reporting between the countries of the UK: England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Wales.

The United Kingdom's response to the COVID-19 pandemic consists of various measures by the healthcare community, the British and devolved governments, the military and the research sector.

This article outlines the history of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom. Though later reporting indicated that there may have been some cases dating from late 2019, COVID-19 was confirmed to be spreading in the UK by the end of January 2020. The country was initially relatively slow implementing restrictions but a legally enforced stay-at-home order had been introduced by late March. Restrictions were steadily eased across the UK in late spring and early summer that year.

The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom from January to June 2022.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in England during 2022. There are significant differences in the legislation and the reporting between the countries of the UK: England, Scotland, Northern Ireland, and Wales.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom in 2023.












