
RV Tauri is a star in the constellation Taurus. It is a yellow supergiant and is the prototype of a class of pulsating variables known as RV Tauri variables. It is a post-AGB star and a spectroscopic binary about 4,700 light years away.

KY Cygni is a red supergiant of spectral class M3.5Ia located in the constellation Cygnus. It is approximately 5,000 light-years away.

V354 Cephei is a red supergiant star located within the Milky Way. It is an irregular variable located over 8,900 light-years away from the Sun. It has an estimated radius of 685 solar radii. If it were placed in the center of the Solar System, it would extend to between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
17 Camelopardalis is a single star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Camelopardalis, located roughly 960 light years away from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, red-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.44. This object is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −20 km/s.

WOH G64 is an unusual red supergiant (RSG) star in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) satellite galaxy in the southern constellation of Dorado. It is one of the largest known stars, being described as possibly being the largest star known. It is also one of the most luminous and massive red supergiants, with a radius calculated to be around 1,540 times that of the Sun (R☉) and a luminosity around 282,000 times the solar luminosity (L☉).
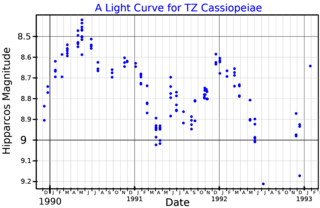
TZ Cassiopeaie(TZ Cas, HIP 117763, SAO 20912) is a variable star in the constellation Cassiopeia with an apparent magnitude of around +9 to +10. It is approximately 8,400 light-years away from Earth. The star is a red supergiant star with a spectral type of M3 and a temperature below 4,000 K.

NML Cygni or V1489 Cygni is a red hypergiant or red supergiant (RSG) in the constellation Cygnus. It is one of the largest stars currently known by radius, and is also one of the most luminous and massive cool hypergiants, as well as one of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way.
HD 101570 is a single star in the southern constellation of Centaurus. It has a yellow hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.93. The star is located at a distance of approximately 1,080 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +18 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of −2.24.

HV 2112 is a cool luminous variable star in the Small Magellanic Cloud. Until 2018, it was considered to be the most likely candidate for a Thorne–Żytkow object, but it is now thought to be an asymptotic giant branch star.
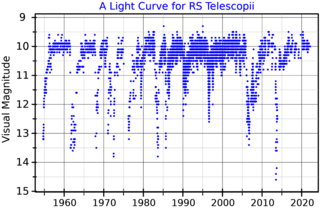
RS Telescopii, abbreviated RS Tel, is a variable star in the southern constellation of Telescopium. It is a dim star with an apparent visual magnitude of 10.67, which is much too faint to be visible without a telescope. The variability of this star was discovered by Evelyn F. Leland and announced by Edward C. Pickering in 1910. It was first studied by Cecilia H. Payne in 1928 at the Harvard College Observatory.

HDE 316285 is a blue supergiant star in the constellation Sagittarius. It is a candidate luminous blue variable and lies about 6,000 light years away in the direction of the galactic centre.

BC Cygni is a red supergiant and pulsating variable star of spectral type M3.5Ia in the constellation Cygnus.

RW Cygni is a semiregular variable star in the constellation Cygnus, about a degree east of 2nd magnitude γ Cygni. Its apparent magnitude varies between 8.05 and 9.70 and its spectral type between M3 and M4.

BI Cygni(BI Cyg, IRC +40408, BD+36 4025) is a red supergiant in the constellation Cygnus. It is an irregular variable star with a maximum brightness of magnitude 8.4 and a minimum of magnitude 9.9. It is considered a member of the stellar Cygnus OB1 association, its distance is around 1,400 parsecs of the Solar System. It is less than a degree south of another variable red supergiant, BC Cygni.

Westerlund 1-20 (abbreviated to Wd 1-20 or just W20) is a red supergiant (RSG) located in the Westerlund 1 super star cluster. Its radius was calculated to be around 965 solar radii (6.72 × 108 km, 4.48 au), making it one of the largest stars discovered so far. This corresponds to a volume 899 million times bigger than the Sun. If placed at the center of the Solar System, the photosphere of Westerlund 1-20 would almost reach the orbit of Jupiter.
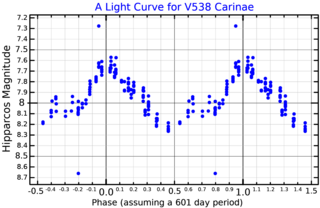
V538 Carinae is a variable star in the constellation of Carina, and a possible red supergiant. If this star replaced the Sun in the Solar System, its photosphere would at least engulf the orbit of Mars.

Trumpler 27-1 is a red supergiant star that is a member of the massive, possible open cluster Trumpler-27, where a blue giant star, a yellow supergiant star, and two Wolf–Rayet stars are also located.

V1936 Aquilae is a blue supergiant and candidate Luminous blue variable located in the nebula Westerhout 51, in the constellation Aquila, about 20,000 light years away. The star was originally identified as a massive star in 2000, and was thought to be an O-type supergiant. However, subsequent analyses have shown it to be not O but B-type, as well as being possibly an LBV.

Y Tauri is a carbon star located in the constellation Taurus. Parallax measurements by Gaia put it at a distance of approximately 2,170 light-years.
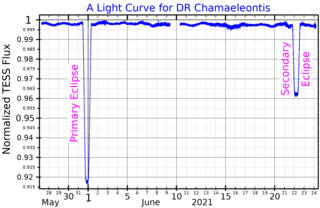
DR Chamaeleontis, also known as HD 93237, is a star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Chamaeleon. The system has an average apparent magnitude of 5.97, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. DR Cha is located relatively far at a distance of 1,060 light years based on Gaia DR3 parallax measurements, but is receding with a poorly constrained heliocentric radial velocity of 18 km/s.
















