KY Cygni is a red supergiant of spectral class M3.5Ia located in the constellation Cygnus. It is approximately 5,000 light-years away.
KW Sagittarii is a red supergiant, located approximately 1,900 parsecs away from the Sun in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius. It is one of the largest-known stars. If placed at the center of the Solar System, the star's surface would engulf Mars.

V354 Cephei is a red supergiant star located within the Milky Way. It is an irregular variable located over 8,900 light-years away from the Sun. It has an estimated radius of 685 solar radii. If it were placed in the center of the Solar System, it would extend to between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.

32 Cygni is the Flamsteed designation for a binary star system in the Cygnus constellation. It is a 4th magnitude star, which can be seen with the naked eye under suitably dark skies. Parallax measurements give an estimated distance of 1,100 light-years (320 parsecs) from the Earth. However, Schröder et al. (2007) suggest the actual value, after correcting for Malmquist bias, may be closer to 1,174 light-years (360 parsecs). Although it is a spectrsocopic binary with components that cannot be separated visually, it has two entries in the Henry Draper Catalogue, with identical magnitudes and positions, but showing the spectral types of the two components.

Cygnus OB2 #12 is an extremely luminous blue hypergiant with an absolute bolometric magnitude of −10.9, among the most luminous stars known in the galaxy. This makes the star nearly two million times more luminous than the Sun, although estimates were even higher when the star was first discovered. It is now known to be a binary, with the companion approximately a tenth as bright. A very approximate initial estimate of the orbit gives the total system mass as 120 M☉ and the period as 30 years.

Cygnus OB2 #8A is a double-lined spectroscopic binary located near the centre of the Cygnus OB2 association located 5,500 light years away.

NO Aurigae is a pulsating variable star in the constellation Auriga. It is an unusually-luminous asymptotic giant branch star about 3,500 light years away.

V602 Carinae is a red supergiant and variable star of spectral type of M3 in the constellation Carina. It is one of largest known stars.
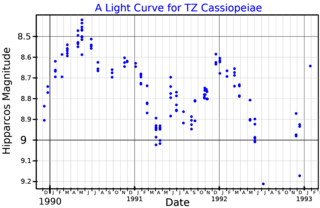
TZ Cassiopeiae(TZ Cas, HIP 117763, SAO 20912) is a variable star in the constellation Cassiopeia with an apparent magnitude of around +9 to +10. It is approximately 8,400 light-years away from Earth. The star is a red supergiant star with a spectral type of M3 and a temperature around 3,600 K.
63 Cygni is a single star in the northern constellation of Cygnus, located around 1,030 light years away from Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as an orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.56. 63 Cyg is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −26 km/s.

55 Cygni is a blue supergiant star in the constellation Cygnus. It is thought to be a member of the Cygnus OB7 stellar association at about 2,700 light years.
AH Scorpii is a red supergiant variable star located in the constellation Scorpius. It is one of the largest stars known by radius and is also one of the most luminous red supergiant stars in the Milky Way.

31 Cygni, also known as ο1 Cygni, Omicron1 Cygni, or V695 Cygni, is a triple star system about 750 light years away in the constellation Cygnus.

RS Persei is a red supergiant variable star located in the Double Cluster in Perseus. The star's apparent magnitude varies from 7.82 to 10.0, meaning it is never visible to the naked eye.

HDE 316285 is a blue supergiant star in the constellation Sagittarius. It is a candidate luminous blue variable and lies about 6,000 light years away in the direction of the Galactic Center.

BC Cygni is a red supergiant and pulsating variable star of spectral type M3.5Ia in the constellation Cygnus.

RW Cygni is a semiregular variable star in the constellation Cygnus, about a degree east of 2nd magnitude γ Cygni. Its apparent magnitude varies between 8.05 and 9.70 and its spectral type between M3 and M4.

BO Carinae, also known as HD 93420, is an irregular variable star in the constellation Carina.

V1027 Cygni is a luminous yellow supergiant star located in the constellation of Cygnus, about 14,000 light years away. For a time, it was thought that it could be a low-mass post-AGB star, however recent parallax measurements published in Gaia DR3 have shown this to likely not be the case, and instead it is likely a massive yellow supergiant star.

AZ Cygni is a large red supergiant in the constellation of Cygnus. It is located 2,090 parsecs from Earth. It has been studied by the CHARA array in order to understand the surface variations of red supergiants.