Aramaic is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, southeastern Anatolia, Eastern Arabia and the Sinai Peninsula, where it has been continually written and spoken in different varieties for over three thousand years.
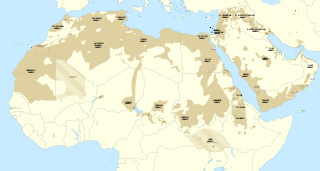
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic, Amharic, Aramaic, Hebrew, and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Malta, and in large immigrant and expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis.
The Syriac language, also known as Syriac Aramaic and Classical Syriac ܠܫܢܐ ܥܬܝܩܐ, is an Aramaic language. The language is a dialect that emerged during the first century AD from a local Aramaic dialect that was spoken in the ancient region of Osroene, centered in the city of Edessa. During the Early Christian period, it became the main literary language of various Aramaic-speaking Christian communities in the historical region of Ancient Syria and throughout the Near East. As a liturgical language of Syriac Christianity, it gained a prominent role among Eastern Christian communities that used both Eastern Syriac and Western Syriac rites. Following the spread of Syriac Christianity, it also became a liturgical language of eastern Christian communities as far as India and China. It flourished from the 4th to the 8th century, and continued to have an important role during the next centuries, but by the end of the Middle Ages it was gradually reduced to liturgical use, since the role of vernacular language among its native speakers was overtaken by several emerging Neo-Aramaic dialects.
The Arameans, or Aramaeans, were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East that was first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BC. The Aramean homeland, sometimes known as the land of Aram, encompassed central regions of modern Syria.
Turoyo, also referred to as Surayt, or modern Suryoyo, is a Central Neo-Aramaic language traditionally spoken in the Tur Abdin region in southeastern Turkey and in northern Syria. Turoyo speakers are mostly adherents of the Syriac Orthodox Church, but there are also some Turoyo-speaking adherents of the Assyrian Church of the East and the Chaldean Catholic Church, especially from the towns of Midyat and Qamishli. The language is also spoken throughout diaspora, among modern Assyrians/Syriacs. It is classified as a vulnerable language. Most speakers use the Classical Syriac language for literature and worship. Turoyo is not mutually intelligible with Western Neo-Aramaic, having been separated for over a thousand years; its closest relatives are Mlaḥsô and western varieties of Northeastern Neo-Aramaic like Suret.

The term Melkite, also written Melchite, refers to various Eastern Christian churches of the Byzantine Rite and their members originating in West Asia. The term comes from the common Central Semitic root m-l-k, meaning "royal", referring to the loyalty to the Byzantine emperor. The term acquired religious connotations as denominational designation for those Christians who accepted imperial religious policies, based on Christological resolutions of the Council of Chalcedon (451).
Western Neo-Aramaic, more commonly referred to as Siryon, is a modern Western Aramaic language. Today, it is spoken by Christian and Muslim Arameans (Syriacs) in only two villages – Maaloula and Jubb'adin, until the Syrian Civil War also in Bakhʽa – in the Anti-Lebanon Mountains of western Syria. Bakhʽa was completely destroyed during the war and all the survivors fled to other parts of Syria or to Lebanon. Western Neo-Aramaic is believed to be the closest living language to the language of Jesus, whose first language, according to scholarly consensus, was Galilean Aramaic belonging to the Western branch as well; all other remaining Neo-Aramaic languages are of the Eastern branch.

Judaeo-Aramaic languages represent a group of Hebrew-influenced Aramaic and Neo-Aramaic languages.
The Neo-Aramaic or Modern Aramaic languages are varieties of Aramaic that evolved during the late medieval and early modern periods, and continue to the present day as vernacular (spoken) languages of modern Aramaic-speaking communities. Within the field of Aramaic studies, classification of Neo-Aramaic languages has been a subject of particular interest among scholars, who proposed several divisions, into two, three or four primary groups.
Central Neo-Aramaic languages represent a specific group of Neo-Aramaic languages, that is designated as Central in reference to its geographical position between Western Neo-Aramaic and other Eastern Aramaic groups. Its linguistic homeland is located in northern parts of the historical region of Syria. The group includes the Turoyo language as a spoken language of the Tur Abdin region and various groups in diaspora, and Mlahsô language that is recently extinct as a spoken language.

Arabic is the official language of Syria and is the most widely spoken language in the country. Several modern Arabic dialects are used in everyday life, most notably Levantine in the west and Mesopotamian in the northeast.

Arabs represent the major ethnicity in Syria, in addition to the presence of several, much smaller ethnic groups.

Christian Palestinian Aramaic was a Western Aramaic dialect used by the Melkite Christian community, probably of Jewish descent, in Palestine, Transjordan and Sinai between the fifth and thirteenth centuries. It is preserved in inscriptions, manuscripts and amulets. All the medieval Western Aramaic dialects are defined by religious community. CPA is closely related to its counterparts, Jewish Palestinian Aramaic (JPA) and Samaritan Aramaic (SA). CPA shows a specific vocabulary that is often not paralleled in the adjacent Western Aramaic dialects.

Terms for Syriac Christians are endonymic (native) and exonymic (foreign) terms, that are used as designations for Syriac Christians, as adherents of Syriac Christianity. In its widest scope, Syriac Christianity encompass all Christian denominations that follow East Syriac Rite or West Syriac Rite, and thus use Classical Syriac as their main liturgical language. Traditional divisions among Syriac Christians along denominational lines are reflected in the use of various theological and ecclesiological designations, both historical and modern. Specific terms such as: Jacobites, Saint Thomas Syrian Christians, Maronites, Melkites, Nasranis, and Nestorians have been used in reference to distinctive groups and branches of Eastern Christianity, including those of Syriac liturgical and linguistic traditions. Some of those terms are polysemic, and their uses have been a subject of terminological disputes between different communities, and also among scholars.
Eastern Aramaic refers to a group of dialects that evolved historically from the varieties of Aramaic spoken in the core territories of Mesopotamia and further expanded into northern Syria, eastern Arabia and northwestern Iran. This is in contrast to the Western Aramaic varieties found predominantly in the southern Levant, encompassing most parts of modern western Syria and Palestine region. Most speakers are Assyrians, although there is a minority of Mizrahi Jews and Mandaeans who also speak modern varieties of Eastern Aramaic.
Jewish Palestinian Aramaic or Jewish Western Aramaic was a Western Aramaic language spoken by the Jews during the Classic Era in Judea and the Levant, specifically in Hasmonean, Herodian and Roman Judaea and adjacent lands in the late first millennium BCE, and later in Syria Palaestina and Palaestina Secunda in the early first millennium CE. This language is sometimes called Galilean Aramaic, although that term more specifically refers to its Galilean dialect.
Jubb'adin is a village in southern Syria, administratively part of the Rif Dimashq Governorate, located northeast of Damascus in the Qalamoun Mountains. Nearby localities include Saidnaya and Rankous to the southwest, Yabroud and Maaloula to the northeast, and Assal al-Ward to the northwest.
Al-Sarkha, Bakhʽah or Bakhʽa is a former Syrian village in the Yabroud District of the Rif Dimashq Governorate. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), Al-Sarkha had a population of 1,405 in the 2004 census. The village, inhabited by Sunni Muslims of Aramean (Syriac) descent, no longer exists as it was completely destroyed during the Syrian Civil War, and all the survivors fled to other parts of Syria or to Lebanon. It was one of the only three remaining villages where Western Neo-Aramaic was spoken, alongside Maaloula and Jubb'adin.

Aramaic studies are scientific studies of the Aramaic languages and literature. As a specific field within Semitic studies, Aramaic studies are closely related to similar disciplines, like Hebraic studies and Arabic studies.
Lebanese Aramaic, also referred to as Lebanese Syriac or Surien, is an extinct or dormant Western Aramaic language. It was traditionally spoken in the Levant, especially in Mount Lebanon, by Maronite Christians.









