Related Research Articles

Leukemia is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called blasts or leukemia cells. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy.
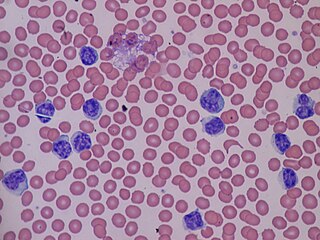
Lymphocytosis is an increase in the number or proportion of lymphocytes in the blood. Absolute lymphocytosis is the condition where there is an increase in the lymphocyte count beyond the normal range while relative lymphocytosis refers to the condition where the proportion of lymphocytes relative to white blood cell count is above the normal range. In adults, absolute lymphocytosis is present when the lymphocyte count is greater than 5000 per microliter (5.0 x 109/L), in older children greater than 7000 per microliter and in infants greater than 9000 per microliter. Lymphocytes normally represent 20% to 40% of circulating white blood cells. When the percentage of lymphocytes exceeds 40%, it is recognized as relative lymphocytosis.

Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes. Early on, there are typically no symptoms. Later, non-painful lymph node swelling, feeling tired, fever, night sweats, or weight loss for no clear reason may occur. Enlargement of the spleen and low red blood cells (anemia) may also occur. It typically worsens gradually over years.

Tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues or tumours of the haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues are tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, lymph, and lymphatic system. Because these tissues are all intimately connected through both the circulatory system and the immune system, a disease affecting one will often affect the others as well, making aplasia, myeloproliferation and lymphoproliferation closely related and often overlapping problems. While uncommon in solid tumors, chromosomal translocations are a common cause of these diseases. This commonly leads to a different approach in diagnosis and treatment of hematological malignancies. Hematological malignancies are malignant neoplasms ("cancer"), and they are generally treated by specialists in hematology and/or oncology. In some centers "hematology/oncology" is a single subspecialty of internal medicine while in others they are considered separate divisions. Not all hematological disorders are malignant ("cancerous"); these other blood conditions may also be managed by a hematologist.

Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the lymphoid line of blood cells characterized by the development of large numbers of immature lymphocytes. Symptoms may include feeling tired, pale skin color, fever, easy bleeding or bruising, enlarged lymph nodes, or bone pain. As an acute leukemia, ALL progresses rapidly and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated.
Acute leukemia or acute leukaemia is a family of serious medical conditions relating to an original diagnosis of leukemia. In most cases, these can be classified according to the lineage, myeloid or lymphoid, of the malignant cells that grow uncontrolled, but some are mixed and for those such an assignment is not possible.
The International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O) is a domain-specific extension of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems for tumor diseases. This classification is widely used by cancer registries.
Lymphoid leukemias are a group of leukemias affecting circulating lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. The lymphocytic leukemias are closely related to lymphomas of the lymphocytes, to the point that some of them are unitary disease entities that can be called by either name. Such diseases are all lymphoproliferative disorders. Most lymphoid leukemias involve a particular subtype of lymphocytes, the B cells.
Lymphoproliferative disorders (LPDs) refer to a specific class of diagnoses, comprising a group of several conditions, in which lymphocytes are produced in excessive quantities. These disorders primarily present in patients who have a compromised immune system. Due to this factor, there are instances of these conditions being equated with "immunoproliferative disorders"; although, in terms of nomenclature, lymphoproliferative disorders are a subclass of immunoproliferative disorders—along with hypergammaglobulinemia and paraproteinemias.

Neprilysin, also known as membrane metallo-endopeptidase (MME), neutral endopeptidase (NEP), cluster of differentiation 10 (CD10), and common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MME gene. Neprilysin is a zinc-dependent metalloprotease that cleaves peptides at the amino side of hydrophobic residues and inactivates several peptide hormones including glucagon, enkephalins, substance P, neurotensin, oxytocin, and bradykinin. It also degrades the amyloid beta peptide whose abnormal folding and aggregation in neural tissue has been implicated as a cause of Alzheimer's disease. Synthesized as a membrane-bound protein, the neprilysin ectodomain is released into the extracellular domain after it has been transported from the Golgi apparatus to the cell surface.
Richter's transformation (RT), also known as Richter's syndrome, is the conversion of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or its variant, small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), into a new and more aggressively malignant disease. CLL is the circulation of malignant B lymphocytes with or without the infiltration of these cells into lymphatic or other tissues while SLL is the infiltration of these malignant B lymphocytes into lymphatic and/or other tissues with little or no circulation of these cells in the blood. CLL along with its SLL variant are grouped together in the term CLL/SLL.

DNA-binding protein Ikaros also known as Ikaros family zinc finger protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IKZF1 gene.

Precursor B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia is a form of lymphoid leukemia in which too many B-cell lymphoblasts are found in the blood and bone marrow. It is the most common type of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). It is sometimes additionally classified as a lymphoma, as designated leukemia/lymphoma. ALL is the most prevalent childhood malignancy, with precursor B-cell ALL (B-ALL) accounting for approximately 75–80% of newly diagnosed pediatric ALL cases.

In molecular biology MicroRNA-223 (miR-223) is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms. miR-223 is a hematopoietic specific microRNA with crucial functions in myeloid lineage development. It plays an essential role in promoting granulocytic differentiation while also being associated with the suppression of erythrocytic differentiation. miR-223 is commonly repressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and leukemia. Higher expression levels of miRNA-223 are associated with extranodal marginal-zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue of the stomach and recurrent ovarian cancer. In some cancers the microRNA-223 down-regulation is correlated with higher tumor burden, disease aggressiveness, and poor prognostic factors. MicroRNA-223 is also associated with rheumatoid arthritis, sepsis, type 2 diabetes, and hepatic ischemia.
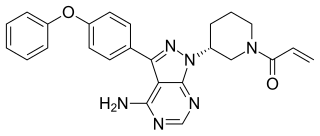
Ibrutinib, sold under the brand name Imbruvica among others, is a small molecule drug that inhibits B-cell proliferation and survival by irreversibly binding the protein Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK). Blocking BTK inhibits the B-cell receptor pathway, which is often aberrantly active in B cell cancers. Ibrutinib is therefore used to treat such cancers, including mantle cell lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and Waldenström's macroglobulinemia. Ibrutinib also binds to C-terminal Src Kinases. These are off-target receptors for the BTK inhibitor. Ibrutinib binds to these receptors and inhibits the kinase from promoting cell differentiation and growth. This leads to many different side effects like left atrial enlargement and atrial fibrillation during the treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Denintuzumab mafodotin is a humanized monoclonal antibody-drug conjugate designed for the treatment of CD19-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia and B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It consists of an anti-CD19 mAb linked to monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF), a cytotoxic agent. This drug was developed by Seattle Genetics.
Camidanlumab tesirine is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) composed of a human antibody that binds to the protein CD25, conjugated to a pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer toxin. The experimental drug, developed by ADC Therapeutics is being tested in clinical trials for the treatment of B-cell Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), and for the treatment of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML).

T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is a type of acute lymphoblastic leukemia with aggressive malignant neoplasm of the bone marrow. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a condition where immature white blood cells accumulate in the bone marrow, subsequently crowding out normal white blood cells and create build-up in the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. The two most common types of ALL are B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes, where the first protects the body against viruses and bacteria through antibody production which can directly destroy target cells or trigger others to do so, whilst the latter directly destroy bacteria or cells infected with viruses. Approximately 20% of all ALL patients are categorized specifically to suffer from T-ALL and it is seen to be more prevalent in the adult population in comparison to children, with incidences shown to diminish with age. Amongst T-ALL cases in the pediatric population, a median onset of age 9 has been identified and the disease is particularly prominent amongst adolescents. The disease stems from cytogenic and molecular abnormalities, resulting in disruption of developmental pathways controlling thymocyte development, tumor suppressor development, and alterations in control of cell growth and proliferation. Distinct from adult T-cell leukemia where T-cell lymphotropic virus Type I causes malignant maturation of T-cells, T-ALL is a precursor for lymphoid neoplasm. Its clinical presentation most commonly includes infiltration of the central nervous system (CNS), and further identifies mediastinal mass presence originating from the thymus, along with extramedullary involvement of multiple organs including the lymph node as a result of hyperleukocytosis.
References
- ↑ "B-Cell Leukemia (Concept Id: C2004493) - MedGen - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 21 November 2021.