
WR 136 is a Wolf–Rayet star located in the constellation Cygnus. It is in the center of the Crescent Nebula. Its age is estimated to be around 4.7 million years and it is nearing the end of its life. Within a few hundred thousand years, it is expected to explode as a supernova.

WR 102ea is a Wolf–Rayet star in the Sagittarius constellation. It is the third most luminous star in the Quintuplet cluster after WR 102hb. With a luminosity of 2,500,000 times solar, it is also one of the most luminous stars known. Despite the high luminosity it can only be observed at infra-red wavelengths due to the dimming effect of intervening dust on visual light.

WR 22, also known as V429 Carinae or HR 4188, is an eclipsing binary star system in the constellation Carina. The system contains a Wolf-Rayet (WR) star that is one of the most massive and most luminous stars known, and is also a bright X-ray source due to colliding winds with a less massive O class companion. Its eclipsing nature and apparent magnitude make it very useful for constraining the properties of luminous hydrogen-rich WR stars.

WR 148 is a spectroscopic binary in the constellation Cygnus. The primary star is a Wolf–Rayet star and one of the most luminous stars known. The secondary has been suspected of being a stellar-mass black hole but may be a class O main sequence star.
WR 142 is a Wolf-Rayet star in the constellation Cygnus, an extremely rare star on the WO oxygen sequence. It is a luminous and very hot star, highly evolved and close to exploding as a supernova. It is suspected to be a binary star with a companion orbiting about 1 AU away.
WR 102 is a Wolf–Rayet star in the constellation Sagittarius, an extremely rare star on the WO oxygen sequence. It is a luminous and very hot star, highly evolved and close to exploding as a supernova.
WR 114 is a Wolf-Rayet star in the constellation of Scutum. It is an early type star of the carbon sequence (WCE) classified as WC5.

WR 93b is a Wolf-Rayet star in the constellation Scorpius, an extremely rare star on the WO oxygen sequence. It appears near NGC 6357 in the tail of the scorpion.
WR 135 is a variable Wolf-Rayet star located around 6,000 light years away from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus, surrounded by a faint bubble nebula blown by the intense radiation and fast wind from the star. It is just over four times the radius of the sun, but due to a temperature of 63,000 K it is 250,000 times as luminous as the sun.
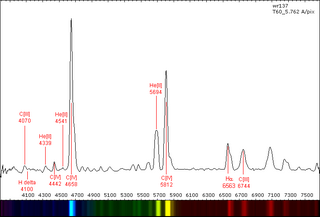
WR 137 is a variable Wolf-Rayet star located around 6,000 light years away from Earth in the constellation of Cygnus.
WR 111 is a Wolf-Rayet (WR) star in the constellation Sagittarius. It is magnitude 7.8 and lies about 5,150 light-years away. It is one of the brightest and most closely studied WR stars.

WR 86 is a visual binary in the constellation Scorpius consisting of a Wolf-Rayet star and a β Cephei variable. It lies 2° west of NGC 6357 on the edge of the Great Rift in the Milky Way in the tail of the Scorpion.
WR 2 is a Wolf-Rayet star located around 8,000 light years away from Earth in the constellation of Cassiopeia, in the stellar association Cassiopeia OB1. It is smaller than the Sun, but due to a temperature over 140,000 K it is 282,000 times as luminous as the Sun. With a radius of 89% that of the Sun, it is the smallest known WN star in the Milky Way.
WR 3 is a Wolf-Rayet star located around 9,500 light years away from Earth in the constellation of Cassiopeia.
WR 128 is a Wolf–Rayet star located about 9,500 light years away in the constellation of Sagitta. A member of the WN class, WR 128's spectrum resembles that of a H-free WN4 star, but hydrogen is clearly present in the star, making it the only known hydrogen-rich WN4 star in the galaxy. However, similar H-rich very early WN stars can be found in the LMC and especially in the SMC, but the only other galactic examples of this are WR 3 and WR 152.
WR 69 is a Wolf–Rayet star located 11,350 light years away in the constellation of Triangulum Australe. It is classified as a WC9 star, belonging to the late-type carbon sequence. WR 69 is also a prolific dust maker, hence the "d" in its spectral type.

WR 120 is a binary containing two Wolf-Rayet stars in the constellation of Scutum, around 10,000 light years away. The primary is a hydrogen-free weak-lined WN7 star, the secondary is a hydrogen-free WN3 or 4 star, and the system is a possible member of the cluster Dolidze 33. From our point of view, WR 120 is reddened by 4.82 magnitudes, and it has the variable designation of V462 Scuti.
BAT99-7 is a WN-type Wolf-Rayet star located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, in the constellation of Dorado, about 160,000 light years away. The star has a spectrum containing extremely broad emission lines, and is the prototype for the "round line" stars, Wolf-Rayet stars whose spectra are characterized by strong and broad emission lines with round line profiles. The broad emission lines hint at an extremely high temperature of nearly 160,000 Kelvin, which would make it the hottest of all WN stars with known temperatures, as well as an extraordinarily large mass loss rate for a Wolf-Rayet star in the LMC, at 10−4.48 M☉/yr, which means that every 30,200 years, the star loses 1 solar mass worth of mass.








