
Ergot or ergot fungi refers to a group of fungi of the genus Claviceps.
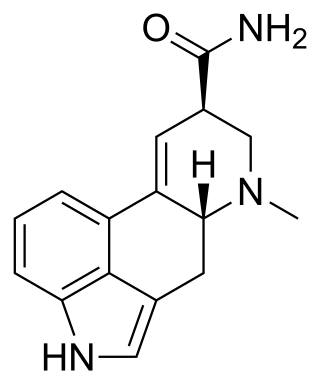
Ergine, also known as d-lysergic acid amide (LSA) and d-lysergamide, is an ergoline alkaloid that occurs in various species of vines of the Convolvulaceae and some species of fungi. The psychedelic properties in the seeds of ololiuhqui, Hawaiian baby woodrose and morning glories have been linked to ergine and/or isoergine, its epimer, as it is an alkaloid present in the seeds.
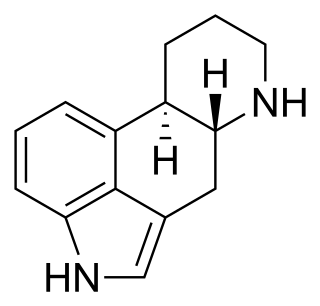
Ergoline is a chemical compound whose structural skeleton is contained in a variety of alkaloids, referred to as ergoline derivatives or ergoline alkaloids. Ergoline alkaloids, one being ergine, were initially characterized in ergot. Some of these are implicated in the condition ergotism, which can take a convulsive form or a gangrenous form. Even so, many ergoline alkaloids have been found to be clinically useful. Annual world production of ergot alkaloids has been estimated at 5,000–8,000 kg of all ergopeptines and 10,000–15,000 kg of lysergic acid, used primarily in the manufacture of semi-synthetic derivatives.

Lysergic acid, also known as D-lysergic acid and (+)-lysergic acid, is a precursor for a wide range of ergoline alkaloids that are produced by the ergot fungus and found in the seeds of Turbina corymbosa (ololiuhqui), Argyreia nervosa, and Ipomoea tricolor.
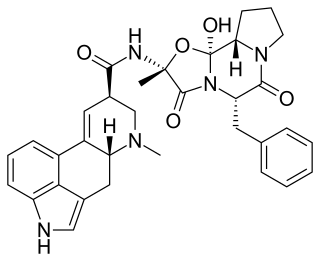
Ergotamine, sold under the brand names Cafergot and Ergomar among others, is an ergopeptine and part of the ergot family of alkaloids; it is structurally and biochemically closely related to ergoline. It possesses structural similarity to several neurotransmitters, and has biological activity as a vasoconstrictor.
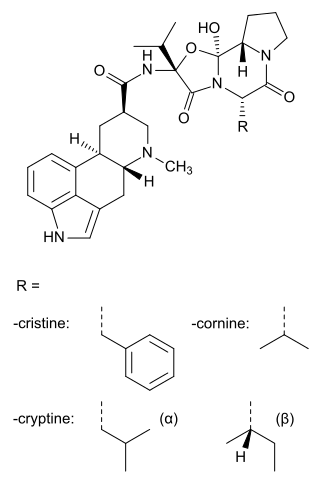
Ergoloid mesylates (USAN), co-dergocrine mesilate (BAN) or dihydroergotoxine mesylate, trade name Hydergine, is a mixture of the methanesulfonate salts of three dihydrogenated ergot alkaloids.

Methylergometrine, also known as methylergonovine and sold under the brand name Methergine, is a medication of the ergoline and lysergamide groups which is used as an oxytocic in obstetrics and in the treatment of migraine. It reportedly produces psychedelic effects similar to those of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) at high doses.

Indole alkaloids are a class of alkaloids containing a structural moiety of indole; many indole alkaloids also include isoprene groups and are thus called terpene indole or secologanin tryptamine alkaloids. Containing more than 4100 known different compounds, it is one of the largest classes of alkaloids. Many of them possess significant physiological activity and some of them are used in medicine. The amino acid tryptophan is the biochemical precursor of indole alkaloids.

Claviceps purpurea is an ergot fungus that grows on the ears of rye and related cereal and forage plants. Consumption of grains or seeds contaminated with the survival structure of this fungus, the ergot sclerotium, can cause ergotism in humans and other mammals. C. purpurea most commonly affects outcrossing species such as rye, as well as triticale, wheat and barley. It affects oats only rarely.

Ergocryptine is an ergopeptine and one of the ergoline alkaloids. It is isolated from ergot or fermentation broth and it serves as starting material for the production of bromocriptine. Two isomers of ergocryptine exist, α-ergocryptine and β-ergocryptine. The beta differs from the alpha form only in the position of a single methyl group, which is a consequence of the biosynthesis in which the proteinogenic amino acid leucine is replaced by isoleucine. β-Ergocryptine was first identified in 1967 by Albert Hofmann. Ergot from different sources have different ratios of the two isomers.

A loline alkaloid is a member of the 1-aminopyrrolizidines, which are bioactive natural products with several distinct biological and chemical features. The lolines are insecticidal and insect-deterrent compounds that are produced in grasses infected by endophytic fungal symbionts of the genus Epichloë. Lolines increase resistance of endophyte-infected grasses to insect herbivores, and may also protect the infected plants from environmental stresses such as drought and spatial competition. They are alkaloids, organic compounds containing basic nitrogen atoms. The basic chemical structure of the lolines comprises a saturated pyrrolizidine ring, a primary amine at the C-1 carbon, and an internal ether bridge—a hallmark feature of the lolines, which is uncommon in organic compounds—joining two distant ring carbons. Different substituents at the C-1 amine, such as methyl, formyl, and acetyl groups, yield loline species that have variable bioactivity against insects. Besides endophyte–grass symbionts, loline alkaloids have also been identified in some other plant species; namely, Adenocarpus species and Argyreia mollis.
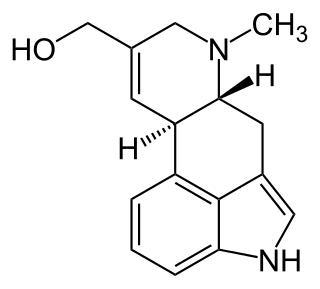
Elymoclavine is an ergot alkaloid. It can be produced from C. fusiformis from Pennisetum typhoideum. It is a precursor in the biosynthesis of D-(+)-lysergic acid. Ergot alkaloids are natural products derived from L-tryptophan. They are often toxic for humans and animals. Despite that they are also well known for their pharmacological activities.
Chanoclavine-I dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.332, easD (gene), fgaDH (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name chanoclavine-I:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalises the following chemical reaction
Fumigaclavine B O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name acetyl-CoA:fumigaclavine B O-acetyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
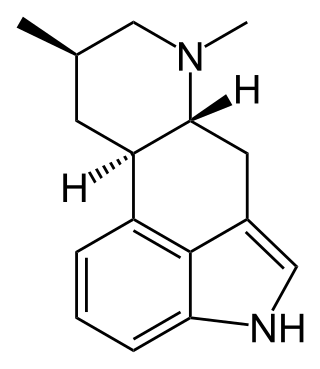
Festuclavine is an ergoline fungal isolate.

Akuammicine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is found in the Apocynaceae family of plants including Picralima nitida, Vinca minor and the Aspidosperma.

Epoxyagroclavine is an ergot alkaloid made by permafrost Penicillium.

Paliclavine is an ergot alkaloid precursor.
Penicillium gorlenkoanum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces citrinin, costaclavine and epicostaclavine.
Penicillium sizovae is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces agroclavine-I and epoxyagroclavine-I.
















