
In mathematical analysis, a null set is a Lebesgue measurable set of real numbers that has measure zero. This can be characterized as a set that can be covered by a countable union of intervals of arbitrarily small total length.
In probability theory, the central limit theorem (CLT) states that, under appropriate conditions, the distribution of a normalized version of the sample mean converges to a standard normal distribution. This holds even if the original variables themselves are not normally distributed. There are several versions of the CLT, each applying in the context of different conditions.
In mathematics, an infinite series of numbers is said to converge absolutely if the sum of the absolute values of the summands is finite. More precisely, a real or complex series is said to converge absolutely if for some real number Similarly, an improper integral of a function, is said to converge absolutely if the integral of the absolute value of the integrand is finite—that is, if A convergent series that is not absolutely convergent is called conditionally convergent.
In probability theory and statistics, a Gaussian process is a stochastic process, such that every finite collection of those random variables has a multivariate normal distribution. The distribution of a Gaussian process is the joint distribution of all those random variables, and as such, it is a distribution over functions with a continuous domain, e.g. time or space.
In probability theory, the central limit theorem states that, under certain circumstances, the probability distribution of the scaled mean of a random sample converges to a normal distribution as the sample size increases to infinity. Under stronger assumptions, the Berry–Esseen theorem, or Berry–Esseen inequality, gives a more quantitative result, because it also specifies the rate at which this convergence takes place by giving a bound on the maximal error of approximation between the normal distribution and the true distribution of the scaled sample mean. The approximation is measured by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov distance. In the case of independent samples, the convergence rate is n−1/2, where n is the sample size, and the constant is estimated in terms of the third absolute normalized moment.
In functional analysis, a reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS) is a Hilbert space of functions in which point evaluation is a continuous linear functional. Roughly speaking, this means that if two functions and in the RKHS are close in norm, i.e., is small, then and are also pointwise close, i.e., is small for all . The converse does not need to be true. Informally, this can be shown by looking at the supremum norm: the sequence of functions converges pointwise, but does not converge uniformly i.e. does not converge with respect to the supremum norm.

In mathematics, the universality of zeta functions is the remarkable ability of the Riemann zeta function and other similar functions to approximate arbitrary non-vanishing holomorphic functions arbitrarily well.
In the mathematical field of mathematical analysis, Lusin's theorem or Lusin's criterion states that an almost-everywhere finite function is measurable if and only if it is a continuous function on nearly all its domain. In the informal formulation of J. E. Littlewood, "every measurable function is nearly continuous".
String diagrams are a formal graphical language for representing morphisms in monoidal categories, or more generally 2-cells in 2-categories. They are a prominent tool in applied category theory. When interpreted in the monoidal category of vector spaces and linear maps with the tensor product, string diagrams are called tensor networks or Penrose graphical notation. This has led to the development of categorical quantum mechanics where the axioms of quantum theory are expressed in the language of monoidal categories.

In complex analysis, a branch of mathematics, a holomorphic function is said to be of exponential type C if its growth is bounded by the exponential function for some real-valued constant as . When a function is bounded in this way, it is then possible to express it as certain kinds of convergent summations over a series of other complex functions, as well as understanding when it is possible to apply techniques such as Borel summation, or, for example, to apply the Mellin transform, or to perform approximations using the Euler–Maclaurin formula. The general case is handled by Nachbin's theorem, which defines the analogous notion of -type for a general function as opposed to .
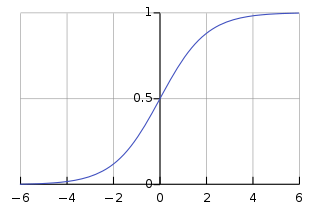
The softmax function, also known as softargmax or normalized exponential function, converts a vector of K real numbers into a probability distribution of K possible outcomes. It is a generalization of the logistic function to multiple dimensions, and used in multinomial logistic regression. The softmax function is often used as the last activation function of a neural network to normalize the output of a network to a probability distribution over predicted output classes.

Long short-term memory (LSTM) is a type of recurrent neural network (RNN) aimed at dealing with the vanishing gradient problem present in traditional RNNs. Its relative insensitivity to gap length is its advantage over other RNNs, hidden Markov models and other sequence learning methods. It aims to provide a short-term memory for RNN that can last thousands of timesteps, thus "long short-term memory". It is applicable to classification, processing and predicting data based on time series, such as in handwriting, speech recognition, machine translation, speech activity detection, robot control, video games, and healthcare.
The activation function of a node in an artificial neural network is a function that calculates the output of the node based on its individual inputs and their weights. Nontrivial problems can be solved using only a few nodes if the activation function is nonlinear. Modern activation functions include the smooth version of the ReLU, the GELU, which was used in the 2018 BERT model, the logistic (sigmoid) function used in the 2012 speech recognition model developed by Hinton et al, the ReLU used in the 2012 AlexNet computer vision model and in the 2015 ResNet model.
In machine learning, the vanishing gradient problem is encountered when training neural networks with gradient-based learning methods and backpropagation. In such methods, during each iteration of training each of the neural networks weights receives an update proportional to the partial derivative of the error function with respect to the current weight. The problem is that as the sequence length increases, the gradient magnitude typically is expected to decrease, slowing the training process. In the worst case, this may completely stop the neural network from further training. As one example of the problem cause, traditional activation functions such as the hyperbolic tangent function have gradients in the range [-1,1], and backpropagation computes gradients by the chain rule. This has the effect of multiplying n of these small numbers to compute gradients of the early layers in an n-layer network, meaning that the gradient decreases exponentially with n while the early layers train very slowly.
In machine learning, a Hyper basis function network, or HyperBF network, is a generalization of radial basis function (RBF) networks concept, where the Mahalanobis-like distance is used instead of Euclidean distance measure. Hyper basis function networks were first introduced by Poggio and Girosi in the 1990 paper “Networks for Approximation and Learning”.
Gated recurrent units (GRUs) are a gating mechanism in recurrent neural networks, introduced in 2014 by Kyunghyun Cho et al. The GRU is like a long short-term memory (LSTM) with a gating mechanism to input or forget certain features, but lacks a context vector or output gate, resulting in fewer parameters than LSTM. GRU's performance on certain tasks of polyphonic music modeling, speech signal modeling and natural language processing was found to be similar to that of LSTM. GRUs showed that gating is indeed helpful in general, and Bengio's team came to no concrete conclusion on which of the two gating units was better.
In the study of artificial neural networks (ANNs), the neural tangent kernel (NTK) is a kernel that describes the evolution of deep artificial neural networks during their training by gradient descent. It allows ANNs to be studied using theoretical tools from kernel methods.
A Neural Network Gaussian Process (NNGP) is a Gaussian process (GP) obtained as the limit of a certain type of sequence of neural networks. Specifically, a wide variety of network architectures converges to a GP in the infinitely wide limit, in the sense of distribution. The concept constitutes an intensional definition, i.e., a NNGP is just a GP, but distinguished by how it is obtained.
The Fréchet inception distance (FID) is a metric used to assess the quality of images created by a generative model, like a generative adversarial network (GAN). Unlike the earlier inception score (IS), which evaluates only the distribution of generated images, the FID compares the distribution of generated images with the distribution of a set of real images. The FID metric does not completely replace the IS metric. Classifiers that achieve the best (lowest) FID score tend to have greater sample variety while classifiers achieving the best (highest) IS score tend to have better quality within individual images.
Neural operators are a class of deep learning architectures designed to learn maps between infinite-dimensional function spaces. Neural operators represent an extension of traditional artificial neural networks, marking a departure from the typical focus on learning mappings between finite-dimensional Euclidean spaces or finite sets. Neural operators directly learn operators between function spaces; they can receive input functions, and the output function can be evaluated at any discretization.






























































































