Related Research Articles
TrES-1b is an extrasolar planet approximately 523 light-years away in the constellation of Lyra. The planet's mass and radius indicate that it is a Jovian planet with a similar bulk composition to Jupiter. Unlike Jupiter, but similar to many other planets detected around other stars, TrES-1 is located very close to its star, and belongs to the class of planets known as hot Jupiters. The planet was discovered orbiting around GSC 02652-01324.
The Trans-Atlantic Exoplanet Survey, or TrES, used three 4-inch (10 cm) telescopes located at Lowell Observatory, Palomar Observatory, and Teide Observatory to locate exoplanets. It was made using the network of small, relatively inexpensive telescopes designed to look specifically for planets orbiting bright stars using the transit method. The array used 4-inch Schmidt telescopes having CCD cameras and automated search routines. The survey was created by David Charbonneau of the Center for Astrophysics, Timothy Brown of the National Center for Atmospheric Research, and Edward Dunham of Lowell Observatory.

TrES-2b (Kepler-1b) is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star GSC 03549-02811 located 750 light years away from the Solar System. The planet was identified in 2011 as the darkest known exoplanet, reflecting less than 1% of any light that hits it. Reflecting less light than charcoal, on the surface the planet is said to be pitch black. The planet's mass and radius indicate that it is a gas giant with a bulk composition similar to that of Jupiter. Unlike Jupiter, but similar to many planets detected around other stars, TrES-2b is located very close to its star and belongs to the class of planets known as hot Jupiters. This system was within the field of view of the Kepler spacecraft.
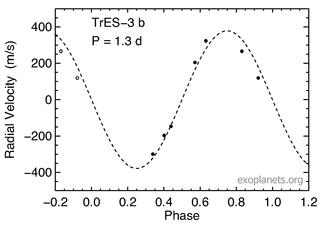
TrES-3b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star GSC 03089-00929. It has an orbital period of just 31 hours and nearly twice the mass of Jupiter.
The XO Project is an international team of amateur and professional astronomers tasked with identifying extrasolar planets. They are led by Peter R. McCullough of the Space Telescope Science Institute. It is primarily funded by NASA's Origins Program and the Director's Discretionary Fund of the Space Telescope Science Institute.

TrES-4b is an extrasolar planet, and one of the largest exoplanets ever found, after WASP-12b, WASP-17b, CT Chamaeleontis b, GQ Lupi b and HD 100546 b. It was discovered in 2006, and announced in 2007, by the Trans-Atlantic Exoplanet Survey, using the transit method. It is approximately 1,400 light-years (430 pc) away orbiting the star GSC 02620-00648, in the constellation Hercules.
HAT-P-5 is a 12th magnitude star in the constellation Lyra, approximately 1,000 light years away from Earth. It is a spectral type G star, about 1.16 solar masses and radii greater than the Sun, and only 200 kelvins hotter. It is estimated to be 2.6 billion years old.

HAT-P-5b is a transiting extrasolar planet located approximately 1000 light-years away in the constellation of Lyra, orbiting the star HAT-P-5. It is a hot Jupiter with a mass 6% greater than Jupiter and a radius 26% greater than Jupiter, corresponding to a density of 0.66 g/cm3, which is less than water. This planet was found by Bakos et al. on October 9, 2007.
Lupus-TR-3 is a star located in the southern constellation Lupus. It has an apparent magnitude of 17.4, making it visible only in power telescopes. Its distance is not well known, but it is estimated to be roughly 2,000 parsecs away from the Solar System.

GSC 03549-02811 is a yellow main-sequence star similar to the Sun. This star is located approximately 704 light-years away in the constellation of Draco. The apparent magnitude of this star is 11.41, which means it is not visible to the naked eye but can be seen with a medium-sized amateur telescope on a clear dark night. The age of this star is about 5 billion years.
GSC 03089-00929 is a magnitude 12 star located approximately 760 light-years away in the constellation of Hercules. This star is a G type main sequence star that is similar to but slightly cooler than the Sun. This star is identified in SIMBAD as a variable star per the 1SWASP survey.
GSC 02620-00648 is a double star in the constellation Hercules. The brighter of the pair is a magnitude 12 star located approximately 1,660 light-years away. This star is about 1.18 times as massive as the Sun.

WASP-17b is an exoplanet in the constellation Scorpius that is orbiting the star WASP-17. Its discovery was announced on 11 August 2009. It is the first planet discovered to have a retrograde orbit, meaning it orbits in a direction counter to the rotation of its host star. This discovery challenged traditional planetary formation theory. In terms of diameter, WASP-17b is one of the largest exoplanets discovered and at half Jupiter's mass, this made it the most puffy planet known in 2010. On 3 December 2013, scientists working with the Hubble Space Telescope reported detecting water in the exoplanet's atmosphere.

Kepler-5b is one of the first five planets discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft. It is a Hot Jupiter that orbits a subgiant star that is more massive, larger, and more diffuse than the Sun is. Kepler-5 was first flagged as the location of a possibly transiting planet, and was reclassified as a Kepler Object of Interest until follow-up observations confirmed the planet's existence and many of its characteristics. The planet's discovery was announced at a meeting of the American Astronomical Society on January 4, 2010. The planet has approximately twice the mass of Jupiter, and is about 1.5 times larger. It is also fifteen times hotter than Jupiter. Kepler-5b orbits Kepler-5 every 3.5 days at a distance of approximately 0.051 AU.

Kepler-8b is the fifth of the first five exoplanets discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft, which aims to discover planets in a region of the sky between the constellations Lyra and Cygnus that transit their host stars. The planet is the hottest of the five. Kepler-8b was the only planet discovered in Kepler-8's orbit, and is larger than Jupiter. It orbits its host star every 3.5 days. The planet also demonstrates the Rossiter–McLaughlin effect, where the planet's orbit affects the redshifting of the spectrum of the host star. Kepler-8b was announced to the public on January 4, 2010 at a conference in Washington, D.C. after radial velocity measurements conducted at the W.M. Keck Observatory confirmed its detection by Kepler.
Kepler-5 is a star located in the constellation Cygnus in the field of view of the Kepler Mission, a NASA project aimed at detecting planets in transit of, or passing in front of, their host stars as seen from Earth. One closely orbiting, Jupiter-like planet, named Kepler-5b, has been detected around Kepler-5. Kepler-5's planet was one of the first five planets to be discovered by the Kepler spacecraft; its discovery was announced on January 4, 2010 at the 215th meeting of the American Astronomical Society after being verified by a variety of observatories. Kepler-5 is larger and more massive than the Sun, but has a similar metallicity, a major factor in planet formation.
Qatar-1 is an orange main sequence star in the constellation of Draco.
GSC 03949-00967 is a G-type main-sequence star about 1190 light-years away. It is older than the Sun, yet is enriched by heavy elements compared to the Sun, having 160% of solar abundance.
Qatar-3 is a 12th magnitude star located in the northern constellation Andromeda. It is host to a transiting planet. With a radial velocity of 10.99 km/s, it is drifting away from the Solar System, and is currently located 2,400 light years away based on its annual parallax.
References
- ↑ "Exoplanet TrES-5b". Suburban Observatory. September 3, 2023. Retrieved September 3, 2023.
- ↑ Mandushev, Georgi; Quinn, Samuel N.; Buchhave, Lars A.; Dunham, Edward W.; Rabus, Markus; Oetiker, Brian; Latham, David W.; Charbonneau, David; Brown, Timothy M.; Belmonte, Juan A.; O'Donovan, Francis T. (2011), "TrES-5: A Massive Jupiter-sized Planet Transiting A Cool G-dwarf", The Astrophysical Journal, 741 (2): 114, arXiv: 1108.3572 , Bibcode:2011ApJ...741..114M, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/741/2/114, S2CID 118671116