The thalamus is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon. Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, allowing hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness.

The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the cingulate sulcus. The cingulate cortex is usually considered part of the limbic lobe.

The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.

Brodmann area 9, or BA9, is part of the frontal cortex in the brain of humans and other primates. It contributes to the dorsolateral and medial prefrontal cortex.
Anosognosia is a condition in which a person with a disability is cognitively unaware of having it due to an underlying physical condition. Anosognosia results from physiological damage to brain structures, typically to the parietal lobe or a diffuse lesion on the fronto-temporal-parietal area in the right hemisphere, and is thus a neuropsychiatric disorder. A deficit of self-awareness, it was first named by the neurologist Joseph Babinski in 1914. Phenomenologically, anosognosia has similarities to denial, which is a psychological defense mechanism; attempts have been made at a unified explanation. Anosognosia is sometimes accompanied by asomatognosia, a form of neglect in which patients deny ownership of body parts such as their limbs. The term is from Ancient Greek ἀ- a-, "without", νόσος nosos, "disease" and γνῶσις gnōsis, "knowledge".

The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs and the auditory parts of the sensory system.

The pulvinar nuclei or nuclei of the pulvinar are the nuclei located in the thalamus. As a group they make up the collection called the pulvinar of the thalamus, usually just called the pulvinar.
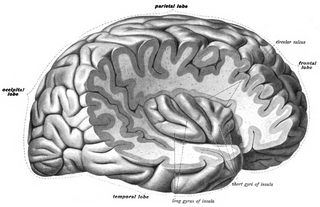
The insular cortex is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus within each hemisphere of the mammalian brain.

The cerebellar vermis is located in the medial, cortico-nuclear zone of the cerebellum, which is in the posterior fossa of the cranium. The primary fissure in the vermis curves ventrolaterally to the superior surface of the cerebellum, dividing it into anterior and posterior lobes. Functionally, the vermis is associated with bodily posture and locomotion. The vermis is included within the spinocerebellum and receives somatic sensory input from the head and proximal body parts via ascending spinal pathways.

The angular gyrus is a region of the brain lying mainly in the anterolateral region of parietal lobe, that lies near the superior edge of the temporal lobe, and immediately posterior to the supramarginal gyrus. Its significance is in transferring visual information to Wernicke's area, in order to make meaning out of visually perceived words. It is also involved in a number of processes related to language, number processing and spatial cognition, memory retrieval, attention, and theory of mind. It is Brodmann area 39 of the human brain.

Language processing refers to the way humans use words to communicate ideas and feelings, and how such communications are processed and understood. Language processing is considered to be a uniquely human ability that is not produced with the same grammatical understanding or systematicity in even human's closest primate relatives.
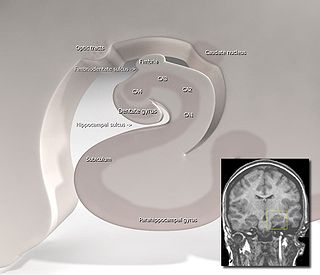
The subiculum is the most inferior component of the hippocampal formation. It lies between the entorhinal cortex and the CA1 subfield of the hippocampus proper.
Head direction (HD) cells are neurons found in a number of brain regions that increase their firing rates above baseline levels only when the animal's head points in a specific direction. They have been reported in rats, monkeys, mice, chinchillas and bats, but are thought to be common to all mammals, perhaps all vertebrates and perhaps even some invertebrates, and to underlie the "sense of direction". When the animal's head is facing in the cell's "preferred firing direction" these neurons fire at a steady rate, but firing decreases back to baseline rates as the animal's head turns away from the preferred direction.

The flocculus is a small lobe of the cerebellum at the posterior border of the middle cerebellar peduncle anterior to the biventer lobule. Like other parts of the cerebellum, the flocculus is involved in motor control. It is an essential part of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, and aids in the learning of basic motor skills in the brain.

The olfactory tubercle (OT), also known as the tuberculum olfactorium, is a multi-sensory processing center that is contained within the olfactory cortex and ventral striatum and plays a role in reward cognition. The OT has also been shown to play a role in locomotor and attentional behaviors, particularly in relation to social and sensory responsiveness, and it may be necessary for behavioral flexibility. The OT is interconnected with numerous brain regions, especially the sensory, arousal, and reward centers, thus making it a potentially critical interface between processing of sensory information and the subsequent behavioral responses.
The perirhinal cortex is a cortical region in the medial temporal lobe that is made up of Brodmann areas 35 and 36. It receives highly processed sensory information from all sensory regions, and is generally accepted to be an important region for memory. It is bordered caudally by postrhinal cortex or parahippocampal cortex and ventrally and medially by entorhinal cortex.
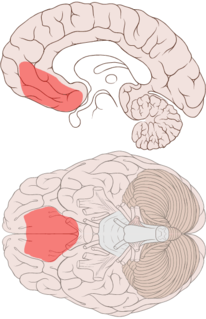
The ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) is a part of the prefrontal cortex in the mammalian brain. The ventral medial prefrontal is located in the frontal lobe at the bottom of the cerebral hemispheres and is implicated in the processing of risk and fear, as it is critical in the regulation of amygdala activity in humans. It also plays a role in the inhibition of emotional responses, and in the process of decision making and self control. It is also involved in the cognitive evaluation of morality.
Recognition memory, a subcategory of declarative memory, is the ability to recognize previously encountered events, objects, or people. When the previously experienced event is reexperienced, this environmental content is matched to stored memory representations, eliciting matching signals. As first established by psychology experiments in the 1970s, recognition memory for pictures is quite remarkable: humans can remember thousands of images at high accuracy after seeing each only once and only for a few seconds.

The nucleus reuniens is a component of the thalamic midline nuclear group. In the human brain, it is located in the interthalamic adhesion.
The parabrachial nuclei, also known as the parabrachial complex, are a group of nuclei in the dorsolateral pons that surrounds the superior cerebellar peduncle as it enters the brainstem from the cerebellum. They are named from the Latin term for the superior cerebellar peduncle, the brachium conjunctivum. In the human brain, the expansion of the superior cerebellar peduncle expands the parabrachial nuclei, which form a thin strip of grey matter over most of the peduncle. The parabrachial nuclei are typically divided along the lines suggested by Baxter and Olszewski in humans, into a medial parabrachial nucleus and lateral parabrachial nucleus. These have in turn been subdivided into a dozen subnuclei: the superior, dorsal, ventral, internal, external and extreme lateral subnuclei; the lateral crescent and subparabrachial nucleus along the ventrolateral margin of the lateral parabrachial complex; and the medial and external medial subnuclei