
Visakhapatnam, also known as Vizag, Viśākha or Waltair, is the largest and most populous metropolitan city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is between the Eastern Ghats and the coast of the Bay of Bengal. It is the second largest city on the east coast of India after Chennai, and the fourth-largest in South India. It is one of the four smart cities of Andhra Pradesh selected under the Smart Cities Mission and is the headquarters of Visakhapatnam district. With an estimated output of $43.5 billion, it is the ninth-largest contributor to India's gross domestic product as of 2016.

The Golden Quadrilateral is a national highway network connecting several major industrial, agricultural and cultural centres of India. It forms a quadrilateral with all the four major metro cities of India forming the vertices, viz., Delhi (north), Kolkata (east), Mumbai (west) and Chennai (south). Other major cities connected by this network include Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Balasore, Bhadrak, Bhubaneswar, Cuttack, Berhampur, Durgapur, Faridabad, Guntur, Gurugram, Jaipur, Kanpur, Pune, Kolhapur, Surat, Vijayawada, Eluru, Ajmer, Visakhapatnam, Bodhgaya, Varanasi, Prayagraj, Agra, Mathura, Dhanbad, Gandhinagar, Udaipur, and Vadodara. The main objective of these super highways is to reduce the travel time between the major cities of India, running roughly along the perimeter of the country. The North–South corridor linking Srinagar and Kanyakumari, and East–West corridor linking Silchar (Assam) and Porbandar (Gujarat) are additional projects. These highway projects are implemented by the National Highway Authority Of India (NHAI). At 5,846 kilometres (3,633 mi), it is the largest highway project in India and the fifth longest in the world. It is the first phase of the National Highways Development Project (NHDP), and consists of two, four, and six-lane express highways, built at a cost of ₹600 billion (US$7.5 billion). The project was planned in 1999, launched in 2001, and was completed in 7 January 2012.

Vijayawada, formerly known as Bezawada, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located on the banks of the Krishna River surrounded by the hills of the Eastern Ghats, known as the Indrakeeladri Hills. The city is home to the important Hindu shrine of Kanaka Durga Temple. It geographically lies on the center spot of Andhra Pradesh. The city has been described as the commercial, political, cultural and educational capital of Andhra Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of NTR district. The Prakasam Barrage across the Krishna River connects the NTR and Guntur districts.

Gannavaram is a suburb of Vijayawada in Krishna district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is also the mandal headquarters of Gannavaram mandal which is administered under Gudivada revenue division. It is a major suburb of Vijayawada in the North East side.Vijayawada International Airport, Medha IT Park, IT companies like HCL Tech and TechMahindra are located here.

Araku Valley is a hill station in Alluri Sitharama Raju district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh, lying 111 km west of Visakhapatnam city. It is a valley in the Eastern Ghats inhabited by different tribes, mainly Araku Tribes.

Gajuwaka is a major residential area of Visakhapatnam City, India. This neighborhood of Visakhapatnam is considered the biggest shopping district in Andhra Pradesh by revenue. Though conceived as a residential locality, it is now one of the principal shopping districts of the city. The Gajuwaka area of Visakhapatnam has the highest per capita income in Andhra Pradesh.

Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation, officially Andhra Pradesh Raastra Roadu Ravaana Samstha, is the state-owned road transport corporation in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. Its headquarters is located at NTR Administrative Block of RTC House in Pandit Nehru bus station of Vijayawada. Many other Indian metro towns in Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Odisha, Yanam, Kerala, Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh are also linked with the APSRTC services.
Pedagantyada is a neighbourhood in the city of Visakhapatnam, India. It is one of the 46 mandals in Visakhapatnam District. It is under the administration of Visakhapatnam revenue division and the headquarters is located at Pedagantyada beside Gajuwaka. The Mandal is bounded by Mulagada and Gajuwaka mandals. It is a major Suburb in Visakhapatnam and got merged in Greater Visakhapatnam Municipal Corporation in 2005. Organisations like Visakhapatnam Steel Plant, and Gangavaram Port are located in this area.

Pendurthi is a neighbourhood in the city of Visakhapatnam, India. The neighbourhood is considered as the major residential and commercial area in the city. It is located within the jurisdiction of the Greater Visakhapatnam Municipal Corporation, which is responsible for the civic amenities in Pendurthi. It is located on the west fringe of Visakhapatnam city. Pendurthi is one of the peaceful neighborhoods of Western Vizag. The pincode of Pendurthi is 531173.
Chilakaluripet is a city in Palnadu district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the Mandal headquarters of Chilakaluripet Mandal in Narasaraopet Revenue Division.

The economy of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh is primarily dependent on agriculture, which directly and indirectly employs 62% of the population. GSDP as per the first revised estimate, for the year 2023-24 is ₹15,40,000 crore.The state is ranked 1st in the country for the year 2021-22 in terms of the Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) growth at constant prices with growth rate of 11.43%. The state GSDP is expected to grow at a rate of 17% for the year 2023-24.

Visakhapatnam BRTS :-The implementation of the bus rapid transit system has been taken up as a high-capacity public transport system in Visakhapatnam keeping in view the projected multi-fold increase in traffic and constraints of road capacity. A Bus Rapid Transit System (BRTS) was approved for the city under the Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission. This project was started in 2008 and most of the route has been constructed except for a 2km stretch near Simhachalam. The delay is due to issues in land acquisition from railways, defence and private parties.

Madhurawada is a major business and residential area of Visakhapatnam in the state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located on the Visakhapatnam-Vizianagaram stretch of National Highway 16 around 16 km from the city center of Visakhapatnam.
GMR Visakhapatnam International Airport is an international airport and a greenfield airport under construction at Bhogapuram in Vizianagaram district, about 40 kilometres (25 mi) north-east of Visakhapatnam.

There are various modes of transportation available in Eluru, a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh, and its region. It includes auto rickshaws, bicycles to mass transit systems – such as buses and trains. The city was once famed for its traffic problems with the railway gates at Vatluru, Venkatraopet, Powerpet, Old bus stand and Eastern Locks areas. When the National Highway passed through the city, the traffic hurried to pass over the railway gates in the city and outskirts, which makes traffic worse.
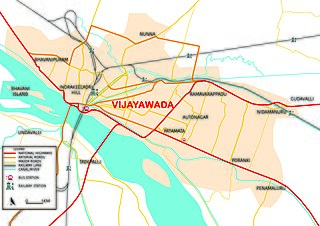
Transport in Vijayawada is the network of roads, railways, rapid transit system in the second largest city of Andhra Pradesh. The city of Vijayawada also serves as the central hub of transport and logistics within the state.
Anakapalli mandal is one of the mandals in located in Anakapalli district of the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. It is administered under Anakapalli revenue division and its headquarters are located at Anakapalli. It is bounded by Kasimkota Mandal towards west, Munagapaka Mandal towards South, Paravada Mandal towards East, Achutapuram Mandal towards South.
Transport in Visakhapatnam is the network of roads, railways, rapid transit system in the largest city of Andhra Pradesh. The city of Visakhapatnam also serves as the central hub of transport and logistics on the East coast of India and hence it is called as City Of Destiny.

There are various modes of transportation available in Nellore and its region. It includes auto rickshaws, bicycles to mass transit systems - such as buses, trains and ships.
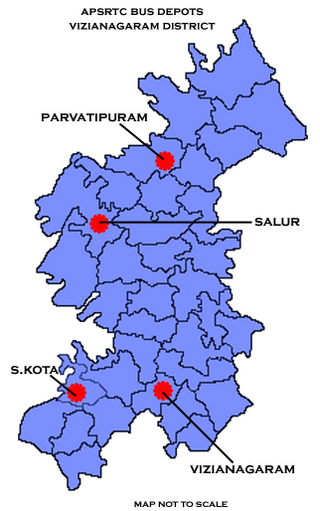
There are various modes of transportation available in Vizianagaram and its Neighbourhoods. It includes auto rickshaws, bicycles to mass transit systems - such as buses, trains and flights.




















